Enzyme cofactors
Download as PPTX, PDF23 likes22,366 views
Many enzymes require non-protein cofactors to help catalyze reactions. There are two main types of enzymes: simple protein enzymes and conjugated enzymes, which contain both a protein and non-protein cofactor. The cofactor, combined with the protein apoenzyme, form the active holoenzyme. Cofactors can be inorganic ions or organic coenzymes and prosthetic groups. Coenzymes often function as carriers in redox or group transfer reactions and many are vitamin derivatives, acting as precursors. Common coenzymes include coenzyme A, NAD+, FAD, pyridoxal phosphate, and tetrahydrofolate. Metal ions also play important roles in many enzyme reactions by
1 of 17
Downloaded 226 times













Recommended
Biosynthesis of purine & pyrimidine 



Biosynthesis of purine & pyrimidine Government Pharmacy College Sajong, Government of Sikkim This document discusses the biosynthesis of purines and pyrimidines. It explains that purines and pyrimidines are synthesized through de novo and salvage pathways. The de novo pathway involves multiple enzyme-catalyzed steps to convert simple precursors into the complex purine and pyrimidine nucleotides. This includes converting ribose-5-phosphate into inosine monophosphate (IMP) through 10 steps for purine synthesis. IMP is then used to synthesize adenine monophosphate (AMP) and guanine monophosphate (GMP). The salvage pathway recovers bases and nucleotides from degraded DNA and RNA. Pyrimidine synthesis is described as simpler than purine synthesis.
Definitions and types of coenzymes



Definitions and types of coenzymesJasmineJuliet Coenzyme - Introduction, Definition, Examples for coenzyme, reaction catalysed by coenzyme, Types of coenzymes - cosubstrate and prosthetic group coenzymes, second type of classification of coenzyme- hydrogen group transfer , other than hydrogen group transfer.
Determination of primary structure of proteins



Determination of primary structure of proteinsPradeep Singh Narwat The document discusses the determination of the primary structure of proteins. It begins by explaining that proteins are composed of amino acid residues linked by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain. The primary structure refers to the specific sequence of amino acids in this chain. Mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry techniques are used to analyze protein fragments obtained through enzymatic or chemical cleavage to determine the amino acid sequence and thereby elucidate the primary structure.
Oxidative Phosphorylation



Oxidative PhosphorylationA Biodiction : A Unit of Dr. Divya Sharma Oxidative Phosphorylation in Plants
It is like a summary of oxidative phosphorylation and reference to textbooks is required before presentation.
Properties of enzymes



Properties of enzymesjagan vana Enzymes have several key properties including their catalytic property, specificity, reversibility, and sensitivity to heat and pH. They act as catalysts in biochemical reactions, only affecting their specific substrates, and can operate reversibly or irreversibly depending on conditions. An enzyme's activity is also dependent on factors like temperature and acidity levels.
Purine and Pyrimidine biosynthesis



Purine and Pyrimidine biosynthesisSripati Abhiram Sahoo Nucleotide Biosynthesis involves 2 processes. one is Denovo synthesis and other is Salvage pathway. An outline of both the processes has given in this presentation.
Purine degradation



Purine degradationsridevi244 This document summarizes purine biosynthesis and degradation. Purine is synthesized through an 11 step pathway forming IMP, the parent nucleotide. IMP is then used to synthesize AMP and GMP. Purines are broken down to uric acid through a multi-step process. Gout is caused by excessive uric acid formation due to increased purine biosynthesis or decreased excretion leading to uric acid crystal deposition in joints.
Classification and nomenclature of enzymes 



Classification and nomenclature of enzymes UNIVERSITY OF SARGODHA This document discusses the classification and nomenclature of enzymes. It describes three naming systems: trivial names which provide no functional information; systematic names which indicate the substrate and type of reaction; and EC (Enzyme Commission) numbers which classify enzymes into six main classes based on the type of chemical reaction catalyzed. The six classes are oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases. EC numbers are a four-digit code that precisely identifies each enzyme and its catalytic activity.
Substrate level phosphorylation and it's mechanism || Biochemistry || B Pharm...



Substrate level phosphorylation and it's mechanism || Biochemistry || B Pharm...K.K.Wagh College of Pharmacy, Nashik Substrate level phosphorylation and it's mechanism || Biochemistry || B Pharmacy || Project || slideshare || biology || chemistry
*images use in this ppt is only for educational purpose
In this presentation, i tell about substrate level phosphorylation
Phosphorylation involves the transfer of phosphate
group from one compound to other.
➢ Substrate level phosphorylation is a direct
phosphorylation of ADP with a phosphatase group by
using the energy obtain from a coupled reaction.
➢ Occurs in cytoplasm ( glycolysis – due to aerobic and
anaerobic condition) and in mitochondrial matrix ( krebs
cycle – anaerobic condition)
Secondary Structure Of Protein (Repeating structure of protein)



Secondary Structure Of Protein (Repeating structure of protein)Amrutha Hari This document discusses the structure of proteins at various levels. It describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures. The secondary structures discussed in detail include the alpha helix, beta pleated sheet, random coil, collagen helix, and beta turn. The alpha helix and beta pleated sheet are stabilized by hydrogen bonding between amino acids. The collagen helix structure provides strength and is the main component of connective tissues. Genetic disorders like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and osteogenesis imperfecta result from defects in collagen structures. Ramachandran plots are used to visualize allowed backbone dihedral angles in protein structures.
Amino acid biosynthesis grp assignment ppt



Amino acid biosynthesis grp assignment pptGloria Okenze The document summarizes amino acid biosynthesis in mammals. It discusses the different families of amino acids and how they are synthesized from common precursors like glutamate. It describes regulation of biosynthesis through feedback inhibition. Finally, it outlines some genetic diseases that result from defects in amino acid metabolism, like phenylketonuria and homocystinuria.
properties of enzyme



properties of enzymeRakhi Adarsh Enzymes have a high degree of specificity, catalyzing only one particular reaction. They are not used up in the reactions they catalyze and can be reused repeatedly to catalyze more reactions. Enzymes catalyze reactions with great specificity and are reusable, catalyzing multiple reactions without being consumed.
Mechanism of action of lysozyme



Mechanism of action of lysozymeAkshay Wakte It represents the enzyme lysozyme with its structure and its mechanism of action on the components of the cell layers.
Enzymes



EnzymesJayakara Bhandary The document discusses enzymes and their classification. It defines enzymes as biological catalysts that are usually proteins and increase the rate of chemical reactions. It describes the six main classes of enzymes based on their catalytic activity as well as the Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system. The key points are that enzymes have unique active sites that substrates fit into, they are most active at optimal temperatures and pH levels, and their reaction rates depend on enzyme and substrate concentrations.
Metabolism of essential and non essential amino acids 20



Metabolism of essential and non essential amino acids 20mariagul6 This document summarizes the metabolism of essential and non-essential amino acids in humans. It explains that non-essential amino acids can be synthesized in the body, while essential amino acids cannot and must come from diet. It describes the two main pathways of amino acid metabolism as transamination and deamination. Transamination transfers amino groups between amino acids, while deamination removes amino groups to form ammonia. The carbon skeletons of amino acids can be broken down into seven key intermediates, determining if the amino acid is glucogenic, ketogenic, or both. Genetic defects in amino acid metabolism pathways can cause serious disease.
Allosteric enzymes



Allosteric enzymesRachana Tiwari 1) Allosteric enzymes have additional sites called allosteric sites that are distinct from the active site. Binding of an effector molecule to these sites can induce a conformational change in the active site, increasing or decreasing the enzyme's activity.
2) There are two main models that describe allosteric regulation - the concerted model where binding causes simultaneous changes in all subunits, and the sequential model where changes occur sequentially.
3) Allosteric enzymes exhibit sigmoidal kinetics curves rather than traditional hyperbolic curves due to their cooperative binding behavior. Positive allosteric effectors increase enzyme activity while negative effectors decrease it.
DEAMINATION AND DECARBOXYLATION



DEAMINATION AND DECARBOXYLATIONRabia Khan Baber Deamination and decarboxylation are processes that break down amino acids. Deamination removes an amine group from an amino acid, releasing ammonia. There are two types of deamination - oxidative deamination uses oxidation to remove the amine group, while non-oxidative uses other reactions. Decarboxylation removes a carboxyl group from an amino acid, releasing carbon dioxide. Both processes help convert excess amino acids into usable byproducts that can be removed from the body.
Nucleotides an introduction



Nucleotides an introductionBahauddin Zakariya University lahore Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. They consist of three components: a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. The nitrogenous bases include purines like adenine and guanine, and pyrimidines like cytosine and thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA. The pentose sugars are either deoxyribose in DNA or ribose in RNA. Successive nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bonds between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the hydroxyl group of the next. This forms the hydrophilic backbone of nucleic acids and gives them polarity with distinct 5' and 3' ends. The specific hydrogen bonding between nucleotide base pairs
Bacterial cell wall polysaccharides kssd



Bacterial cell wall polysaccharides kssdsujathashanmugasunda1 Introduction-Cell wall and functions
Gram +ve and -ve cell wall
Bacterial cell wall - structure
Peptidoglycan-Composition and Structure
Types of polysaccharidesBacterial cell wall
Functions of polysaccharides in Bacterial cell wall
Enzymes definitions, types & classification



Enzymes definitions, types & classificationJasmineJuliet Enzyme - Introduction, Biocatalysts, Definition of enzymes, Types of enzymes, classification of enzyme, Nomenclature of enzymes, EC number, Types of enzymes with examples, and reaction.
History of enzymes.



History of enzymes.Ravi Raj Kamal This document provides a history of enzymes, beginning with early references to enzymatic processes in ancient texts. It describes key discoveries such as Kirchoff's observation of starch hydrolysis, Pasteur's conclusion that fermentation requires living yeast cells, and Buchner's demonstration of cell-free fermentation. Major milestones include the first isolation of an enzyme (diastase) in 1833, Sumner's purification and crystallization of urease in 1926, and the determination of enzyme structures using X-ray crystallography beginning in 1965. The document also notes the discovery of ribozymes in the 1980s and restriction enzymes in the 1960s-1970s.
Pentose phosphate pathway,hmp shunt



Pentose phosphate pathway,hmp shuntSchool of Biosciences, MACFAST College, Tiruvalla, Kerala, India The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), also known as the hexose monophosphate shunt (HMP) or phosphogluconate pathway, is an alternative glucose metabolism pathway to glycolysis. It is more complex than glycolysis and takes place in the cytosol. The PPP is important for generating NADPH for biosynthesis of fatty acids, steriods, and maintaining glutathione levels, as well as producing pentoses used in nucleic acid synthesis. The pathway contains oxidative and non-oxidative phases, with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase being the regulatory enzymes controlled by NADPH and pentose levels.
Lec 4 level 3-de (enzymes, coenzymes, cofactors)



Lec 4 level 3-de (enzymes, coenzymes, cofactors)dream10f This document discusses enzymes, coenzymes, and cofactors. It covers the classification, structure, and function of enzymes. Key points include:
1. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts and increase the rate of biochemical reactions without being consumed.
2. Coenzymes and cofactors are non-protein molecules required for enzymatic activity. Coenzymes include NAD+, FAD, and ATP.
3. Enzymes can be classified based on their catalytic action, such as oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases.
Protein structure: details



Protein structure: detailsdamarisb This document discusses the different levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. The primary structure refers to the amino acid sequence. Secondary structure includes alpha helices, beta sheets, and beta turns formed by hydrogen bonding between amino acids. Tertiary structure is the 3D conformation determined by interactions between side chains. Quaternary structure refers to the arrangement of multiple polypeptide subunits in multimeric proteins. The structures are determined through techniques like X-ray crystallography and NMR.
Enzyme catalysis mechanisms involved



Enzyme catalysis mechanisms involvedDavid Enoma Enzymes use several catalytic mechanisms to lower the free energy of transition states and greatly increase reaction rates, including acid-base catalysis, covalent catalysis, metal ion catalysis, and bringing substrates into close proximity and proper orientation. Acid-base catalysis involves proton transfer from catalytic amino acid side chains. Covalent catalysis transiently forms covalent bonds between enzyme and substrate. Metal ion catalysis uses transition metals to orient substrates, mediate redox reactions, or stabilize charges. Proximity and orientation align substrates for reaction, while catalysis by approximation brings two substrates together for reaction.
Transcription in eukaryotes



Transcription in eukaryotesHemantkrdu The document summarizes transcription in eukaryotes. It discusses that eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases - Pol I, Pol II, and Pol III. Pol II is responsible for transcribing protein-encoding genes and requires general transcription factors for initiation. Transcription involves initiation, elongation, and termination phases. The RNA polymerase forms a pre-initiation complex at the promoter and then adds nucleotides during elongation. Termination occurs after RNA processing and polyadenylation.
Amino acid 



Amino acid sridarshini chandra Amino acids are organic compounds that contain an amino group, a carboxyl group, a central carbon atom, and a side chain. There are 20 standard amino acids that are the building blocks of proteins. Amino acids can be classified based on their structure, polarity, nutritional requirements, and metabolic fate. They perform important functions including serving as monomers for protein synthesis, participating in cellular processes, and acting as precursors for other compounds.
Enzymes properties, nomenclature and classification



Enzymes properties, nomenclature and classificationJasmineJuliet Enzymes - Definition, Introduction about biocatalysts, Properties of enzymes, Specificity, capacity for regulation, Example for enzyme at specific pH, Nomenclature of enzymes, Systematic name, common name, enzyme commission number, Classification of enzymes: Oxidoreductase, Transferase, lyases, ligases, isomerases, hydrolases.
Co enzymes



Co enzymesPulkit Agarwal This document discusses co-enzymes and their functions. It defines co-factors as non-protein components that assist enzymes in biochemical transformations, and can be organic or inorganic. Organic co-factors include vitamins like NAD+, Coenzyme A, and flavin mononucleotide. Inorganic co-factors include metal ions like copper, iron, and magnesium. Co-enzymes are loosely bound co-factors that transport groups between enzymes, and include NAD+, Coenzyme A, flavin adenine dinucleotide, and adenosine triphosphate. Specific examples of enzymes requiring various co-enzymes are provided.
Cofactor and Coenzyme.ppt



Cofactor and Coenzyme.pptRohithK65 1. Cofactors and coenzymes assist enzymes in catalyzing reactions. Cofactors are tightly bound to enzymes while coenzymes bind reversibly.
2. Common coenzymes include NAD+, FAD, coenzyme A, biotin, thiamine pyrophosphate, and pyridoxal phosphate. They transfer elements like electrons, acyl groups, and amino groups between reactions.
3. Coenzymes can be classified as metabolite or vitamin-derived. Vitamin-derived coenzymes include NAD+, FAD, coenzyme A, and others that derive from vitamins like niacin, riboflavin, pantot
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Substrate level phosphorylation and it's mechanism || Biochemistry || B Pharm...



Substrate level phosphorylation and it's mechanism || Biochemistry || B Pharm...K.K.Wagh College of Pharmacy, Nashik Substrate level phosphorylation and it's mechanism || Biochemistry || B Pharmacy || Project || slideshare || biology || chemistry
*images use in this ppt is only for educational purpose
In this presentation, i tell about substrate level phosphorylation
Phosphorylation involves the transfer of phosphate
group from one compound to other.
➢ Substrate level phosphorylation is a direct
phosphorylation of ADP with a phosphatase group by
using the energy obtain from a coupled reaction.
➢ Occurs in cytoplasm ( glycolysis – due to aerobic and
anaerobic condition) and in mitochondrial matrix ( krebs
cycle – anaerobic condition)
Secondary Structure Of Protein (Repeating structure of protein)



Secondary Structure Of Protein (Repeating structure of protein)Amrutha Hari This document discusses the structure of proteins at various levels. It describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures. The secondary structures discussed in detail include the alpha helix, beta pleated sheet, random coil, collagen helix, and beta turn. The alpha helix and beta pleated sheet are stabilized by hydrogen bonding between amino acids. The collagen helix structure provides strength and is the main component of connective tissues. Genetic disorders like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and osteogenesis imperfecta result from defects in collagen structures. Ramachandran plots are used to visualize allowed backbone dihedral angles in protein structures.
Amino acid biosynthesis grp assignment ppt



Amino acid biosynthesis grp assignment pptGloria Okenze The document summarizes amino acid biosynthesis in mammals. It discusses the different families of amino acids and how they are synthesized from common precursors like glutamate. It describes regulation of biosynthesis through feedback inhibition. Finally, it outlines some genetic diseases that result from defects in amino acid metabolism, like phenylketonuria and homocystinuria.
properties of enzyme



properties of enzymeRakhi Adarsh Enzymes have a high degree of specificity, catalyzing only one particular reaction. They are not used up in the reactions they catalyze and can be reused repeatedly to catalyze more reactions. Enzymes catalyze reactions with great specificity and are reusable, catalyzing multiple reactions without being consumed.
Mechanism of action of lysozyme



Mechanism of action of lysozymeAkshay Wakte It represents the enzyme lysozyme with its structure and its mechanism of action on the components of the cell layers.
Enzymes



EnzymesJayakara Bhandary The document discusses enzymes and their classification. It defines enzymes as biological catalysts that are usually proteins and increase the rate of chemical reactions. It describes the six main classes of enzymes based on their catalytic activity as well as the Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system. The key points are that enzymes have unique active sites that substrates fit into, they are most active at optimal temperatures and pH levels, and their reaction rates depend on enzyme and substrate concentrations.
Metabolism of essential and non essential amino acids 20



Metabolism of essential and non essential amino acids 20mariagul6 This document summarizes the metabolism of essential and non-essential amino acids in humans. It explains that non-essential amino acids can be synthesized in the body, while essential amino acids cannot and must come from diet. It describes the two main pathways of amino acid metabolism as transamination and deamination. Transamination transfers amino groups between amino acids, while deamination removes amino groups to form ammonia. The carbon skeletons of amino acids can be broken down into seven key intermediates, determining if the amino acid is glucogenic, ketogenic, or both. Genetic defects in amino acid metabolism pathways can cause serious disease.
Allosteric enzymes



Allosteric enzymesRachana Tiwari 1) Allosteric enzymes have additional sites called allosteric sites that are distinct from the active site. Binding of an effector molecule to these sites can induce a conformational change in the active site, increasing or decreasing the enzyme's activity.
2) There are two main models that describe allosteric regulation - the concerted model where binding causes simultaneous changes in all subunits, and the sequential model where changes occur sequentially.
3) Allosteric enzymes exhibit sigmoidal kinetics curves rather than traditional hyperbolic curves due to their cooperative binding behavior. Positive allosteric effectors increase enzyme activity while negative effectors decrease it.
DEAMINATION AND DECARBOXYLATION



DEAMINATION AND DECARBOXYLATIONRabia Khan Baber Deamination and decarboxylation are processes that break down amino acids. Deamination removes an amine group from an amino acid, releasing ammonia. There are two types of deamination - oxidative deamination uses oxidation to remove the amine group, while non-oxidative uses other reactions. Decarboxylation removes a carboxyl group from an amino acid, releasing carbon dioxide. Both processes help convert excess amino acids into usable byproducts that can be removed from the body.
Nucleotides an introduction



Nucleotides an introductionBahauddin Zakariya University lahore Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. They consist of three components: a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. The nitrogenous bases include purines like adenine and guanine, and pyrimidines like cytosine and thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA. The pentose sugars are either deoxyribose in DNA or ribose in RNA. Successive nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bonds between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the hydroxyl group of the next. This forms the hydrophilic backbone of nucleic acids and gives them polarity with distinct 5' and 3' ends. The specific hydrogen bonding between nucleotide base pairs
Bacterial cell wall polysaccharides kssd



Bacterial cell wall polysaccharides kssdsujathashanmugasunda1 Introduction-Cell wall and functions
Gram +ve and -ve cell wall
Bacterial cell wall - structure
Peptidoglycan-Composition and Structure
Types of polysaccharidesBacterial cell wall
Functions of polysaccharides in Bacterial cell wall
Enzymes definitions, types & classification



Enzymes definitions, types & classificationJasmineJuliet Enzyme - Introduction, Biocatalysts, Definition of enzymes, Types of enzymes, classification of enzyme, Nomenclature of enzymes, EC number, Types of enzymes with examples, and reaction.
History of enzymes.



History of enzymes.Ravi Raj Kamal This document provides a history of enzymes, beginning with early references to enzymatic processes in ancient texts. It describes key discoveries such as Kirchoff's observation of starch hydrolysis, Pasteur's conclusion that fermentation requires living yeast cells, and Buchner's demonstration of cell-free fermentation. Major milestones include the first isolation of an enzyme (diastase) in 1833, Sumner's purification and crystallization of urease in 1926, and the determination of enzyme structures using X-ray crystallography beginning in 1965. The document also notes the discovery of ribozymes in the 1980s and restriction enzymes in the 1960s-1970s.
Pentose phosphate pathway,hmp shunt



Pentose phosphate pathway,hmp shuntSchool of Biosciences, MACFAST College, Tiruvalla, Kerala, India The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), also known as the hexose monophosphate shunt (HMP) or phosphogluconate pathway, is an alternative glucose metabolism pathway to glycolysis. It is more complex than glycolysis and takes place in the cytosol. The PPP is important for generating NADPH for biosynthesis of fatty acids, steriods, and maintaining glutathione levels, as well as producing pentoses used in nucleic acid synthesis. The pathway contains oxidative and non-oxidative phases, with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase being the regulatory enzymes controlled by NADPH and pentose levels.
Lec 4 level 3-de (enzymes, coenzymes, cofactors)



Lec 4 level 3-de (enzymes, coenzymes, cofactors)dream10f This document discusses enzymes, coenzymes, and cofactors. It covers the classification, structure, and function of enzymes. Key points include:
1. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts and increase the rate of biochemical reactions without being consumed.
2. Coenzymes and cofactors are non-protein molecules required for enzymatic activity. Coenzymes include NAD+, FAD, and ATP.
3. Enzymes can be classified based on their catalytic action, such as oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases.
Protein structure: details



Protein structure: detailsdamarisb This document discusses the different levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. The primary structure refers to the amino acid sequence. Secondary structure includes alpha helices, beta sheets, and beta turns formed by hydrogen bonding between amino acids. Tertiary structure is the 3D conformation determined by interactions between side chains. Quaternary structure refers to the arrangement of multiple polypeptide subunits in multimeric proteins. The structures are determined through techniques like X-ray crystallography and NMR.
Enzyme catalysis mechanisms involved



Enzyme catalysis mechanisms involvedDavid Enoma Enzymes use several catalytic mechanisms to lower the free energy of transition states and greatly increase reaction rates, including acid-base catalysis, covalent catalysis, metal ion catalysis, and bringing substrates into close proximity and proper orientation. Acid-base catalysis involves proton transfer from catalytic amino acid side chains. Covalent catalysis transiently forms covalent bonds between enzyme and substrate. Metal ion catalysis uses transition metals to orient substrates, mediate redox reactions, or stabilize charges. Proximity and orientation align substrates for reaction, while catalysis by approximation brings two substrates together for reaction.
Transcription in eukaryotes



Transcription in eukaryotesHemantkrdu The document summarizes transcription in eukaryotes. It discusses that eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases - Pol I, Pol II, and Pol III. Pol II is responsible for transcribing protein-encoding genes and requires general transcription factors for initiation. Transcription involves initiation, elongation, and termination phases. The RNA polymerase forms a pre-initiation complex at the promoter and then adds nucleotides during elongation. Termination occurs after RNA processing and polyadenylation.
Amino acid 



Amino acid sridarshini chandra Amino acids are organic compounds that contain an amino group, a carboxyl group, a central carbon atom, and a side chain. There are 20 standard amino acids that are the building blocks of proteins. Amino acids can be classified based on their structure, polarity, nutritional requirements, and metabolic fate. They perform important functions including serving as monomers for protein synthesis, participating in cellular processes, and acting as precursors for other compounds.
Enzymes properties, nomenclature and classification



Enzymes properties, nomenclature and classificationJasmineJuliet Enzymes - Definition, Introduction about biocatalysts, Properties of enzymes, Specificity, capacity for regulation, Example for enzyme at specific pH, Nomenclature of enzymes, Systematic name, common name, enzyme commission number, Classification of enzymes: Oxidoreductase, Transferase, lyases, ligases, isomerases, hydrolases.
Substrate level phosphorylation and it's mechanism || Biochemistry || B Pharm...



Substrate level phosphorylation and it's mechanism || Biochemistry || B Pharm...K.K.Wagh College of Pharmacy, Nashik
Similar to Enzyme cofactors (20)
Co enzymes



Co enzymesPulkit Agarwal This document discusses co-enzymes and their functions. It defines co-factors as non-protein components that assist enzymes in biochemical transformations, and can be organic or inorganic. Organic co-factors include vitamins like NAD+, Coenzyme A, and flavin mononucleotide. Inorganic co-factors include metal ions like copper, iron, and magnesium. Co-enzymes are loosely bound co-factors that transport groups between enzymes, and include NAD+, Coenzyme A, flavin adenine dinucleotide, and adenosine triphosphate. Specific examples of enzymes requiring various co-enzymes are provided.
Cofactor and Coenzyme.ppt



Cofactor and Coenzyme.pptRohithK65 1. Cofactors and coenzymes assist enzymes in catalyzing reactions. Cofactors are tightly bound to enzymes while coenzymes bind reversibly.
2. Common coenzymes include NAD+, FAD, coenzyme A, biotin, thiamine pyrophosphate, and pyridoxal phosphate. They transfer elements like electrons, acyl groups, and amino groups between reactions.
3. Coenzymes can be classified as metabolite or vitamin-derived. Vitamin-derived coenzymes include NAD+, FAD, coenzyme A, and others that derive from vitamins like niacin, riboflavin, pantot
Enzyme cofactors 



Enzyme cofactors RobinSingh419 Many enzymes require non-protein cofactors to help catalyze reactions. There are two types of enzymes: simple protein enzymes composed only of polypeptide chains, and conjugated enzymes containing both a protein and non-protein cofactor. The cofactor, combined with the protein apoenzyme, form the active holoenzyme. Cofactors can be inorganic ions or complex organic coenzymes, and can be tightly bound prosthetic groups or loosely attached coenzymes. Vitamins often act as precursors to coenzymes, helping enzymes function in catalytic reactions.
Teena_sem_4_Coenzyme_.pptx



Teena_sem_4_Coenzyme_.pptxSPCGC AJMER This document summarizes key coenzymes and their functions. It discusses how Fritz Albert Lipmann received the 1953 Nobel Prize for discovering coenzyme A. Coenzymes such as NAD+, NADP+, FMN, FAD, vitamin B12, and coenzyme A are described. NAD+ and NADP+ help transfer hydrogen atoms during redox reactions. FMN and FAD also participate in redox reactions through the transfer of electrons. Coenzyme A transfers acyl groups and is required for important metabolic reactions. Vitamin B12 is required for DNA, amino acid and fatty acid synthesis. Coenzymes are essential components of enzymes that help drive important biochemical transformations in the
Coenzymes and their functions



Coenzymes and their functionsSarah Hamid Coenzymes are organic molecules that bind to enzymes and help catalyze biochemical reactions without being consumed in the process. Some important coenzymes discussed include thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), coenzyme A (CoA), and flavin mononucleotide (FMN). TPP acts as a cofactor in carbohydrate metabolism. CoA facilitates fatty acid synthesis and energy production. FMN assists in oxidation-reduction reactions as a stronger oxidizing agent than NAD. Coenzymes help convert apoenzymes to active holoenzymes so that essential biochemical reactions can occur.
Coenzymes and Cofactors -pg.pptx



Coenzymes and Cofactors -pg.pptxyonasemiru2 This document provides an overview of advanced enzymology for medical biochemistry students. It covers the basics of enzymes including their components, structure and function. Key points include: enzymes are protein catalysts that lower activation energy; they contain an active site that binds substrates and facilitates reactions; cofactors like metal ions and coenzymes contribute to reactivity. Multi-enzyme systems are discussed where intermediates are transferred between enzymes without diffusing. Different isolation, purification and characterization methods for enzymes are also summarized.
Enzymes-.pdf



Enzymes-.pdfAlodiaPastorizo Metabolism involves the breakdown (catabolism) and building (anabolism) of molecules in the body. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze metabolic reactions and are made up of amino acids folded into shapes with active sites. Enzymes require cofactors like vitamins and minerals to function as holoenzymes in reactions. Enzyme activity is affected by factors like temperature, substrate concentration, and pH - with each enzyme having optimal conditions for maximum reaction rates.
Vitamins & Coenzymes



Vitamins & CoenzymesÜlger Ahmet 1. Vitamins are organic molecules that serve as cofactors for enzyme reactions and must be obtained through diet as they cannot be synthesized by the body.
2. Vitamins are classified as either water-soluble or fat-soluble, with water-soluble vitamins including all B vitamins and vitamin C, and fat-soluble vitamins being vitamins A, D, E, and K.
3. Each vitamin has a specific biochemical function, such as vitamin C serving as an antioxidant and cofactor for collagen synthesis, vitamin B12 acting as a cofactor for fatty acid and amino acid metabolism, and vitamin K being required for blood clotting through gamma-carboxylation of glutamate residues.
Inborn error of metabolism 2019



Inborn error of metabolism 2019Hosin Abass This document discusses inborn errors of metabolism, which are genetic disorders caused by defects in metabolic enzymes or pathways. It defines key metabolic terms like metabolism, catabolism, anabolism, cofactors, coenzymes, apoenzymes and holoenzymes. It also summarizes several important metabolic pathways in the human body like glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, fatty acid synthesis and breakdown, and amino acid and carbohydrate metabolism. Tandem mass spectrometry is highlighted as an important technique for diagnosing inborn errors of metabolism through newborn screening.
Cofactors, Coenzymes, Abzymes and Ribozymes.pptx



Cofactors, Coenzymes, Abzymes and Ribozymes.pptxCherry Cofactors, Coenzymes, Abzymes and Ribozymes.pptx
Enzyme ppt



Enzyme pptbirtucandemeke This document summarizes the chemistry of enzymes, including their classification and chemical composition. It discusses that enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts and speed up reactions. Enzymes are classified in multiple ways, including based on their site of action as intracellular endoenzymes or extracellular exoenzymes, and based on the reaction they control using the EC system of six main classes: oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases. The document also describes several key enzyme terminology concepts, such as cofactors, coenzymes, prosthetic groups, and substrates.
Vitamin



VitaminLam Nguyen Vitamins are organic compounds that are needed in small amounts for normal physiological functions. There are two groups of vitamins - fat soluble (A, D, E, K) and water soluble (B vitamins and vitamin C). Most vitamins act as cofactors for enzymes by providing "chemical teeth". Thiamine (B1) was the first vitamin discovered. It is a cofactor for enzymes involved in carbohydrate metabolism, forming thiamine pyrophosphate which acts as an ylid during reactions. Deficiency can cause beriberi with symptoms like neuropathy.
Co enz



Co enzGeeta Jaiswal This document discusses co-enzymes, which are non-protein parts of enzymes that help enzymes be active. Co-enzymes can be classified based on their functional characteristics, such as transferring groups other than hydrogen, or transferring hydrogen. They can also be classified based on their structures, with many being derivatives of adenosine monophosphate. Co-enzymes work with enzymes and help transfer atoms or groups between substrates. They are required for many reactions in the body and are related to different B vitamins. Some enzymes are initially produced as inactive proenzymes and require activation by other enzymes or pH changes before becoming active.
Human Physiology Biochemicals



Human Physiology BiochemicalsStephan Van Breenen This document summarizes key concepts about biomolecules and human physiology. It discusses the four major classes of biomolecules - carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleotides - including their structures, functions, and examples. It also describes protein structure and interactions, including binding sites, affinity, competition, and modulation of binding. Overall, the document provides a concise overview of fundamental biochemical concepts and biomolecules important for human physiology.
lipids, Def. Classification, Function.pptx



lipids, Def. Classification, Function.pptxABHIJIT BHOYAR The document defines lipids and classifies them. It discusses that lipids are a diverse group of organic compounds that are hydrophobic and insoluble in water. Lipids serve important functions like energy storage, cellular structure, signaling and energy transport. Lipids are classified as simple lipids, complex lipids, derived lipids and miscellaneous lipids. Simple lipids include fats, oils and waxes. Complex lipids contain additional groups like phosphate, carbohydrates or proteins. The document provides examples and descriptions of different lipid classes.
enzyme and coenzym



enzyme and coenzymMohammad k Younus This document discusses coenzymes, cofactors, and enzyme inhibition. It defines cofactors as non-protein compounds required for enzyme biological activity, and divides them into organic and inorganic groups. Coenzymes are loosely bound cofactors that assist enzyme functioning and transport chemical groups between enzymes. Many coenzymes are related to vitamins. Enzyme inhibitors can be competitive or non-competitive, and examples are given of their medical and poison applications.
MICROBtruru4u47474u4u4u44uy5uruhrIO.pptx



MICROBtruru4u47474u4u4u44uy5uruhrIO.pptxsmitpanchal8619 Xxjdjdudueii4db f. Drjjr re brueue 3bebidid enejdje ebjdchebcjdi ici ifi igi it8ivigi ifi igi ivifi ivi igi iv8v8t8g9g8gg8 8rig 4br rbr r g. F r. Brhd dbf chf. Jfn bdode ci9d be v8db fi ir. Odjcf. Ifj f ficbr cir rjfbr cjrn rirjf fn8cbf fifjr girbf firXxjdjdudueii4db f. Drjjr re brueue 3bebidid enejdje ebjdchebcjdi ici ifi igi it8ivigi ifi igi ivifi ivi igi iv8v8t8g9g8gg8 8rig 4br rbr r g. F r. Brhd dbf chf. Jfn bdode ci9d be v8db fi ir. Odjcf. Ifj f ficbr cir rjfbr cjrn rirjf fn8cbf fifjr girbf firXxjdjdudueii4db f. Drjjr re brueue 3bebidid enejdje ebjdchebcjdi ici ifi igi it8ivigi ifi igi ivifi ivi igi iv8v8t8g9g8gg8 8rig 4br rbr r g. F r. Brhd dbf chf. Jfn bdode ci9d be v8db fi ir. Odjcf. Ifj f ficbr cir rjfbr cjrn rirjf fn8cbf fifjr girbf firXxjdjdudueii4db f. Drjjr re brueue 3bebidid enejdje ebjdchebcjdi ici ifi igi it8ivigi ifi igi ivifi ivi igi iv8v8t8g9g8gg8 8rig 4br rbr r g. F r. Brhd dbf chf. Jfn bdode ci9d be v8db fi ir. Odjcf. Ifj f ficbr cir rjfbr cjrn rirjf fn8cbf fifjr girbf firXxjdjdudueii4db f. Drjjr re brueue 3bebidid enejdje ebjdchebcjdi ici ifi igi it8ivigi ifi igi ivifi ivi igi iv8v8t8g9g8gg8 8rig 4br rbr r g. F r. Brhd dbf chf. Jfn bdode ci9d be v8db fi ir. Odjcf. Ifj f ficbr cir rjfbr cjrn rirjf fn8cbf fifjr girbf firXxjdjdudueii4db f. Drjjr re brueue 3bebidid enejdje ebjdchebcjdi ici ifi igi it8ivigi ifi igi ivifi ivi igi iv8v8t8g9g8gg8 8rig 4br rbr r g. F r. Brhd dbf chf. Jfn bdode ci9d be v8db fi ir. Odjcf. Ifj f ficbr cir rjfbr cjrn rirjf fn8cbf fifjr girbf firXxjdjdudueii4db f. Drjjr re brueue 3bebidid enejdje ebjdchebcjdi ici ifi igi it8ivigi ifi igi ivifi ivi igi iv8v8t8g9g8gg8 8rig 4br rbr r g. F r. Brhd dbf chf. Jfn bdode ci9d be v8db fi ir. Odjcf. Ifj f ficbr cir rjfbr cjrn rirjf fn8cbf fifjr girbf firXxjdjdudueii4db f. Drjjr re brueue 3bebidid enejdje ebjdchebcjdi ici ifi igi it8ivigi ifi igi ivifi ivi igi iv8v8t8g9g8gg8 8rig 4br rbr r g. F r. Brhd dbf chf. Jfn bdode ci9d be v8db fi ir. Odjcf. Ifj f ficbr cir rjfbr cjrn rirjf fn8cbf fifjr girbf firXxjdjdudueii4db f. Drjjr re brueue 3bebidid enejdje ebjdchebcjdi ici ifi igi it8ivigi ifi igi ivifi ivi igi iv8v8t8g9g8gg8 8rig 4br rbr r g. F r. Brhd dbf chf. Jfn bdode ci9d be v8db fi ir. Odjcf. Ifj f ficbr cir rjfbr cjrn rirjf fn8cbf fifjr girbf firXxjdjdudueii4db f. Drjjr re brueue 3bebidid enejdje ebjdchebcjdi ici ifi igi it8ivigi ifi igi ivifi ivi igi iv8v8t8g9g8gg8 8rig 4br rbr r g. F r. Brhd dbf chf. Jfn bdode ci9d be v8db fi ir. Odjcf. Ifj f ficbr cir rjfbr cjrn rirjf fn8cbf fifjr girbf firXxjdjdudueii4db f. Drjjr re brueue 3bebidid enejdje ebjdchebcjdi ici ifi igi it8ivigi ifi igi ivifi ivi igi iv8v8t8g9g8gg8 8rig 4br rbr r g. F r. Brhd dbf chf. Jfn bdode ci9d be v8db fi ir. Odjcf. Ifj f ficbr cir rjfbr cjrn rirjf fn8cbf fifjr girbf firXxjdjdudueii4db f. Drjjr re brueue 3bebidid enejdje ebjdchebcjdi ici ifi igi it8ivigi ifi igi ivifi ivi igi iv8v8t8g9g8gg8 8rig 4br rbr r g. F r. Brhd dbf chf. Jfn bdode ci9d be v8db fi ir. Odjcf. Ifj f ficbr cir rjf
Coenzymes and Cofactors -pg.pptx



Coenzymes and Cofactors -pg.pptxGetahunAlega This document provides an overview of enzymes for medical biochemistry students. It defines enzymes as protein catalysts and describes their key components and functions. Enzymes contain an active site that binds substrates and facilitates reactions. Some enzymes require cofactors like metal ions or coenzymes to function. Multi-enzyme systems involve enzymes working together in complexes or pathways. The document outlines techniques for isolating and characterizing purified enzymes.
More from Muhammad Mudassir (20)
Significance of silicon

Significance of siliconMuhammad Mudassir Silicon is the second most common element in the Earth's crust. Silicones are polymeric organosilicon compounds containing Si-O-Si linkages and Si-C bonds. They have many useful properties including low conductivity, thermal stability, chemical inertness, and resistance to oxygen, ozone, and UV light. Silicones have various applications including use in textiles as coatings and softeners, in medicine as elastomers for devices like catheters, and in plants and human health where silicon plays a role in photosynthesis, stress resistance, and bone/tissue health.
Conducting polymers



Conducting polymersMuhammad Mudassir This document outlines how plastics can become conductive through a process called doping. It discusses that polymers are normally insulating but certain polymers like polyacetylene can conduct electricity when doped. Doping involves introducing charges into the polymer through oxidation or reduction. This leaves holes that allow electrons to move along the polymer chain. Factors that affect conductivity include the number of charge carriers, their mobility, temperature, and presence of doping materials. Applications of conductive plastics include uses in electronics, solar cells, LEDs, electromagnetic shielding, and smart windows.
Water splitting on semiconductor catalysts under visible light irradiation

Water splitting on semiconductor catalysts under visible light irradiationMuhammad Mudassir This document discusses photocatalytic water splitting to produce hydrogen fuel using solar energy. It begins by outlining the need to find renewable hydrogen production methods, as fossil fuel reserves are depleting. It then explains that photocatalytic water splitting uses a photocatalyst to split water into hydrogen and oxygen when exposed to sunlight, providing a renewable method. However, the process is not yet highly efficient due to recombination of the photogenerated charge carriers in the photocatalyst before they can react at the surface to split water. Improving the efficiency and durability of photocatalysts remains an ongoing challenge.
Natural and chemical biocides



Natural and chemical biocidesMuhammad Mudassir This document discusses biocides, which are formulations containing active substances that control or destroy harmful organisms. It provides background information on biocides, including types (chemical and natural), major classes, and common active ingredients. The document outlines both arguments for biocides, such as increased food supply and farmer profits, and risks, like negative health and environmental impacts. It also describes common applications of biocides in areas like agriculture, swimming pools, cosmetics/pharmaceuticals, and medical device sterilization. In conclusion, the document states that biocide use should be minimized and carefully regulated due to the risks involved.
Artificial sweeteners



Artificial sweetenersMuhammad Mudassir Artificial sweeteners are used as sugar substitutes that provide sweetness with fewer calories than sugar. Some are produced naturally while others like aspartame, saccharin, acesulfame-K, sucralose, and neotame are synthesized. They are used by those watching their sugar intake, managing diabetes, or concerned with weight gain. While safe for most in moderation, artificial sweeteners come with restrictions for those with rare conditions like phenylketonuria. They are many times sweeter than sugar but provide no calories, making them a popular sugar substitute.
Supramolecular chemistry



Supramolecular chemistryMuhammad Mudassir Supramolecular chemistry is the chemistry of intermolecular bonds between two or more chemical species. It was pioneered in the late 19th century and Nobel Prizes have been awarded for its development. Supramolecular interactions include ion-ion, ion-dipole, and dipole-dipole interactions. Building blocks include macrocycles, structural units, and biologically derived units. Control relies on thermodynamics and the molecular environment. Applications include materials technology, catalysis, medicine, and other devices. Intensive research is enabling new functional materials and more effective catalysis through template-directed synthesis.
Reactive dyes



Reactive dyesMuhammad Mudassir Reactive dyes are organic dyes that form covalent bonds with cellulose fibers. They were first commercially produced in 1956 and have advantages like excellent color fastness and ease of washing. Reactive dyes contain three parts - a chromophore for color, a reactive group that bonds to fibers, and a bridging group connecting these. Dyeing involves exhaustion of dye onto fibers, fixation through alkaline conditions forming covalent bonds, and washing unfixed dye away. Reactive dyeing gives very colorfast results due to the strong covalent bonds formed.
Mesoporous materials



Mesoporous materialsMuhammad Mudassir Mesoporous materials have pore sizes between 2-50 nm which gives them high surface areas of 400-1000 m2/g. Common types include MCM-41, MCM-48, MCM-50, HMS, and SBA-15. They can be synthesized using hard or soft templating methods. Applications include drug delivery, adsorption, chromatography, catalysis, sensors, and diagnostics due to their chemical stability, large pore volumes, and tunable surface properties.
Cationic and anionic res ponsive gels



Cationic and anionic res ponsive gelsMuhammad Mudassir This document discusses cationic and anionic responsive microgels. It defines microgels as crosslinked, polymeric, colloidal particles that can swell and deswell in response to stimuli. It classifies microgels based on the nature of crosslinks and response. Cationic microgels contain basic groups while anionic microgels contain acidic groups. Their properties change with pH and ionic strength. Microgels can be synthesized via precipitation or microemulsion polymerization. Applications include use in coatings, pharmaceuticals, and materials reinforcement.
Application of ionic liquids in pharmaceuticals



Application of ionic liquids in pharmaceuticalsMuhammad Mudassir Ionic liquids are salts that are liquid below ambient temperature. They are composed solely of ions without water. Ionic liquids based on imidazole have been well studied as novel solvents. Ionic liquids have wide-ranging properties including low vapor pressure, high viscosity, thermal stability, and ability to dissolve both polar and nonpolar compounds. They have various applications in pharmaceuticals as solvents, for drug delivery, and to address issues like low drug solubility and polymorphism.
Recent advances in battery science and technology



Recent advances in battery science and technologyMuhammad Mudassir This document discusses the history and types of batteries. It begins with defining batteries and describing their invention by Volta in 1800. It then discusses the increasing demand for batteries to power electronics and electric vehicles. The document outlines several recent advances in batteries, including sodium-ion and solid-state designs that improve safety. It concludes that continued research in nanoscience and new materials could enable breakthroughs in sustainable battery technologies.
Mossbauer spectroscopy



Mossbauer spectroscopyMuhammad Mudassir Mossbauer spectroscopy uses gamma ray absorption to probe the local electronic environment of atomic nuclei. It works by measuring small shifts in the resonant absorption peaks of nuclei in different chemical states. The document outlines the basic principles, typical methods, applications in physics, chemistry, biology, mineralogy and metallurgy, as well as limitations, of Mossbauer spectroscopy.
Microbial fuel cells



Microbial fuel cellsMuhammad Mudassir Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) are bioelectrochemical systems that use bacteria to generate electricity. MFCs can be categorized as mediated or unmediated. Mediated MFCs use chemical mediators to transfer electrons from bacteria to an anode, while unmediated MFCs directly transfer electrons via bacterial membrane proteins. MFCs have the potential to generate electricity from wastewater treatment and can be used as biosensors to measure pollutant levels. However, challenges remain in improving catalytic rates, energy production levels, and reducing costs before widespread applications can be realized.
Liqued crystals



Liqued crystalsMuhammad Mudassir Liquid crystals are an intermediate phase between solid and liquid that have properties of both. They lack a fixed shape but their molecules align in the same direction, giving them orientational order. There are several types of liquid crystals including nematic, smectic, and cholesteric that differ in their molecular arrangements. Liquid crystals are used widely in applications like digital displays, thermometers, and protective clothing due to their optical and thermal properties.
Composites of nano zincoxide for efficientphotocatalytic activity



Composites of nano zincoxide for efficientphotocatalytic activityMuhammad Mudassir This document discusses composites of nano zinc oxide for efficient photocatalytic activity. It introduces various nanocomposites including ZnO-CuO and explains their properties. The document then describes the preparation of pure ZnO nanostructures and ZnO-CuO nanocomposites via hydrothermal methods. It investigates the photocatalytic activity of ZnO-CuO composites in degrading methyl orange dye under UV light and finds they have higher degradation rates than pure ZnO. In conclusion, hydrothermally synthesized ZnO/CuO nanocomposites have enhanced photocatalytic properties due to efficient charge transfer between ZnO and CuO.
Bio energy uses in pakistan



Bio energy uses in pakistanMuhammad Mudassir This document discusses biomass energy conversion and biogas generation in Pakistan. It explains that biomass, or bioenergy, includes organic materials like wood, crops, and animal waste that can be used for energy. Biomass undergoes either fermentation or anaerobic digestion by microorganisms to produce biogas, which is 55-65% methane. Biogas plants are classified based on their design and process, and types discussed include single-stage continuous plants, double-stage continuous plants, floating drum plants, and fixed-dome plants. The document outlines prospects for bioenergy in Pakistan and applications such as cooking, lighting, electricity generation, and fertilizer production.
Fly ash and its applications



Fly ash and its applicationsMuhammad Mudassir Fly ash has various applications including for desulphurization. For desulphurization, an absorbent is synthesized by mixing fly ash, calcium oxide, and calcium sulfate. This absorbent is then used to remove sulfur dioxide from flue gases through reactions that are affected by factors like absorbent particle size, temperature, humidity, and sulfur dioxide concentration. The desulphurization capacity increases with higher humidity but decreases with lower sulfur dioxide concentration and larger particle size, while temperature has a negligible impact. Fly ash thus helps reduce air pollution from coal burning, though it also has limitations like containing radioactive materials.
Removal of heavy metal by nano metal oxide



Removal of heavy metal by nano metal oxideMuhammad Mudassir This document discusses the removal of heavy metals from water using nano metal oxides. It introduces heavy metals as relatively high density metals that are toxic, like lead, arsenic, cadmium and mercury. Heavy metals accumulate in organisms and can be harmful. Nano metal oxides like ZnO are effective at removing heavy metals from water through adsorption and photocatalysis mechanisms involving the absorption of light and production of electron-hole pairs on the nanoparticle surface. This allows for the reduction of heavy metals or reaction with electron acceptors. Nano metal oxides provide an efficient and low-cost approach for heavy metal removal through these photocatalytic processes.
Majour source of energy alternative of fuel



Majour source of energy alternative of fuelMuhammad Mudassir This document discusses different sources of energy, including fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas. It also discusses alternative and renewable sources of energy like solar, wind, tidal, biomass and nuclear energy. Fossil fuels are non-renewable and their combustion produces greenhouse gases, but they are easily combustible and produce large amounts of energy. Renewable sources like solar, wind and tidal do not produce emissions but have limitations around availability. Nuclear energy produces through fission or fusion reactions but has risks. In conclusion, non-renewable resources will be depleted so renewable alternatives need further development to meet future energy demands.
Ionic liqueds



Ionic liquedsMuhammad Mudassir This document provides an overview of ionic liquids, including their history, composition, properties, applications, and toxicity concerns. Ionic liquids are molten salts that are liquid at or near room temperature. They are composed of a combination of ions, most commonly organic cations paired with inorganic anions, which results in their unusually low melting points. Ionic liquids have numerous advantageous properties, such as low volatility, high thermal stability, and wide liquid range, making them promising as green replacements for traditional organic solvents. However, concerns remain around the toxicity of some ionic liquids, particularly those containing halogen ions, which could release toxic species in water.
Recently uploaded (20)
Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping



Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports TapingKusal Goonewardena Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping: Pathway to Sports Medicine Excellence
This presentation was delivered in Colombo, Sri Lanka, at the Institute of Sports Medicine to an audience of sports physiotherapists, exercise scientists, athletic trainers, and healthcare professionals. Led by Kusal Goonewardena (PhD Candidate - Muscle Fatigue, APA Titled Sports & Exercise Physiotherapist) and Gayath Jayasinghe (Sports Scientist), the session provided comprehensive training on soft tissue assessment, treatment techniques, and essential sports taping methods.
Key topics covered:
✅ Soft Tissue Therapy – The science behind muscle, fascia, and joint assessment for optimal treatment outcomes.
✅ Sports Taping Techniques – Practical applications for injury prevention and rehabilitation, including ankle, knee, shoulder, thoracic, and cervical spine taping.
✅ Sports Trainer Level 1 Course by Sports Medicine Australia – A gateway to professional development, career opportunities, and working in Australia.
This training mirrors the Elite Akademy Sports Medicine standards, ensuring evidence-based approaches to injury management and athlete care.
If you are a sports professional looking to enhance your clinical skills and open doors to global opportunities, this presentation is for you.
Helping Autistic Girls Shine Webinar Slides



Helping Autistic Girls Shine Webinar SlidesPooky Knightsmith For more information about my speaking and training work, visit: https://www.pookyknightsmith.com/speaking/
Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptx



Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptxSamruddhi Khonde 📢 Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
🔬 Antibiotics have revolutionized medicine, playing a crucial role in combating bacterial infections. Among them, Beta-Lactam antibiotics remain the most widely used class due to their effectiveness against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. This guide provides a detailed overview of their history, classification, chemical structures, mode of action, resistance mechanisms, SAR, and clinical applications.
📌 What You’ll Learn in This Presentation
✅ History & Evolution of Antibiotics
✅ Cell Wall Structure of Gram-Positive & Gram-Negative Bacteria
✅ Beta-Lactam Antibiotics: Classification & Subtypes
✅ Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems & Monobactams
✅ Mode of Action (MOA) & Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
✅ Beta-Lactamase Inhibitors & Resistance Mechanisms
✅ Clinical Applications & Challenges.
🚀 Why You Should Check This Out?
Essential for pharmacy, medical & life sciences students.
Provides insights into antibiotic resistance & pharmaceutical trends.
Useful for healthcare professionals & researchers in drug discovery.
👉 Swipe through & explore the world of antibiotics today!
🔔 Like, Share & Follow for more in-depth pharma insights!
NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdf



NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdfDolisha Warbi NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION, Introduction, definition, types - macronutrient and micronutrient, food pyramid, meal planning, nutritional assessment of individual, family and community by using appropriate method, nutrition education, nutritional rehabilitation, nutritional deficiency disorder, law/policies regarding nutrition in India, food hygiene, food fortification, food handling and storage, food preservation, food preparation, food purchase, food consumption, food borne diseases, food poisoning
Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdf



Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdfRommel Regala This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.
Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptx



Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptxKhurshid Ahmed Ansari Validity is an important characteristic of a test. A test having low validity is of little use. Validity is the accuracy with which a test measures whatever it is supposed to measure. Validity can be low, moderate or high. There are many factors which affect the validity of a test. If these factors are controlled, then the validity of the test can be maintained to a high level. In the power point presentation, factors affecting validity are discussed with the help of concrete examples.
Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat
RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ (Railway Assistant Loco Pilot)



RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ (Railway Assistant Loco Pilot)SONU HEETSON RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ PDF Free Download. Railway Assistant Loco Pilot Mechanic Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Important Questions.
Functional Muscle Testing of Facial Muscles.pdf



Functional Muscle Testing of Facial Muscles.pdfSamarHosni3 Functional Muscle Testing of Facial Muscles.pdf
Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHat
BỘ TEST KIỂM TRA GIỮA KÌ 2 - TIẾNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUẨN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



BỘ TEST KIỂM TRA GIỮA KÌ 2 - TIẾNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUẨN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection https://app.box.com/s/ij1ty3vm7el9i4qfrr41o756xycbahmg
Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoy



Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoyEconomic and Social Research Institute NAPD Annual Symposium
“Equity in our Schools: Does the system deliver for all young people?”
How to Configure Recurring Revenue in Odoo 17 CRM



How to Configure Recurring Revenue in Odoo 17 CRMCeline George This slide will represent how to configure Recurring revenue. Recurring revenue are the income generated at a particular interval. Typically, the interval can be monthly, yearly, or we can customize the intervals for a product or service based on its subscription or contract.
One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo Slides



One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo SlidesCeline George In this slide, we’ll discuss the one click RFQ Cancellation in odoo 18. One-Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 is a feature that allows users to quickly and easily cancel Request for Quotations (RFQs) with a single click.
BỘ TEST KIỂM TRA GIỮA KÌ 2 - TIẾNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUẨN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



BỘ TEST KIỂM TRA GIỮA KÌ 2 - TIẾNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUẨN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Enzyme cofactors
- 2. Many enzymes need non-protein parts called cofactors that help in catalysis Two Types of Enzymes 1. Simple Protein Enzymes = Composed of a polypeptide chain (protein only 2. Conjugated Enzymes = Protein + Non- proteinous part ----The non-proteinous part of a conjugated enzyme is called a cofactor while the proteinous part of an enzyme is referred to as apoenzyme…… Cofactor + apoenzyme = Holoenzyme
- 3. Only the combination of an apoenzyme with its cofactor (i.e., a holoenzyme) is operative (a holoenzyme also refers to the assembled form of a multiple subunit protein).
- 4. • The cofactors can be inorganic ions or coenzymes (complex organic or metallo-organic molecules). • Some cofactors bind to the enzyme protein very tightly (non-covalently or covalently), they are thus called prosthetic groups, while loosely attached non- proteineous components are called as Coenzymes • Coenzymes usually function as transient carriers of specific function groups. Coenzymes can act as Co- Substrate…. • Vitamins (organic nutrients required in small amount in the diet) have been found to often act as precursors of coenzymes.
- 6. Prosthetic group is present in enzymes and non- enzyme proteins. Prosthetic group is always tightly attached to the proteinous part of an enzyme, Prosthetic group mainly participate in Redox reactions Example is heme, a prosthetic group present in cytochrome oxidase….
- 7. Coenzymes are of two types 1. Group transferring coenzymes….they are involved in transferring group from one substrate to another substrate (a) Coenzyme-A is involved in the transfer of acyl group from one substrate to another substrate (b) Biotin is involved is in transfer of –COO (c) Pyridoxal phosphate is involved in transfer of amino group 2. Electron transferring coenzymes …they are involved in redox reactions (a) NAD and NADH+H (b) FAD and FADH2 Most of the coenzymes are Vitamin B derivatives Coenzymes can act as co-substrates
- 8. (Vitamins)
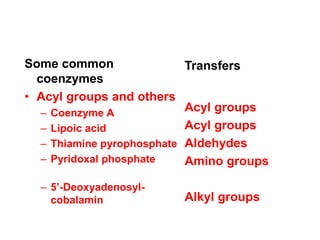
- 9. Some common coenzymes • Acyl groups and others – Coenzyme A – Lipoic acid – Thiamine pyrophosphate – Pyridoxal phosphate – 5’-Deoxyadenosyl- cobalamin Transfers Acyl groups Acyl groups Aldehydes Amino groups Alkyl groups
- 10. Thiamine (Thiamine pyrophosphate…..Vitamin B1) • Catalyzes decarboxylation of keto acids, a feature of primary metabolism • e.g. pyruvic acid → acetaldehyde in glycolysis • pyruvic acid → acetyl-CoA usually found in phosphate form
- 11. Flavin Adenine mononeucleotide and Flavin adenine dinucleotide (Vitamin B2) • Involved in redox rxns of C-C bonds •Metabolism of carbs, fat, protein
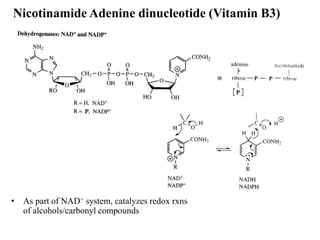
- 12. Nicotinamide Adenine dinucleotide (Vitamin B3) • As part of NAD+ system, catalyzes redox rxns of alcohols/carbonyl compounds
- 13. Coenzyme A (Panthothenic acid OR Vitamin B5) • Synthesis of fatty acids (acetate pathway), some peptides, phenylpropanoids, isoprenoids • Fat, carbs and protein metabolism
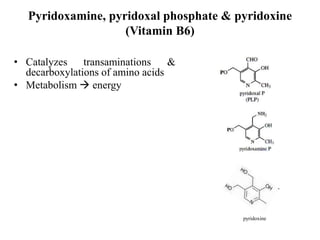
- 14. Pyridoxamine, pyridoxal phosphate & pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) • Catalyzes transaminations & decarboxylations of amino acids • Metabolism energy pyridoxine
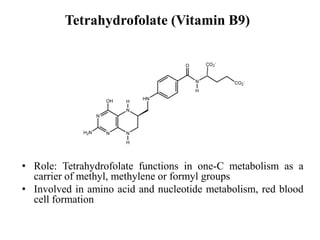
- 15. Tetrahydrofolate (Vitamin B9) • Role: Tetrahydrofolate functions in one-C metabolism as a carrier of methyl, methylene or formyl groups • Involved in amino acid and nucleotide metabolism, red blood cell formation
- 16. Metal ions perform three distinct functions during enzyme catalysis 1. Mediating Oxidation-reduction reactions through reversible changes in the metal ion oxidation state 2. Binds to substrate and properly orient them for reactions 3. Electrostatically stabilizes or shield negative charges ------------ ---1/3 of all known enzymes require metal ions for their catalytic activities 1. Metalloenzymes…metal ion is tightly bound to the enzyme 2. Metal activated enzymes….metal ion is loosely attached to the enzyme Two types of Enzymes on the basis of metal ions







