8) law and society
- 1. LAW AND SOCIETY INTRODUCTION TO LAW 1 LAW 012 CREDIT TO EN. MUHAMMAD UMAR ABD. RAZAK
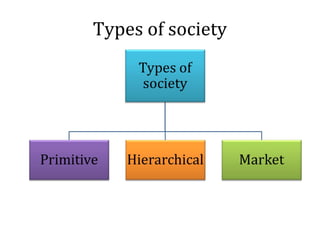
- 2. WHAT IS SOCIETY? • The term derived from a Latin word ‘socious’ that means association or companionship – a larger group of individuals who are associative with each other. • Society is the system in which people live together in organized communities. • It may be defined as an organization of people with a particular interest or purpose. • Men and animals are different. Human’s conduct is controlled through moral standards, religious doctrines, social traditions and legal rules.
- 5. • No organized legal system then. During primitive years, the controls of action were informal. • Political institutions were simple. The nexus that bind the society was morality. • Any member of society who breached the norms of the society will be disciplined by way of punishment and social embarrassment. • There was neither criminal nor prison during primitive years like we have today. • The community was the right holder and individuals cannot claim any right over the society’s rights. Thus, a hunter will have to share his meat with his community.
- 7. • Feudalistic society. At the top of the hierarchy is the king who must be obeyed by his subjects. • Mystical belief was that the king has a divine power or represented God in certain way. • The king was the owner of the land and could disposes them at his convenience. • Feudal society was built upon contracts of allegiance between man and man.
- 9. • Known as market society as the society is being dominated by capitalist system and ideology. The main characteristic of market societies are: – Based on social contract between equals. – The society recognizes individual freedom where men are equal before the law. – Every person has the opportunity to climb the social ladder. – The dominant idea of social justice were the result of market system.
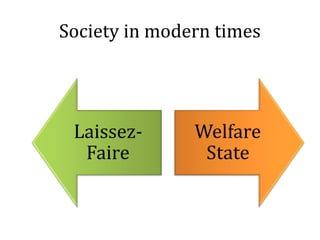
- 10. Society in modern times
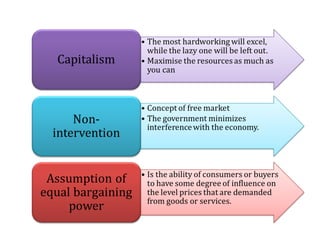
- 11. Laissez- faire • An economic doctrine that opposes governmental regulation of or interference in commerce beyond the minimum necessary for a free-enterprise system to operate according to its own economic laws. • Non-interference in the affairs of others.
- 13. Welfare State • A social system whereby the state assumes primary responsibility for the welfare of its citizens, as in matters of health care, education, employment, and social security. • Few countries that practices welfare state concept: Saudi Arabia, Brunei, Oman, Kuwait, United States, United Kingdom.
- 14. • A social system whereby the state assumes primary responsibility for the welfare of its citizens, as in matters of health care, education, employment, and social security. • Few countries that practices welfare state concept: Saudi Arabia, Brunei, Oman, Kuwait, United States, United Kingdom.
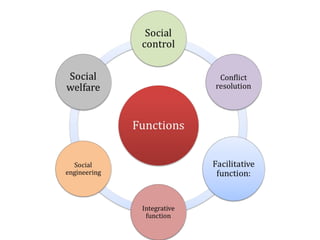
- 17. Social Control • Law is used as one mode to control the society. • Formal form of control – insufficiency of informal form of control. • The use of law as a penal instrument to prohibit and prosecute criminals – deter crime • The law prescribes the standard procedures to arrest, the prosecuting processes and sentencing. • There is a specialized agency to enforce the control i.e. PDRM, Immigration, JPJ etc. • Control via external pressures either positive or negative sanctions. Negative sanction are penalties/punishment imposed on those who violate the rules. Example of positive sanction is promotion, reward, bonus.
- 18. • The laws enacted by legislature and implemented by court decisions define criminal and delinquent behaviour as well as specifying the sanctions imposed for violations.
- 19. Conflict resolution • We bound to be caught in the conflict between human. For e.g. family members, business associates, member of the public, public with the government etc. • The use of law to address the grievance among the members of the society. • There is 2 aspects in conflict resolution: formalized mechanism and procedures. • There are rights and liabilities that should be defended and enforced.
- 20. • Meanwhile, there is a designated institution to resolve the conflict: – Negotiation – Conciliation – Mediation – Arbitration – Court hearing – ombudsman
- 21. Facilitative function • The use of law to give effect to certain private arrangements and social relationship, between individuals and between groups. • According to Lwellyn, every society has certain basic needs for e.g. business, housing, consumer product, medical treatment, education, employment etc. • The law plays a role to assist those needs above. • The law provide the framework for the members of the society to determine their conflict resolution.
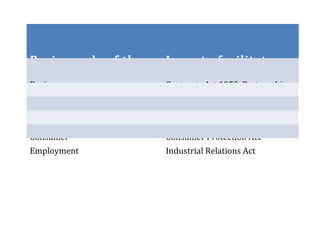
- 22. Basic needs of the society Laws to facilitate the needs Business Contracts Act 1950, Partnership Act, Housing Housing law Medical treatment Medical Act 1970 Consumer Consumer Protection Act Employment Industrial Relations Act
- 23. Integrative Function/ Social Cohesion • The law promotes and social cohesion. Cohesion refers to the action or fact of forming a united whole/solidarity. • “Bersatu teguh, bercerai roboh” is the best way to describe this. • Law is used to unite the society. The social cohesion work across the spectrum in the society. For e.g. family members, club members, political parties members etc.
- 24. Social engineering • Law can be used to steer the social engineering in the society. The term of “social engineering” derived from Roscoe Pound where he believed law is an agent for a change in the society. • The parliament may legislate a law to regulate behaviour . For e.g. Sedition Act- to curb sensitive issues such as race relations, sex equality etc. • Social engineering laws and policies such as the Federal Constitution (special rights to the Bumiputras, New Economic Policy are meant to restructure the imbalance in the society).
- 25. Social Change • Change ? Something that exists that did not exist previously or the absence of something that formerly existed. • Social change ? Large numbers of people are engaging in group activities and relationship that are different from those in which they or their parents engaged previously. • Modification in the way people work, rear a family, educate their children, govern themselves and seek ultimate meaning in life. • Sometimes law has been deliberately used to change society. • E.g. : Soviet Union
- 26. Advantages of using law as an instrument of social change • More focus, specific. • The aims & objectives are clearly stated. • Binding force, implementation mechanism is in place. • Legitimacy or validity of such laws. • To avoid political conflict- war, riot, civil war, coup d’etat.
- 27. Social welfare • Law can also be used to manage various governmental public benefits such as educational centers. • Through the concept of welfare state- laws are being used to achieve social justice, social welfare, eradication of poverty and economic exploitation.
- 28. Conclusion • Law plays an important role in the society. Look around and name few examples of law that have changed the society. • Law can be an agent of social change to reform the society. (from primitive to market society). • The society may adapt to changes by amending the law according to circumstances and times.