Understanding Service Failure
- 2. Learning Objectives • To understand the Service Provider’s responsibility for managing service quality • To understand the interdependence between marketing/sales, service delivery and the customer • To understand some of the quality gaps that cause service failures
- 3. What is Service Failure? Service Failure is the process of NOT keeping promises Above expectation (great service) 4 Expected 2 Zone of 3 Service 1 Tolerance 5 Below 6 expectation 7 8 9 (poor service) Failed service
- 4. Causes of Service Failure The facilities and environment The expectations Actions (& The systems inactions) of staff 4 2 3 The process 5 1 6 7 8 9 Actions of the Actions of other customer The equipment customers
- 5. What Needs to be Managed? The facilities and environment The expectations Actions (& The systems inactions) of staff The process If something can affect the service then the Service Provider becomes The Service Provider needs to manage responsible for managing it these as well. Actions of the Actions of other customer The equipment customers
- 6. Managing Customers We limit their choices We restrict their movement We tell them what to do
- 7. Managing Other Customers We make them wait We choose which customers to serve
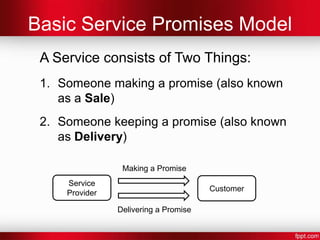
- 9. Basic Service Promises Model A Service consists of Two Things: 1. Someone making a promise (also known as a Sale) 2. Someone keeping a promise (also known as Delivery) Making a Promise Service Customer Provider Delivering a Promise
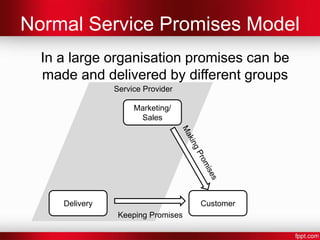
- 10. Normal Service Promises Model In a large organisation promises can be made and delivered by different groups Service Provider Marketing/ Sales Delivery Customer Keeping Promises
- 11. This can complicate things… “This is pest control, how may I help you?” Keeping Promises
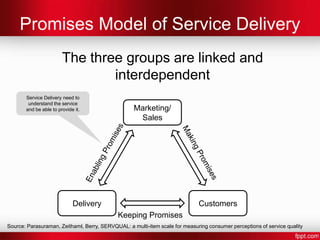
- 12. Promises Model of Service Delivery The three groups are linked and interdependent Service Delivery need to understand the service and be able to provide it. Marketing/ Sales Delivery Customers Keeping Promises Source: Parasuraman, Zeithaml, Berry, SERVQUAL: a multi-item scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality
- 13. Service Failure: Understanding Gaps
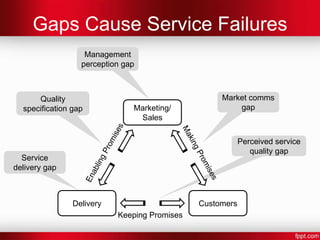
- 14. Gaps Cause Service Failures Management perception gap Quality Market comms specification gap Marketing/ gap Sales Perceived service quality gap Service delivery gap Delivery Customers Keeping Promises
- 15. Management Perception Gap Management perception gap Quality specification gap Marketing/ Sales Market comms gap Management has an inaccurate understanding of Perceived service quality gap Service delivery gap Delivery Keeping Promises Customers quality expectations
- 16. Quality Specification Gap Management perception gap Quality specification gap Marketing/ Sales Market comms gap Service quality specifications do not match management Perceived service quality gap Service delivery gap Delivery Keeping Promises Customers expectations
- 17. Service Delivery Gap Management perception gap Quality specification gap Marketing/ Sales Market comms gap Quality specifications and not met by service delivery Perceived service quality gap Service delivery gap Delivery Customers Keeping Promises
- 18. Market Communications Gap Management perception gap Quality specification gap Marketing/ Sales Market comms gap Messages from marketing do not match the service Perceived service quality gap Service delivery gap Delivery Keeping Promises Customers experience
- 19. Perceived Service Quality Gap Management perception gap Quality specification gap Marketing/ Sales Market comms gap The experienced service does not match expected Perceived service quality gap Service delivery gap Delivery Keeping Promises Customers service
- 20. Final Word on Service Failure • The Service Provider is responsible for managing the service – this includes managing the customer • Gaps in the interactions between the groups create service failures • Once a service failure occurs, the service provider needs to initiate a service recovery process
Editor's Notes
- #2: Title Slide
- #4: The customer’s experience can be mapped through a service sequence. This is an abstract map showing how the perceived quality of service can be affected by the different acts. The customer may have had some great service (service encounter 4) but the final four service encounters will have left the impression of poor service.
- #5: There are a number of things that can affect the quality of the service.
- #6: If something can affect the quality of the service, then the service provider becomes responsible for managing it. Service providers are therefore responsible for managing the customer as well as managing other customers.
- #7: Example of Managing CustomersMenus limit customers to a certain selection of options at a restaurant.Role lanes ensures that customers go the right way.Clear instructions and signposts at airports direct customers to the right place.
- #8: Example of Managing Other CustomersWe make them wait away from the service area.We limit which customers we allow in to be served.
- #9: Title Slide
- #10: Simply, you promise something to a customer (in exchange for money)then you give it to the customer.
- #11: Sales/Marketing may make the promises and the Delivery will keep the promise
- #12: Sales/Marketing may make the promises and the Delivery will keep the promise
- #13: Marketing and Sales make promises to customers.Marketing/Sales also need to ensure that the Delivery arm is enabled to keep those promises.Delivery need to understand what promises have been made and deliver on these to keep the promises.
- #14: Title Slide
- #15: Management Perception GapThere is a disconnect between what managers believe that customers want and what those customers really want.Quality Specification GapThe specification of the service’s quality is deficient meaning that the service delivered is not as expected. The service delivery groups are therefore unable to deliver services to the desired quality.Service Delivery GapThe service delivery groups have the ability to deliver service but do not manage to do so.MarketComms GapThe marketing (or sales) material oversells the service. The customers expectations are set too high and exceed the capability of the service delivery groups.Perceived Quality GapThe customers’ expectations exceed the service provided.
- #16: Management Perception GapThere is a disconnect between what managers believe that customers want and what those customers really want.Quality Specification GapThe specification of the service’s quality is deficient meaning that the service delivered is not as expected. The service delivery groups are therefore unable to deliver services to the desired quality.Service Delivery GapThe service delivery groups have the ability to deliver service but do not manage to do so.MarketComms GapThe marketing (or sales) material oversells the service. The customers expectations are set too high and exceed the capability of the service delivery groups.Perceived Quality GapThe customers’ expectations exceed the service provided.
- #17: Management Perception GapThere is a disconnect between what managers believe that customers want and what those customers really want.Quality Specification GapThe specification of the service’s quality is deficient meaning that the service delivered is not as expected. The service delivery groups are therefore unable to deliver services to the desired quality.Service Delivery GapThe service delivery groups have the ability to deliver service but do not manage to do so.MarketComms GapThe marketing (or sales) material oversells the service. The customers expectations are set too high and exceed the capability of the service delivery groups.Perceived Quality GapThe customers’ expectations exceed the service provided.
- #18: Management Perception GapThere is a disconnect between what managers believe that customers want and what those customers really want.Quality Specification GapThe specification of the service’s quality is deficient meaning that the service delivered is not as expected. The service delivery groups are therefore unable to deliver services to the desired quality.Service Delivery GapThe service delivery groups have the ability to deliver service but do not manage to do so.MarketComms GapThe marketing (or sales) material oversells the service. The customers expectations are set too high and exceed the capability of the service delivery groups.Perceived Quality GapThe customers’ expectations exceed the service provided.
- #19: Management Perception GapThere is a disconnect between what managers believe that customers want and what those customers really want.Quality Specification GapThe specification of the service’s quality is deficient meaning that the service delivered is not as expected. The service delivery groups are therefore unable to deliver services to the desired quality.Service Delivery GapThe service delivery groups have the ability to deliver service but do not manage to do so.MarketComms GapThe marketing (or sales) material oversells the service. The customers expectations are set too high and exceed the capability of the service delivery groups.Perceived Quality GapThe customers’ expectations exceed the service provided.
- #20: Management Perception GapThere is a disconnect between what managers believe that customers want and what those customers really want.Quality Specification GapThe specification of the service’s quality is deficient meaning that the service delivered is not as expected. The service delivery groups are therefore unable to deliver services to the desired quality.Service Delivery GapThe service delivery groups have the ability to deliver service but do not manage to do so.MarketComms GapThe marketing (or sales) material oversells the service. The customers expectations are set too high and exceed the capability of the service delivery groups.Perceived Quality GapThe customers’ expectations exceed the service provided.