knowledge development
- 1. Online Mktg – Knowledge Development © Ramakrishna Kongalla, Assistant Professor Indian Institute of Tourism & Travel Management (An Organization of Ministry of Tourism, Govt. of India) R'tist @ Tourism
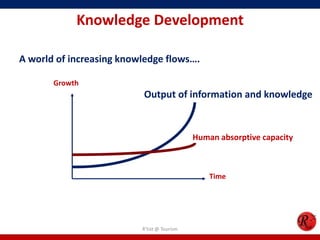
- 2. Knowledge Development A world of increasing knowledge flows…. R'tist @ Tourism Growth Time Output of information and knowledge Human absorptive capacity
- 3. • …that is increasingly connected. R'tist @ Tourism Nodes are individuals and colors represent organizations Casper & Murray 2002
- 4. The extent to which networks of individuals and organizations, markets, and technologies are interconnected across geographic and cultural boundaries – Beech and Chadwick 2004, Friedman 2002 What is your company’s global strategy? From a multi-domestic company to a successful global firm R'tist @ Tourism
- 6. Benefits of knowledge Development • Profitable growth through higher efficiency and innovation – Preventing the waste of valuable resources - avoid reinventing the wheel – Ensuring the use of leading-edge technology and thinking across the firm – Increasing customer satisfaction through shorter lead-times and consistent behavior – Creating a competitive cost structure – Facilitating breakthrough and incremental innovations through combination of technologies and ideas from across and outside the firm • An attractive workplace that encourages cross-functional co-operation across the globe – Attracting and retaining key individuals R'tist @ Tourism
- 7. “We know more than we can tell.” (Michael Polanyi, 1966) R'tist @ Tourism Creating knowledge Embedding knowledge Disseminating knowledge Organizing knowledge C KD
- 8. Information Technology & Knowledge Development 1) Stocks of knowledge: Database and database management systems to collect and hold information 2) Flows of knowledge: Communication channels to connect individuals independent of location R'tist @ Tourism
- 9. Challenges to knowledge databases • Time consuming and difficult – Takes times for writer to document experiences – Takes time for reader to search through databases, information overload – Often weak incentives to contribute golden nuggets • Difficult to understand – Difficult for writer to explain context, tacit ->explicit – Difficult for reader to interpret experience and use in own situation • Data becomes out-of-date very quickly – Difficult to maintain, especially in fast moving industries R'tist @ Tourism
- 10. • Avoid creating information junkyards • Connecting people so that they collaborate, share ideas, and create knowledge R'tist @ Tourism
- 11. Communities • Groups of people who come together to share and to learn from one another face-to-face and/or virtually. • They are held together by a common interest in a body of knowledge and are driven by a desire and need to share problems, experiences, insights, templates, tools, and best practices. • Members deepen their knowledge by interacting on an ongoing basis. • This interaction leads to continuous learning and innovation R'tist @ Tourism
- 12. Role of Communities • Create: Own & develop knowledge – Develop & manage good practice – Build organizational competence • Organize: Develop & manage materials – Develop tools, guidelines, templates – Manage databases • Disseminate: Connect people across boundaries – Who knows what – Home in changing organization & an uprooted society • Embed: Share ideas & insights – Share tacit, complex ideas & insights – Help each other solve problems & find innovations R'tist @ Tourism
- 13. R'tist @ Tourism Helping Best-practice Knowledge stewarding Communities can have a different primary purpose
- 14. R'tist @ Tourism Community membership and roles Coordinator Peripheral Core Group Active
- 15. R'tist @ Tourism Two extreme communities of practice Face-to-face Virtual
- 16. R'tist @ Tourism Organization Don’t forget to support informal external networks at the individual level! Electronic communities Partners Customers and suppliers Previous work and school colleagues External Large portion of new ideas and formal collaboration relationships come from personal external contacts
- 17. R'tist @ Tourism Encourage an open innovation attitude Not all the smart people work for us. We need to work with smart people inside and outside the company. The smart people in our field work for us. If you create the most and the best ideas in the industry, you will win. If you make the best use of internal and external ideas, you will win. Closed attitude Open attitude Chesborough 2003
- 18. Thank You…!!! ©Ramakrishna Kongalla e-mail: [email protected] R'tist @ Tourism