Maintenance of Pumps
- 1. Maintenance Of Pumps Hammad Akber GTE
- 2. Introduction: • Pump: is a machine that converts mechanical energy into fluid energy, the fluid being incompressible. • Types: Following are the 2 basic types. • Dynamic: Centrifugal , Axial. • Displacement: Reciprocating & Rotary.
- 3. MAINTENANCE PHOILOSOPHY: • Maintenance is done on to the machine in order to improve system reliability. Maintenance may be : • Preventive Predictive (Conditional Monitoring) Periodic • Break down • RCM
- 4. PUMP MAJOR COMPONENTS: • Shaft • Impeller • Wear Rings • Stuffing Box • Diffuser Casing • Bearings
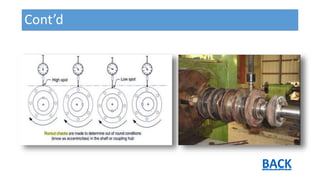
- 5. Shaft Run Out • Runout checks are made to determine out of roundness conditions (eccentricity) in a shaft. Whether shaft is concentric or not ? • Runout occurs due to: a) Machining Process b) Dents from handling. c) Rust patches. d) Rotor bow / sag due to thermal effects, gravity, or other influences/loads. e) Defective or worn bearings in the machine or lathe supports
- 6. Cont’d • Moderate to excessive run out will create moderate to excessive vibration within a pump (may cause rubbing). • Firstly shaft itself is checked and then along with its attached components (wear ring , impeller etc.) • Dial Indicator is attached on axially given points. Variation in readings indicates:
- 7. Balancing & Float Check • Balancing of a rotor is carried out to eliminate the vibration. • Balancing correction weights may eliminate the dynamic forces but they will not resolve the eccentricity issue. • Correction weights may added or material may remove for the balancing. • FLOAT
- 8. Cont’d BACK
- 9. Wear Ring Clearances: • Wear ring provides close clearances to minimize leakage from the discharge to the suction of the impeller. • As the wear ring wears with use , leakage will gradually increases , effecting the pump efficiency. • The gap is destroyed if there is misalignment or shaft deflection. • Clearances is taken through the Feeler Gauge. • Material : SS or Bronze
- 10. Cont’d BACK
- 11. BEARING • Providing Support to a shaft for smooth Running. • Lubrication prevents metal-metal contact. • Thrust Bearings are used to compensate/bear axial load. Bearing inspection is very important during Pump maintenance. Causes of Bearing Failure: Flaking , Spalling , Rust & Corrosion, wear , Babbit metal remove , loss of lubrication etc.
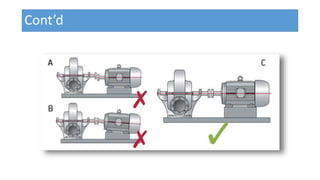
- 12. Shaft Alignment • Shaft alignment is the process to align two or more shafts with each other to within a tolerated margin. It is an absolute requirement for machinery before the machinery is put in service. Therefore pump and motor shafts are aligned before they put into service. • Misalignment between the pump and drive can result in premature bearing failure or other damage.
- 13. Cont’d
- 14. Shaft Alignment
- 15. Inspection During Maintenance: • Pump Impeller. • Mechanical Seal. • Gland Packing. • Shaft Sleeve. • Relieve Valve. • Pump Element (PD).
- 16. Mechanical Seal Seal may fail due to lack of lubrication. Due to which temperature rises at the sealing faces that will damage the elastomer part of the mechanical seal. Pump Vibration. Vibration imparts forces on each part of the seal components. Vibrations may be due to worn bearings.
- 17. Cont’d
- 18. Gland Packing
- 19. Relieve Valve • During Pump Maintenance relief valve is overhaul for cleaning and inspection purpose. • Checking spring stiffness etc.
- 22. QUESTIONS