Intercellular junction
- 1. Intercellular Junction Presented By: 14-Arid-2067 14-Arid-2030 14-Arid-2070 Presented To: Dr. Riaz Hussain Pasha
- 2. Intercellular junctions • A cell junction is a type of structure that exists within the tissue of some multicellular organisms. • specializations of the cellular margins that contribute to the adhesion or allow for communication between cells. • Mostly found in epithelial tissues.
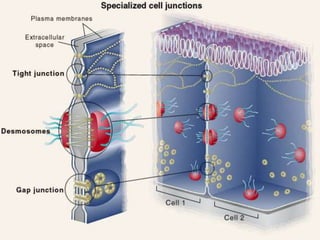
- 3. CONT… There are three main types: • Gap junction (nexus). • Tight junction (zonula occludens) • Anchoring junction -Desmosome (macula adherens) -Hemidesmosome -Adheren (zonula adherens)
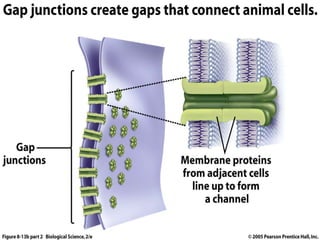
- 5. Gap Junction: • It is a communicating junction. • Gap junctions consist of intercellular channels in the plasma membrane of adjacent cells. • Consist of six connexon proteins arranged to form a doughnut shape structure. • Play role in cardiac muscle contraction.
- 6. Cont… • Helps in signal transfer in brain. • Their size vary in different cells.
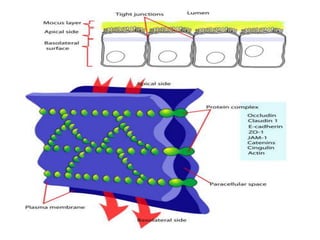
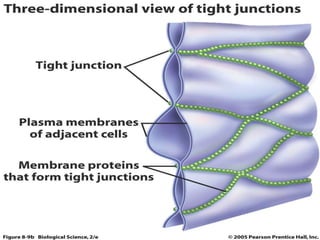
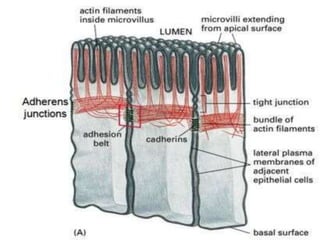
- 8. Tight Junction: • The borders of two cells are fused together, often around the whole perimeter of each cell, forming a continuous belt like junction known as a tight junction or zonula occludens (zonula = latin for belt). • ZO-1 & ZO-2 Link transmembrane proteins (Occludin and Clauding) with Spectrin. • Prevent leakage of fluid. • Found in the apical region around the cell's circumference.
- 9. Cont… • It prevent mobility of transmembrane proteins. • It regulate the movement of water and solutes between epithelial layer. • Lines the gastrointestinal tract.
- 12. Anchoring Junction: • Cells within tissues anchor to one another and to extracellular fluid. • There are following three types: 1. Desmosomes Junction 2. Hemidesmosomes Junction 3. Adherens Juntion
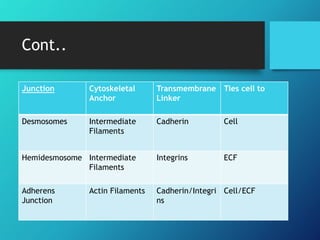
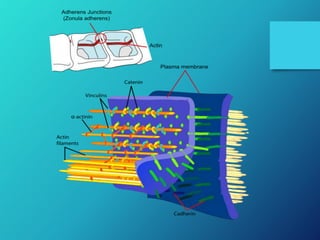
- 13. Cont.. Junction Cytoskeletal Anchor Transmembrane Linker Ties cell to Desmosomes Intermediate Filaments Cadherin Cell Hemidesmosome Intermediate Filaments Integrins ECF Adherens Junction Actin Filaments Cadherin/Integri ns Cell/ECF
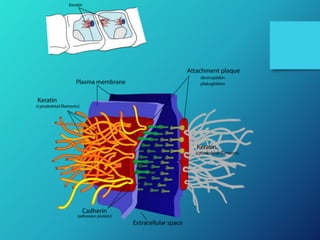
- 14. Desmosomes: • Form cell to cell junction. • Known as Maculae adherens. • Intracellular adaptor proteins connect to intermediate filament and form cytoplasmic plaque. • Cadherin joins the cytoplasmic plaques of two cells.
- 15. Cont… • The gap b/w this junction is 30nm • Found in epidermis of skin and muscle tissues. • Blistering diseases. • Pemphigus. • Hailey-Hailey disease.
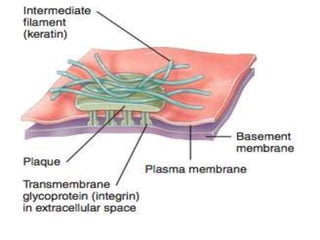
- 17. Hemidesmosomes: • Connect cell to extracellular fluid. • Connect epithelial cells to basement membrane. • Integrins are the linking proteins. • Present in epidermis of skin. • Epidermolysis bullosa.
- 19. Adheren Junction: • Junctions which form junction b/w cell to cell. • Also known as Zonulae adherens. • Lies basal to tight junction. • Microfilaments of two cells are connected by cadherins. • Cytoplasmic face is linked to actin cytoskeleton. • Actin myosin interaction can change the shape of the epithelium.