Introduction skeletal radiology(11月20.)
- 1. MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital SYSU Dr. BILING LIANG
- 2. Musculoskeletal Radiology INTRODUCTION IMAGING TECHNOLOGY NORMAL APPEARANCE BASIC X-RAY SIGN RADIOLOGY DIAGNOSIS OF COMMON DISEASES
- 3. Imaging technology X-ray : plain film Very good X-ray density resolution in bone & joint , the resolution of soft tissue not enough CT : as X-ray, but good for positioning MR : advantage : very good soft tissue resolution disadvantage : not sensitivity to display calcification US : Non-invasive image method, easy to perform Can evaluate the soft tissue abnormalities
- 4. Skeletal CT Soft tissue window : Bone muscle Bone window: Cortical : Trabecula : network Bone marrow cavity : low density
- 5. X-ray plain film & arthrogram
- 6. Normal X-ray appearances Bone – structure & development Joint Spine Soft tissue
- 7. Normal X-ray appearances Bone structure & development Structure : Cortical bone (compact ) Cancellous bone (Trabecula ) Development : intramembranous ossification Endochondral ossification Same histologic structure Different arrangement Cartilage -> bone formation -> remodel -> trabecular bone
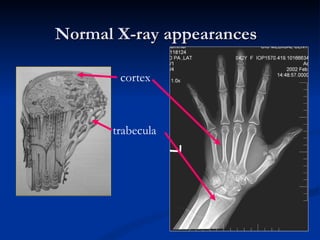
- 8. Normal X-ray appearances cortex trabecula
- 9. Normal pediatric X-ray appearances 4 years , distal femur metaphysis epiphysis Epiphyseal plate
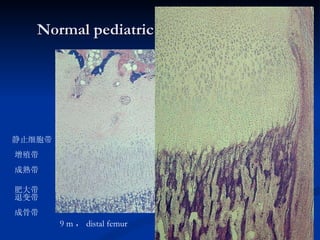
- 10. Normal pediatric X-ray appearances 9 m , distal femur 增殖带 成熟带 肥大带 退变带 成骨带 静止细胞带 {
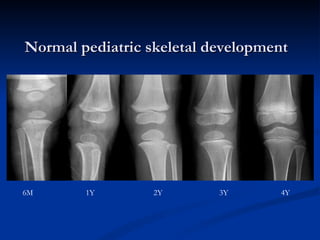
- 11. Normal pediatric skeletal development 6M 1Y 2Y 3Y 4Y
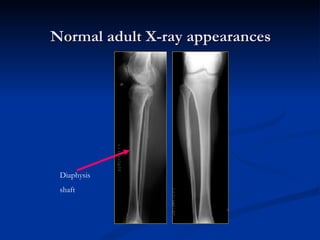
- 12. Normal adult X-ray appearances Diaphysis shaft
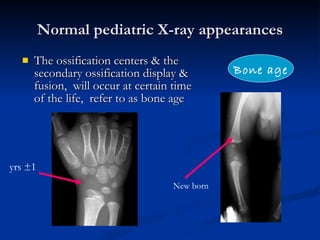
- 13. Normal pediatric X-ray appearances The ossification centers & the secondary ossification display & fusion, will occur at certain time of the life, refer to as bone age Bone age yrs ±1 New born
- 14. Normal X-ray appearances The types of skeleton: Long bone Pediatric : diaphysis 、 metaphysis 、 epiphysis 、 epiphyseal plate Adult : diaphysis (shaft) 、 Short bone Flat bone – hematopoiesis Irregular bone Joint
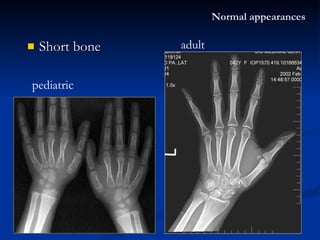
- 15. Short bone Normal appearances pediatric adult
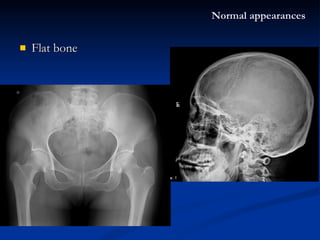
- 16. Flat bone Normal appearances
- 17. Spine Normal appearances
- 18. Normal X-ray appearances Bone Joint -- structure Spine Soft tissue
- 19. Normal X-ray appearances Joint Synovial joint -- knee Fibrous joint -- Cartilaginous joint -- SI Synostosis joint – skull
- 20. Joint is an organ Articular capsule synovium cartilage Cortical bone Ligament & tenden Fluid Joint space cartilage Articular cartilage Epiphyseal cartilage Fibrocartilage dics X-ray
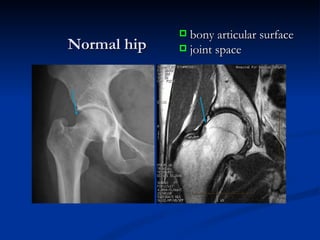
- 22. Normal hip bony articular surface joint space
- 23. Normal joint structure Elbow -- Synovial joint SI joint -- Cartilaginous joint
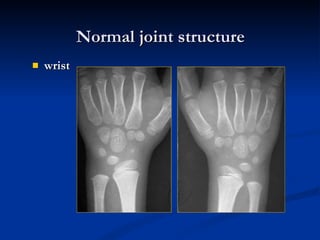
- 24. wrist Normal joint structure
- 25. Basic X-ray signs Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Bone destruction Osteosclerosis Periosteal reaction Calcification Bone necrosis Mineral sedimentation Bone deformity Soft tissue abnormalities Musculoskeletal system Bone Joint Joint swellen Joint dislocation Joint destruction Joint bony/fibrous ankylosis
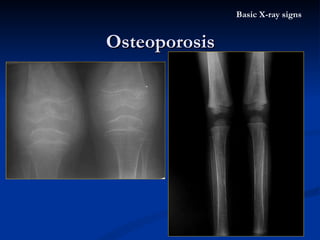
- 26. Osteoporosis Definition : The bone matrix or osteoid specific deficiency Both of the organic material & calcium are decreased, but the ratio of them still normal X-ray appearance : Bone density decreased, local / general The cortex become thinner , the trabeculae become thin and decreased number Pathological fracture Etiology : Common : elderly , immobilization Path : hormonal / vitamine deficiency Basic X-ray signs
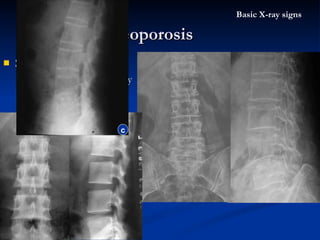
- 27. Spine oteoporosis Vertibral body deformity as “ fish vertibral ” Bone density decreased Trabecula thinner Osteoporosis Basic X-ray signs normal c
- 28. Thallassaemia Chronic haemolytic anaemias cause widening of the spongiosa / cortex thinning in the proximal ends of long bone Osteoporosis Basic X-ray signs
- 29. Osteomalacia Definition : Insufficient mineralization of the osteiod Lack of calcium for bone formation X-ray appearance : Bone density decreased generally, bone become softened and bend or even break, vertebral bodies biconcave (fish vertebrae) The cortex become thinner, “ ground glass ” change, deficient bone formation Pseudo-fracture, Pathological fracture Etiology : Deficient Vitamine D, Calcium (inadequate intake) Excessive loss of calcium in renal disease Basic X-ray signs
- 30. Rickets Bone density decreased Bone softening & bend Metaphysis splaying & the epiphyseal plate widening Osteomalasia Basic X-ray signs
- 31. Rickets Bone density decreased Bone softening & bowed Osteomalasia Basic X-ray signs
- 32. Bone destruction Basic X-ray signs Definition : The pathologic tissue replaced the normal bone structure (cortex or spongiosa) X-ray appearance : Bone density decreased, rarefaction of bone The cortex erosion Etiology : Inflammation or granuloma Tumor or tumor-like lesion
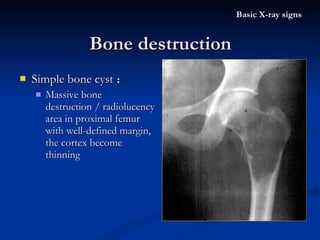
- 33. Simple bone cyst : Massive bone destruction / radiolucency area in proximal femur with well-defined margin, the cortex become thinning Bone destruction Basic X-ray signs
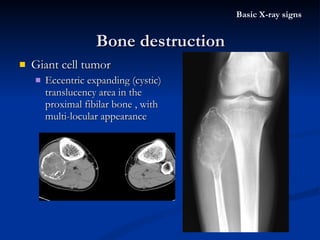
- 34. Giant cell tumor Eccentric expanding (cystic) translucency area in the proximal fibilar bone , with multi-locular appearance Bone destruction Basic X-ray signs
- 35. Giant cell tumor Eccentric expanding (cystic) translucency area in the distal radial bone Bone destruction Basic X-ray signs
- 36. Tuberculosis of right hip Moth-eaten pattern bone destruction in cortex & trabeculae Joint space narrowing Bone destruction Basic X-ray signs
- 37. Osteosclerosis /hyperostosis Basic X-ray signs Definition : Increase of amount of bone matrix in given volume of bone X-ray appearance : Bone density increased Cortex thicken – periosteal growing Bone marrow cavity narrowing – endostosis growing and trabecular thickening Etiology : Inflammation or granuloma (chronic) Trauma & fracture Tumor or tumor-like lesion
- 38. Chronic osteomyelitis : Med-low part of the tibia Cortex thickening Bone marrow cavity narrowing and obliteraed Osteosclerosis Basic X-ray signs
- 39. Chronic osteomyelitis Osteosclerosis of the bone between the areas of destruction Bone marrow cavity narrowing & obliteration Osteosclerosis Basic X-ray signs
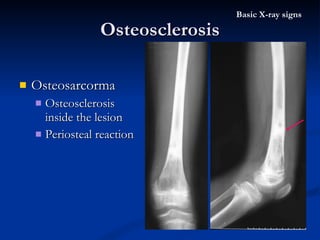
- 40. Osteosarcoma Osteosclerosis inside the lesion Osteosclerosis Basic X-ray signs
- 41. Osteosarcorma Osteosclerosis inside the lesion Periosteal reaction Osteosclerosis Basic X-ray signs
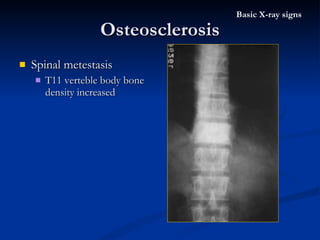
- 42. Spinal metestasis T11 verteble body bone density increased Osteosclerosis Basic X-ray signs
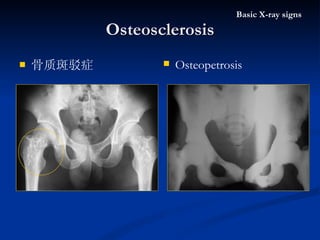
- 43. 骨质斑驳症 Osteosclerosis Basic X-ray signs Osteopetrosis
- 44. Periosteal reaction / periostosis Basic X-ray signs Definition : Periosteal new bone formation cause by various condition stimulated X-ray appearance : The newly developed periosteal bone in different form: lamellae (onion peel) , spicules (sunrays) , lacelike , spurs , et al. Etiology : Inflammation or granuloma (chronic) Trauma & fracture Tumor or tumor-like lesion Codman ’ s triangle: The new periosteal bone become eroded centrally leaving triangle areas of New bone at the edges
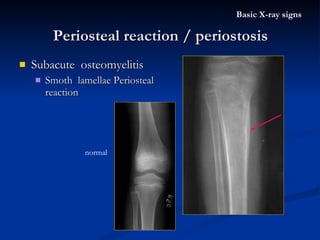
- 45. Subacute osteomyelitis Smoth lamellae Periosteal reaction Periosteal reaction / periostosis Basic X-ray signs normal
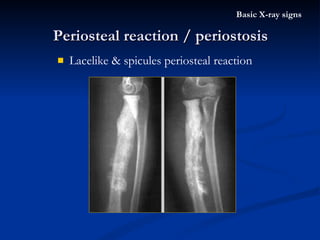
- 46. Lacelike & spicules periosteal reaction Periosteal reaction / periostosis Basic X-ray signs
- 47. Fracture unhealing Massive periosteal reaction surrounding the ulnar fracture area Periosteal reaction / periostosis Basic X-ray signs
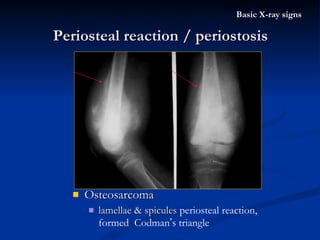
- 48. Osteosarcoma lamellae & spicules periosteal reaction, formed Codman ’ s triangle Periosteal reaction / periostosis Basic X-ray signs
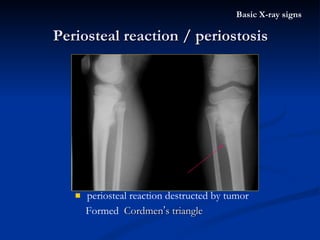
- 49. periosteal reaction destructed by tumor Formed Cordmen ’ s triangle Periosteal reaction / periostosis Basic X-ray signs
- 50. Calcification within bone/cartilage Basic X-ray signs X-ray appearance : The high X-ray density spot inside bone /soft tissue /mass Etiology : Inflammation or granuloma or degeneration , or bone necrosis (chronic) Irregular shape Cartilage tumor Ring shape / half-ring shape
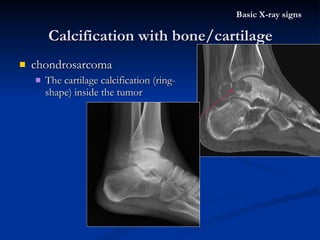
- 51. chondrosarcoma The cartilage calcification (ring-shape) inside the tumor Calcification with bone/cartilage Basic X-ray signs
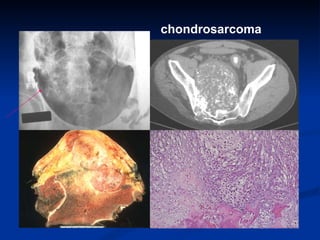
- 52. chondrosarcoma
- 53. Calcification after hematoma Left shoulder surrounded by massive irregular high density shadow Calcification with bone/cartilage Basic X-ray signs
- 54. Bone necrosis Basic X-ray signs Definition : The death of bone tissue caused by gradual vascular impairment ceasation of metabolism of local bone tissue X-ray appearance : Sequestrum – fragment of dense/necrotic bone be separated , the X-ray density “ high ” (sequestrum is normal density , cause by the surrounding bone osteoporosis) Etiology : Inflammation or granuloma (chronic) Trauma & fracture
- 55. Femoral capital epiphysis Slightly increased density of the epiphysis The epiphysis becomed fragment and flattened Osteoporosis of the neighbouring part of the femur Bone necrosis Basic X-ray signs
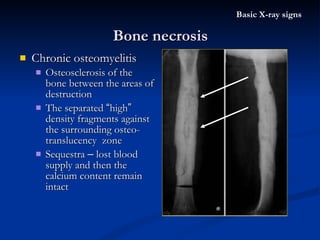
- 56. Chronic osteomyelitis Osteosclerosis of the bone between the areas of destruction The separated “ high ” density fragments against the surrounding osteo-translucency zone Sequestra – lost blood supply and then the calcium content remain intact Bone necrosis Basic X-ray signs
- 57. Mineral sedimentation Basic X-ray signs X-ray appearance : Mineral material , (lead , phosphorus , et al.) excessive sedimentation in bone Dense bands at metaphyseal end High concentrations of fluorine compounds Stimulates endosteal & periosteal osteoblastic activity and bone formation
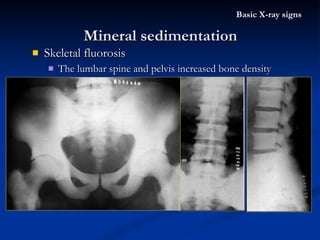
- 58. Skeletal fluorosis The lumbar spine and pelvis increased bone density Mineral sedimentation Basic X-ray signs
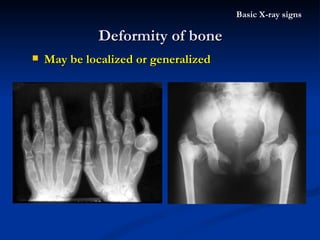
- 59. Deformity of bone Basic X-ray signs May be localized or generalized
- 60. Multiple exostoses Deformity of bone Basic X-ray signs Enlongated finger
- 61. Soft tissue abnormalities Basic X-ray signs May cause by trauma / tumor / infection ……
- 63. Basic X-ray signs Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Bone destruction Osteosclerosis Periosteal reaction Calcification Bone necrosis Mineral sedimentation Bone deformity Soft tissue abnormalities Musculoskeletal system Bone Joint Joint swellen Joint dislocation Joint degeneration Joint destruction Joint bony/fibrous ankylosis
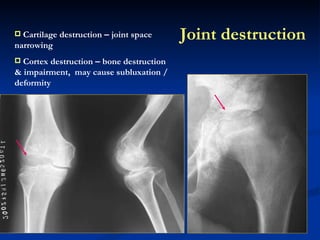
- 64. Joint destruction Cartilage destruction – joint space narrowing Cortex destruction – bone destruction & impairment, may cause subluxation / deformity
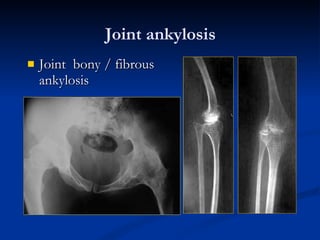
- 65. Joint ankylosis Joint bony / fibrous ankylosis
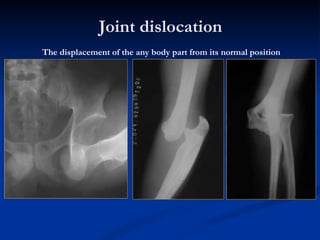
- 66. Joint dislocation The displacement of the any body part from its normal position
- 68. MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY TRAUMA Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital SYSU Dr. BILING LIANG
- 69. Fracture : complete or inconplete break in the continuity of bone or cartilage , this requires a loading force applied to bone Traumatic fracture Stress fracture Pathologic fracture May acompany severe soft tissue torn / bleeding / important organ torn Fracture & dislocation Trauma
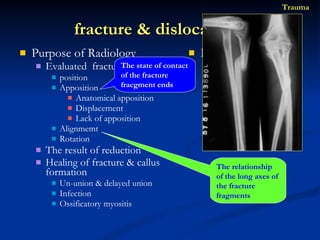
- 70. Purpose of Radiology Evaluated fracture / dislocation position Apposition Anatomical apposition Displacement Lack of apposition Alignmemt Rotation The result of reduction Healing of fracture & callus formation Un-union & delayed union Infection Ossificatory myositis Imagine technique X-ray CT MRI US SCINTIGRAPHY fracture & dislocation Trauma The state of contact of the fracture fracgment ends The relationship of the long axes of the fracture fragments
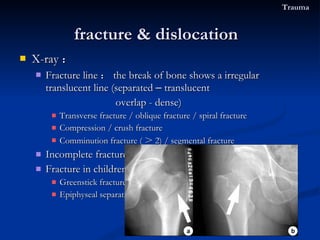
- 71. X-ray : Fracture line : the break of bone shows a irregular translucent line (separated – translucent overlap - dense) Transverse fracture / oblique fracture / spiral fracture Compression / crush fracture Comminution fracture ( > 2) / segmental fracture Incomplete fracture : Fracture in children Greenstick fracture : Epiphyseal separation fracture & dislocation Trauma
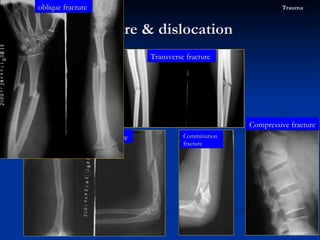
- 72. The fracture types Fracture & dislocation Trauma spiral fracture Transverse fracture Compressive fracture Comminution fracture oblique fracture
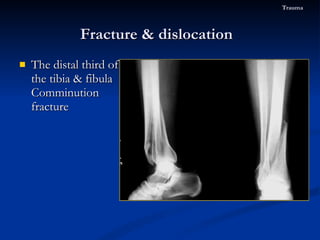
- 73. The distal third of the tibia & fibula Comminution fracture Fracture & dislocation Trauma
- 74. X-ray : Fracture line : the break of bone shows a irregular translucent line Transverse fracture / oblique fracture / spiral fracture Comprese fracture Comminution fracture ( > 2) / segmental fracture Incomplete fracture : Fracture in children Greenstick fracture : Epiphyseal separation fracture & dislocation Trauma angling or buckling of the cortex without the lucent fracture line Epiphysis & cartilage plate separated from the metaphysis
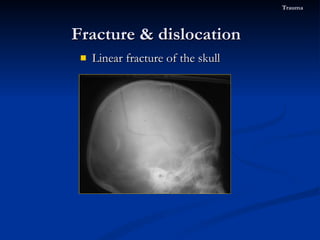
- 75. Linear fracture of the skull Fracture & dislocation Trauma
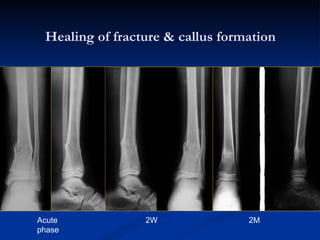
- 76. Healing of fracture & callus formation Acute phase 2W 2M
- 77. Lower humerus fracture – deformity of union Fracture & dislocation Trauma
- 78. Middle tibia & fibela fracture – deformity of union Fracture & dislocation Trauma Apposition Alignmemt
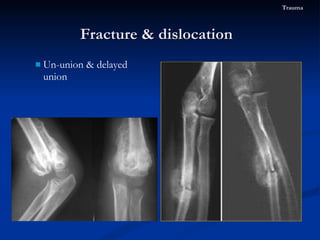
- 79. Un-union & delayed union Fracture & dislocation Trauma
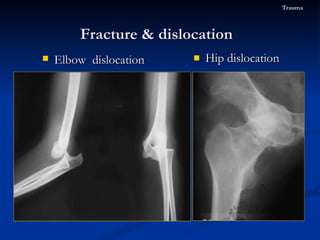
- 80. Hip dislocation Fracture & dislocation Trauma Elbow dislocation
- 81. Colles ’ fracture A transverse fracture through the distal radius With dorsal displacement & angulation of the distal radial fragment Malalignment as “ silver fork ” deformity The ulnar styloid is often detached Fracture & dislocation Trauma
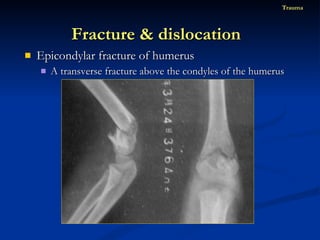
- 82. Epicondylar fracture of humerus A transverse fracture above the condyles of the humerus Fracture & dislocation Trauma
- 83. Epicondylar fracture of humerus A transverse fracture above the condyles of the humerus Fracture & dislocation Trauma
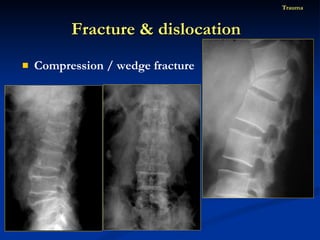
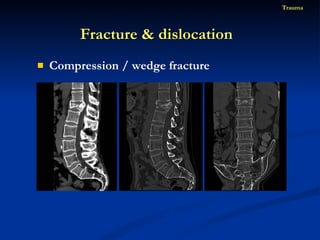
- 84. Compression / wedge fracture Fracture & dislocation Trauma
- 85. Compression / wedge fracture Fracture & dislocation Trauma
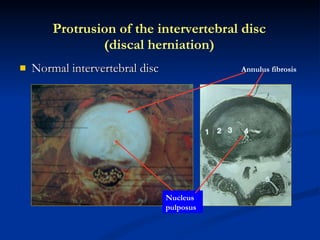
- 87. Normal intervertebral disc Protrusion of the intervertebral disc (discal herniation) Annulus fibrosis Nucleus pulposus
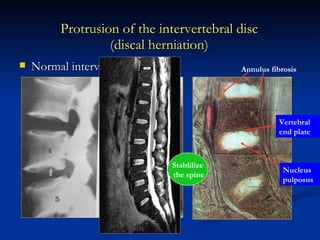
- 88. Protrusion of the intervertebral disc (discal herniation) Normal intervertebral disc Annulus fibrosis Nucleus pulposus Vertebral end plate Stablilize the spine
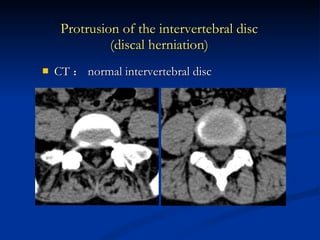
- 89. CT : normal intervertebral disc Protrusion of the intervertebral disc (discal herniation)
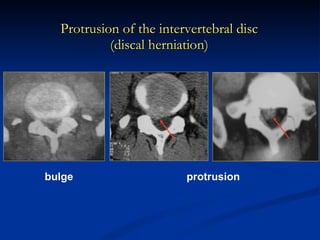
- 90. Protrusion of the intervertebral disc (discal herniation) bulge protrusion
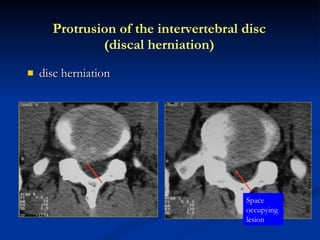
- 91. disc herniation Protrusion of the intervertebral disc (discal herniation) Space occupying lesion
- 92. Disc herniation MRI normal
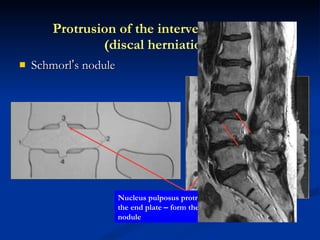
- 93. Schmorl ’ s nodule Protrusion of the intervertebral disc (discal herniation) Annulus fibrosis Nucleus pulposus protruded into the end plate – form the Schmorl ’ s nodule
- 94. Thank you
Editor's Notes
- #66: stiffness of a joint -ankylosis