Anatomy of middle ear
- 1. Dr. Mudasir-ul-islam Postgraduate presentation Government Medical College Srinagar, Kashmir. Oct. 2010.
- 2. Overview Embryology Walls of middle ear Contents of middle ear Spaces of middle ear Blood supply of middle ear Endoscopic pictures
- 7. Tubotympanic recess Proximal part Distal part Malleus and incus Stapes Tensor tympani Stapedius Ligament of malleus Tympanic membrane
- 8. Malformed ossicles Fused stapes Facial nerve Stapedial artery
- 9. • Mesotympanum – Facial recess – Sinus tympani • Hypotympanum • Epitympanum
- 10. Lateral Medial Floor Roof Anterior Posterior
- 11. Bony epitympanum Tympanic membrane Hypotympanum
- 15. Chorda tympani..enters medial surface of fissure through separate canaliculus (canal of Huguier) runs posterior then to fibrous and mucosal layers, across upper part of handle of malleus, along the membrane but below the level of posterior malleolar fold Then enters the posterior canaliculus obliquely and medially downward,through the posterior wall of tympanic cavity to reach facial nerve
- 16. During cortical mastoidectomy the fibrous strands of tympanomastoid suture can often be confused with corda tympani although the angle of white strands of suture lines different from angle of corda
- 18. Tegmen tympani..both petrous andsquamous portion of temporal bone form it Petrosquamous suture,as it does not close till adult life,can lead to infection in extradural space in children Veins..superior petrosal sinus
- 20. Compact or pneumatised bone Separates the hypotympanum from the dome of jugular bulb Thickness varies floor may be deficient..here jugular bulb is covered by fibrous tissue and mucous membrane At the Junction of floor and medial wall tympanic branch of 9th nerve opens into middle ear from origin below the base of skull.
- 21. Lower one third thin plate of bone covering carotid artery perforated by sup and inf caroticotympanic nerves Middle one third orifice of Eustachian tube above this opening is canal for tensor tympani muscle
- 22. Upper one third anterior epitympanic recess small niche anterior to ossicular head can hide residual Cholesteatoma in canal wall up surgery
- 25. Promontory Oval window Round window niche Facial nerve canal
- 27. Covers part of the basal part of cochlea Contains nerves forming tympanic plexus Tympanic branch of ninth nerve may be covered by bone forming a small canal
- 29. Behind and above the oval window Kidney shaped Connects tympanic cavity with the vestibule closed by stapes footplate and annular ligament Size 3.25×1.75
- 30. Lies below and behind the oval window Separated by subiculum(post extension of promontory) Ponticulus..another ridge above subiculum and runs to pyramid on the posterior wall Sinus tympani is where ponticulus and subiculum meet RWM is 2.3×1.9. It is placed at right angles to plane of stapes foot plate
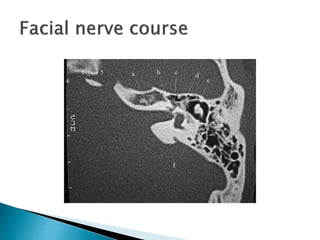
- 32. Facial nerve canal,also called fallopain canal Runs above promontory and oval window in anterosuperior direction Smooth rounded lateral surface has microdehiscenses Along the line of nerve two or three blood vessels are visible(straight) This canal is marked anteriorly by processus cochleariformis and behind by the oval window
- 33. Processus cochleariformis is a curved piece of bone housing tensor tympani muscle tendon Behind the oval window facial canal starts inferiorly ….
- 36. Aditus and antrum Fossa incudus Pyramid Canal within the pyramid curves downwards and backwards to join descending portion of facial nerve canal
- 38. Groove between pyramid facial nerve and annulus of tympanic membrane Shallow lower down Medially is facial nerve Laterally tympanic annulus Corda tympani running obliquely through wall between the two Posterior tympanotomy
- 39. Posterior extent of mesotympanum Lies deep to promontory and facial nerve Most inaccessible site Cholesteatoma in posterior wall is difficult to eradicate Worst region to access is above the pyramid posterior to intact stapes and medial to facial nerve Retrofacial appraoch not possible because posterior SCC blocks access
- 49. Ossicles • Malleus (hammer) • Incus (anvil) • Stapes (stirrup) smallest bone of the body
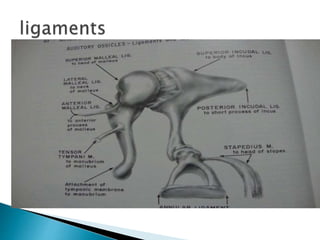
- 56. Malleus Largest 9mm in length Head in epitympanum Suspended by superior malleal ligament Saddle shaped facet on posteromedial surface Articulates with the incus..a synovial joint
- 57. Below neck is the lateral and anterior process of malleus Lateral process receives ant and post folds from tympanic annulus Handle downwards medially and backwards Between mucosal and fibrous layer Closely attached to membrane at lower end fine web of mucosa ossicular reconstruction
- 58. Body Two processes Short process Long process Lenticular process
- 59. Head Neck Ant and posterior crus Foot plate
- 60. Head Points laterally Stapedius tendon gets inserted over the post part of neck and upper portion of post crus Crura arises from broader lower part of neck and ant crus is thinner and less curved than the post one
- 61. Foot plate Convex superior margin Almost straight inferior margin Curved ant and post ends Long axis is horizontal and post end slightly lower than the anterior 3cm long 1.4mm wide Sesamoid bone ..fourth ossicle
- 65. Stapedius Origin..wall of conical cavity within the pyramid and from downward curved continuation of this canal in front of descending portion of facial canal Supplied by small branch of facial nerve
- 68. Origin is wall of bony canal above eustachain tube,cartilaginous portion of tube, greater wing of sphenoid Passes backward into tympanic cavity,along medial wall little below facial nerve Enters processus cochlearformis held by transverse tendon latertally Medial aspect of malleus head Supplied by mandibular nerve via branch from medial pterygoid nerve
- 69. Tensor tympani Inserts on the malleus and acts to tense the tympanic membrane reducing the effectiveness of sound transmission, protecting the inner ear during loud sounds. Innervation from a branch of the mandibular nerve (V3 of CN V).
- 72. Tympanic branch of 9th nerve,also called jacobson’s nerve Caroticotympanic nerves Supplies mucosal layer of TM……
- 75. Mucus secreting Respiratory type Cilia bearing Three distint mucociliary pathways Epitympanic Promontarial Hypotympanic(largest) These pathways coalesce at tympanic orifice of eustachain tube
- 76. Mucosa covers ossicles and tendons Ventilation of epitympanic space… Ant and post istmic tympani Prussack’s space
- 77. Length 45 degrees forwards and medially Bony and cartilaginous parts Mucosa
- 78. Length Isthmus Relation with tensor tympani Relation with carotid canal Cross section
- 79. Length Medial and lateral cartilage Fixed to base of skull between petrous part and greater wing of sphenoid Ends at root of medial pterygoid plate Back Front Apex
- 80. S.No BRANCH PARENT ARTERY REGION SUPPLIED 1 ANT TYMPANIC MAXILLARY TM,MALLEUS,INCUS,ANT TYMPANIC CAVITY 2 STYLOMASTOI D POST AURICULAR POST PART OF TYMPANIC CAVITY,STAPEDIUS MUSCLE 3 MASTOID STYLOMASTOID MASTOID AIR CELLS 4 PETROSAL MIDDLE MENINGEAL ROOF OF MASTOID AND ROOF OF EPITYMPANUM 5 SUP TYMPANIC MIDDLE MENINGEAL MALLEUS ,INCUS, TENSOR TYMPANI 6 INF TYMPANIC ASCENDING PHARYNGEAL MESOTYMPANUM 7 BRANCH ARTERY OF PTERYGOID CANAL MESO AND HYPOTYMPANUM 8 TYMPANIC ARCHES INTERNAL CAROTID MESO AND HYPOTYMPANUM
- 81. Anatomic Considerations • Epitympanum – Above short process of malleus – Contains head of malleus, body of incus and associated ligaments and mucosal folds – Pars flaccida lacks support from a fibrous middle layer
- 82. Anatomic Considerations • Epitympanic cholesteatoma patterns of spread from Prussack’s space – Posterior epitympanum – Posterior mesotympanum – Anterior epitympanum
- 83. Cholesteatoma spread • Posterior epitympanum – through superior incudal space to mastoid antrum
- 84. Cholesteatoma spread – Posterior mesotympanum – inferiorly through posterior pouch of von Troeltsch to stapes, round window, sinus tympani and facial recess
- 85. Cholesteatoma spread • Anterior epitympanum – anterior to head of malleus, may gain access to supratubal recess via anterior pouch of von Troeltsch