Smart Health for Patient Safety & Quality (December 17, 2019)
- 1. Smart Health for Patient Safety & Quality นพ.นวนรรน ธีระอัมพรพันธุ์ 17 ธ.ค. 2562 www.SlideShare.net/Nawanan
- 2. What words come to mind when you hear... Digital Health Transformation
- 4. http://www.ibtimes.com/google-deepminds-alphago-program-defeats-human-go-champion-first-time-ever-2283700 http://deepmind.com/ http://socialmediab2b.com An Era of Smart Machines
- 5. englishmoviez.com Rise of the Machines?
- 7. “Big data is like teenage sex: everyone talks about it, nobody really knows how to do it, everyone thinks everyone else is doing it, so everyone claims they are doing it...” -- Dan Ariely @danariely (2013) Substitute “Big data” with “AI”, “Blockchain”, “IoT” of your choice. -- Nawanan Theera-Ampornpunt (2018)
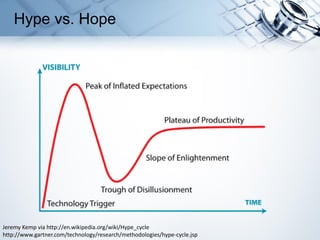
- 8. Hype vs. Hope Jeremy Kemp via http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hype_cycle http://www.gartner.com/technology/research/methodologies/hype-cycle.jsp
- 9. Gartner Hype Cycle 2017 https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/top-trends-in-the-gartner-hype-cycle-for-emerging-technologies-2017/
- 11. A Real-Life Personal Story of My Failure (as a Doctor and as a Son) in Misdiagnosing My Mom Would AI Help?
- 12. • Nothing is certain in medicine & health care • Large variations exist in patient presentations, clinical course, underlying genetic codes, patient & provider behaviors, biological responses & social contexts Why Clinical Judgment Is Still Necessary?
- 13. • Most diseases are not diagnosed by diagnostic criteria, but by patterns of clinical presentation and perceived likelihood of different diseases given available information (differential diagnoses) • Human is good at pattern recognition, while machine is good at logic & computations Why Clinical Judgment Is Still Necessary?
- 14. • Machines are (at best) as good as the input data –Not everything can be digitized or digitally acquired –Not everything digitized is accurate (“Garbage In, Garbage Out”) • Experience, context & human touch matters Why Clinical Judgment Is Still Necessary?
- 16. “To computerize the hospital” “To go paperless” “To become a Digital Hospital” “To Have EHRs” Why Adopting Health IT?
- 17. • “Don’t implement technology just for technology’s sake.” • “Don’t make use of excellent technology. Make excellent use of technology.” (Tangwongsan, Supachai. Personal communication, 2005.) • “Health care IT is not a panacea for all that ails medicine.” (Hersh, 2004) Some “Smart” Quotes
- 19. Being Smart #1: Stop Your “Drooling Reflex”!!
- 20. Being Smart #2: Focus on Information & Process Improvement, Not Technology
- 21. If not “Digital Hospital” or “Paperless Hospital” Then What Should We Aspire to Be?
- 22. “Smart Hospital”
- 24. To treat & to care for their patients to their best abilities, given limited time & resources Image Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Newborn_Examination_1967.jpg (Nevit Dilmen) What Clinicians Want?
- 25. Why Aren’t We Talk About These Words? http://hcca-act.blogspot.com/2011/07/reflections-on-patient-centred-care.html
- 26. The Goal of Health Care The answer is already obvious... “Health” “Care”
- 27. • Safe • Timely • Effective • Patient-Centered • Efficient • Equitable Institute of Medicine, Committee on Quality of Health Care in America. Crossing the quality chasm: a new health system for the 21st century. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; 2001. 337 p. High Quality Care
- 28. (IOM, 2001)(IOM, 2000) (IOM, 2011) Landmark Institute of Medicine Reports
- 29. • Humans are not perfect and are bound to make errors • Highlight problems in U.S. health care system that systematically contributes to medical errors and poor quality • Recommends reform • Health IT plays a role in improving patient safety Summary of These Reports
- 30. 30 • Perception errors Image Source: interaction-dynamics.com To Err Is Human 1: Perception
- 31. 31 Image Source: (Left) http://docwhisperer.wordpress.com/2007/05/31/sleepy-heads/ (Right) http://graphics8.nytimes.com/images/2008/12/05/health/chen_600.jpg To Err Is Human 2: Attention
- 32. 32 Image Source: Suthan Srisangkaew, Department of Pathology, Facutly of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University To Err Is Human 3: Memory
- 33. 33 • Cognitive Errors - Example: Decoy Pricing The Economist Purchase Options • Economist.com subscription $59 • Print subscription $125 • Print & web subscription $125 Ariely (2008) 16 0 84 The Economist Purchase Options • Economist.com subscription $59 • Print & web subscription $125 68 32 # of People # of People To Err Is Human 4: Cognition
- 34. 34Klein JG. Five pitfalls in decisions about diagnosis and prescribing. BMJ. 2005 Apr 2;330(7494):781-3. “Everyone makes mistakes. But our reliance on cognitive processes prone to bias makes treatment errors more likely than we think” Cognitive Biases in Healthcare
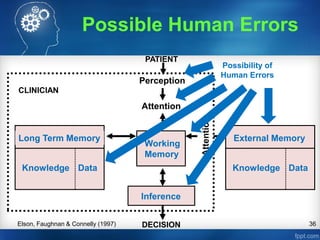
- 35. 35 External Memory Knowledge Data Long Term Memory Knowledge Data Inference DECISION PATIENT Perception Attention Working Memory CLINICIAN Elson, Faughnan & Connelly (1997) Clinical Decision Making
- 36. 36 External Memory Knowledge Data Long Term Memory Knowledge Data Inference DECISION PATIENT Perception Attention Working Memory CLINICIAN Elson, Faughnan & Connelly (1997) Possible Human Errors Possibility of Human Errors
- 38. 38 • Clinical Decision Support (CDS) “is a process for enhancing health-related decisions and actions with pertinent, organized clinical knowledge and patient information to improve health and healthcare delivery” (Including both computer-based & non-computer-based CDS) (Osheroff et al., 2012) What Is A CDS?
- 39. 39 • The real place where most of the values of health IT can be achieved • There are a variety of forms and nature of CDS Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDS)
- 40. 40 • Expert systems –Based on artificial intelligence, machine learning, rules, or statistics –Examples: differential diagnoses, treatment options CDS Examples Shortliffe (1976)
- 41. 41 • Alerts & reminders –Based on specified logical conditions • Drug-allergy checks • Drug-drug interaction checks • Drug-lab interaction checks • Drug-formulary checks • Reminders for preventive services or certain actions (e.g. smoking cessation) • Clinical practice guideline integration (e.g. best practices for chronic disease patients) CDS Examples
- 43. 43 • Reference information or evidence- based knowledge sources –Drug reference databases –Textbooks & journals –Online literature (e.g. PubMed) –Tools that help users easily access references (e.g. Infobuttons) CDS Examples
- 45. 45 • Pre-defined documents –Order sets, personalized “favorites” –Templates for clinical notes –Checklists –Forms • Can be either computer-based or paper-based CDS Examples
- 46. 46 Order Sets Image Source: http://www.hospitalmedicine.org/ResourceRoomRedesign/CSSSIS/html/06Reliable/SSI/Order.cfm
- 47. 47 • Simple UI designed to help clinical decision making –Abnormal lab highlights –Graphs/visualizations for lab results –Filters & sorting functions CDS Examples
- 48. 48 Abnormal Lab Highlights Image Source: http://geekdoctor.blogspot.com/2008/04/designing-ideal-electronic-health.html
- 49. 49 External Memory Knowledge Data Long Term Memory Knowledge Data Inference DECISION PATIENT Perception Attention Working Memory CLINICIAN Elson, Faughnan & Connelly (1997) How CDS Supports Decision Making Abnormal lab highlights
- 50. 50 External Memory Knowledge Data Long Term Memory Knowledge Data Inference DECISION PATIENT Perception Attention Working Memory CLINICIAN Elson, Faughnan & Connelly (1997) How CDS Supports Decision Making Order Sets
- 51. 51 External Memory Knowledge Data Long Term Memory Knowledge Data Inference DECISION PATIENT Perception Attention Working Memory CLINICIAN Elson, Faughnan & Connelly (1997) How CDS Supports Decision Making Drug-Allergy Checks
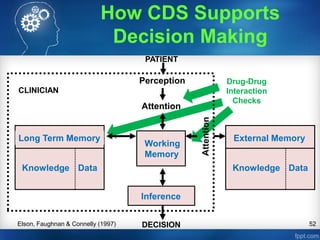
- 52. 52 External Memory Knowledge Data Long Term Memory Knowledge Data Inference DECISION PATIENT Perception Attention Working Memory CLINICIAN Elson, Faughnan & Connelly (1997) How CDS Supports Decision Making Drug-Drug Interaction Checks
- 53. 53 External Memory Knowledge Data Long Term Memory Knowledge Data Inference DECISION PATIENT Perception Attention Working Memory CLINICIAN Elson, Faughnan & Connelly (1997) How CDS Supports Decision Making Clinical Practice Guideline Alerts/Reminders
- 54. 54 External Memory Knowledge Data Long Term Memory Knowledge Data Inference DECISION PATIENT Perception Attention Working Memory CLINICIAN Elson, Faughnan & Connelly (1997) How CDS Supports Decision Making Integration of Evidence-Based Resources (e.g. drug databases, literature)
- 55. 55 External Memory Knowledge Data Long Term Memory Knowledge Data Inference DECISION PATIENT Perception Attention Working Memory CLINICIAN Elson, Faughnan & Connelly (1997) How CDS Supports Decision Making Diagnostic/Treatment Expert Systems
- 56. Being Smart #3: “To Err is Human”
- 57. Being Smart #4: Link IT Values to Quality (Including Safety)
- 59. ภาพรวมของงานด้าน Health IT Intra-Hospital IT • Electronic Health Records & Health IT for Quality & Safety • Digital Transformation • AI, Data Analytics • Hospital IT Quality Improvement (HA-IT) Inter-Hospital IT • Health Information Exchange (HIE) Extra-Hospital IT • Patients: Personal Health Records (PHRs) • Public Health: Disease Surveillance & Analytics Patient at Home
- 60. Strategic Operational ClinicalAdministrative LIS Health Information ExchangeBusiness Intelligence Word Processor Social Media PACS Personal Health Records Clinical Decision Support Systems Computerized Physician Order Entry Electronic Health Records Admission-Discharge-Transfer Master Patient Index Enterprise Resource Planning Vendor-Managed Inventory Customer Relationship Management 4 Quadrants of Hospital IT
- 61. ภาพรวมของงานด้าน Health IT Intra-Hospital IT • Electronic Health Records & Health IT for Quality & Safety • Digital Transformation • AI, Data Analytics • Hospital IT Quality Improvement (HA-IT) Inter-Hospital IT • Health Information Exchange (HIE) Extra-Hospital IT • Patients: Personal Health Records (PHRs) • Public Health: Disease Surveillance & Analytics Patient at Home
- 62. Hospital A Hospital B Clinic D Policymakers Patient at Home Hospital C HIE Platform Health Information Exchange (HIE)
- 63. WHO & ITU Achieving Health Information Exchange (HIE)
- 65. Areas of Health Informatics Patients & Consumers Providers & Patients Healthcare Managers, Policy- Makers, Payers, Epidemiologists, Researchers Copyright Nawanan Theera-Ampornpunt (2018) Clinical Informatics Public Health Informatics Consumer Health Informatics
- 66. Incarnations of Health IT Clinical Informatics Public Health Informatics Consumer Health Informatics HIS/CIS EHRs Computerized Physician Order Entry (CPOE) Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDS) (including AI) Closed Loop Medication PACS/RIS LIS Nursing Apps Disease Surveillance (Active/Passive) Business Intelligence & Dashboards Telemedicine Real-time Syndromic Surveillance mHealth for Public Health Workers & Volunteers PHRs Health Information Exchange (HIE) eReferral mHealth for Consumers Wearable Devices Social Media Copyright Nawanan Theera-Ampornpunt (2018)
- 67. Where We Are Today... Copyright Nawanan Theera-Ampornpunt (2018) Clinical Informatics Public Health Informatics Consumer Health Informatics Technology that focuses on the sick, not the healthy Silos of data within hospitalPoor/unstructured data quality Lack of health data outside hospital Poor data integration across hospitals/clinics Poor data integration for monitoring & evaluation Poor data quality (GIGO) Finance leads clinical outcomes Poor IT change management Cybersecurity & privacy risks Few real examples of precision medicine Little access to own health data Poor patient engagement Poor accuracy of wearables Lack of evidence for health values Health literacy Information Behavioral change Few standards Lack of health IT governance
- 68. • CDS as a replacement or supplement of clinicians? – The demise of the “Greek Oracle” model (Miller & Masarie, 1990) The “Greek Oracle” Model The “Fundamental Theorem” Model Friedman (2009) Wrong Assumption Correct Assumption Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDS)
- 69. Being Smart #5: Don’t Replace Human Users. Use ICT to Help Them Perform Smarter & Better.
- 70. Some Risks of Clinical Decision Support Systems • Alert Fatigue Unintended Consequences of Health IT
- 71. Workarounds Unintended Consequences of Health IT
- 72. Being Smart #6: Health IT Also Have Risks & Unintended Consequences
- 73. Technology ProcessPeople Balanced Focus of Informatics
- 74. Being Smart #7: Balance Your Focus (People, Process, Technology)
- 75. Envisioning a Smart Health Thailand