Overseas France short summary
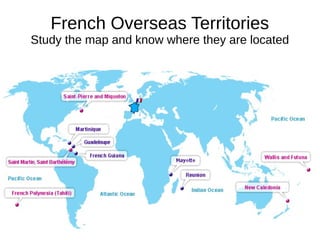
- 1. French Overseas Territories Study the map and know where they are located
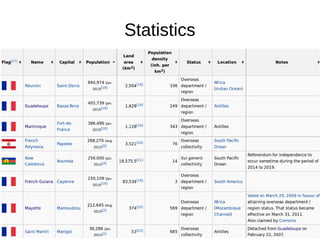
- 2. Statistics
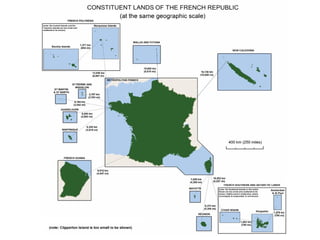
- 3. Population of Overseas France ● Metropolitan (European) France accounts for 82.2% of the land territory, and 95.9% of the population of the French Republic. ● The five overseas departments—Martinique, Guadeloupe, Réunion, French Guiana, and Mayotte— have the same political status as metropolitan France's departments. Overseas collectivities/territories have more autonomy (freedom to make their own laws). ● Metropolitan France = 63 million
- 5. Réunion
- 6. Guadeloupe
- 7. Martinique
- 8. Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- 10. Mayotte
- 11. French Polynesia
- 12. Saint Martin
- 13. Representation in the French National Assembly In the 13th Legislature (2012-2017), the French overseas departments and territories are represented by 27 députés, or 4.7% of the 577 députés in the National Assembly: ● Réunion: 7 députés ● Guadeloupe: 4 députés ● Martinique: 4 députés ● French Polynesia: 3 députés ● French Guiana: 2 députés ● Mayotte: 2 député ● New Caledonia: 2 députés ● Saint Pierre and Miquelon: 1 député ● Saint Martin: 1 député
- 14. Representation in the French Senate Since September 2011, the French overseas departments and territories are represented by 21 senators in the French Senate, or 6.0% of the 343 senators in the Senate: ● Réunion: 4 senators ● Guadeloupe: 3 senators ● French Guiana: 2 senators ● French Polynesia: 2 senators ● Martinique: 2 senators ● Mayotte: 2 senators ● New Caledonia: 2 senators ● Saint Martin: 1 senator ● Saint Pierre and Miquelon: 1 senator
- 15. Though there have been independence movements, overseas France has generally decided to stay part of France ● For example: – Maritinique 80% against more autonomy in 2010. – Mayotte voted not to be independent in 1976 – New Caledonia politics ruled by the anti- independence party. – Guadaloupe's strong independence movements in the 1970s and 1980s lead to more autonomy and now few want full independence.
- 16. Martinique
- 17. Benefits of staying with France ● Stability – Newly independent countries often have long periods of unrest, threat of a dictatorship coming to power. Being part of France is safer. ● Economy – Countries under French rule enjoy economic support from the EU and generally better living standards than their neighbor countries. ● French Identity – Some countries have closer ties to France than to neighbor countries.
- 18. Guadeloupe, during the 2009 Caribbean General Strike
- 19. Negatives of staying with France ● Less autonomy – Only have little or no representation in many laws that govern them. ● High cost of living – French prices, local wages. ● Inequality – similar to colonial system – 2009 Caribbean General Strikes ● Violent riots that shut down the tourist season. ● Anger about cost of goods. ● 1% of the population, the white French descendants, own most of the industry. ● Result: Increased minimum wage, compromise with France.