Membrane separation technology
- 1. Membrane Separation Technology By M.Tech Biotechnology
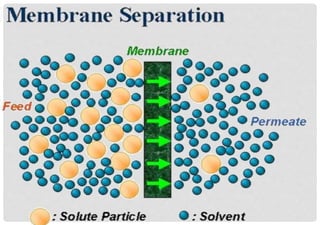
- 2. INTRODUCTION A membrane is a thin semi-permeable barrier which can be used for the following types of separation: 1. Particle-liquid separation 2. Particle-solute separation 3. Solute-solvent separation 4. Solute-solute separation Membranes can separate particles and molecules and over a wide particle size range and molecular weights.
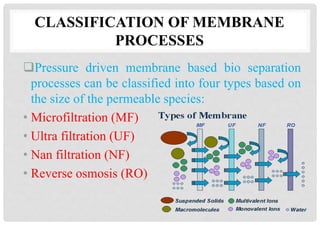
- 4. CLASSIFICATION OF MEMBRANE PROCESSES Pressure driven membrane based bio separation processes can be classified into four types based on the size of the permeable species: • Microfiltration (MF) • Ultra filtration (UF) • Nan filtration (NF) • Reverse osmosis (RO)
- 5. MICROFILTRATION Microfiltration refers to the separation of suspended material such as bacteria by using a membrane with pore sizes of 0.1 to 10um The various applications of microfiltration in biotechnology include: 1. Cell harvesting from bioreactors 2. Virus removal for pharmaceutical products 3. Clarification of fruit juice and beverages 4. Water purification 5. Air filtration 6. Sterilization of products
- 7. ULTRA FILTRATION UF membranes can retain macromolecular solutes. Solute retention is mainly determined by solute size. However, other factors such as solute-solute and solute- membrane interactions can affect solute retention. Depending on the protein to be retained, membrane NMWLs in the range of 1 kD to 1000 kD are used. Two types of UF are Virus filtration(VF) and High Performance tangential flow filtration (HPTFF).
- 8. VF-This process type is used to separate virus particles from proteins or from smaller media components, as either a virus reduction step or a virus harvest step. VF-membrane NMWL ratings range from 100 k D to 500 k D, or up to 0.05 μ m. High performance filtration is a high resolution process where protein-protein separations can be carried out on the basis of both size and charge, resulting in product yields and purification factors similar to chromatography ULTRAFILTRATION
- 9. Membrane NMWLs used for HP TFFare in the range of 10 kD to 300 kD Common applications: removal and recovery of oils, surfactants and paints from waste streams, clarification of wines and juices, and polishing of ultra pure water for bacteria and particle removal
- 10. ULTRA FILTRATION
- 11. NANO FILTRATION Nano filtration (NF) membranes allow salts and other small molecules to pass through but retain larger molecules such as peptides, hormones and sugars. Pore size is of order of nanometers Driving force: pressure difference Common applications: partial softening of feed water, removal of contaminants from water or acid streams, and pretreatment for reverse osmosis or other high purity systems
- 12. NANO FILTRATION
- 13. REVERSE OSMOSIS • Reverse osmosis (RO) separates salts and small molecules from low molecular weight solutes(typically less than 100 daltons) at relatively high pressures using membranes with NMWLs of1 k Da or lower. • Reverse osmosis systems are primarily used to purify tap water to purities that exceed distilled water quality.
- 14. REVERSE OSMOSIS
- 15. MEMBRANE MODULES Flat plate and Frame module Hollow fibers. Spiral wounds
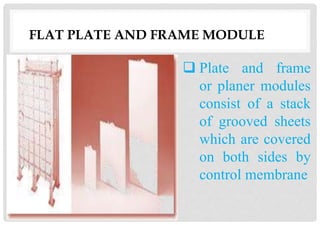
- 16. FLAT PLATE AND FRAME MODULE Plate and frame or planer modules consist of a stack of grooved sheets which are covered on both sides by control membrane
- 17. Each membrane covered sheet alternates with a spacer sheet to form the module stack . The membrane edges are sealed to prevent the mixing of the permeate and the feed solution . The feed solution ,under pressure flows tangentially along each of the porous sheets as it is directed in serpentine manner through the stack The permeate collect in the spacer regions and flows to the permeate outlet . Advantage: more surface area per unit volume than flat sheet membranes FLAT PLATE AND FRAME MODULE
- 18. HOLLOW FIBER Hollow fiber module are comprised a bundle of membrane tubes with narrow dia meters, typically in the range of 0.1 to 2.0 nm . In the hollow fiber module ,the feed stream is pumped in to the inside of the tube and filtrate passes through the membrane to the shell side.
- 19. SPIRAL WOUND MEMBRANE Spiral wound module consist of an envelope of membrane covered sheets and separator sheets which are wound concentrically around a hollow core and then inserted in to a canister. The pressurized feed stream is introduced at one end of canister and flows tangentially along the membrane to the exit port of the canister . The permeate collects in the separator area and flows to the hollow center where it is removed
- 20. SPIRAL ELEMENTS
- 21. APPLICATIONS The particular advantage of membrane separation processes is that they operate without heating and therefore use less energy than conventional thermal separation processes. Therefore, cold separation by means of membrane processes is commonly applied in the food technology, biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries. As an artificial kidney to remove toxic substances by hemo dialysis.
- 22. Nano filtration and reverse osmosis membranes are mainly used for water purification purposes. Microfiltration and ultra filtration is widely used in food and beverage processing (beer microfiltration, apple juice ultra filtration), biotechnological applications and pharmaceutical industry (antibiotic production, protein purification), water purification and wastewater treatment, microelectronics industry, and others
- 23. THANK YOU