Transamination & deamination
- 1. Transamination & Deamination Dr Rohini C Sane
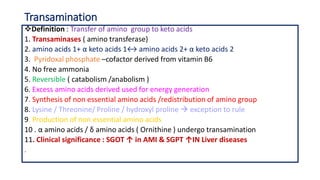
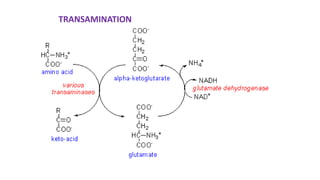
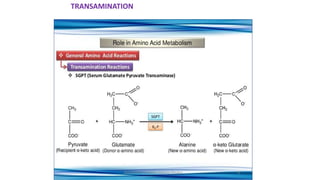
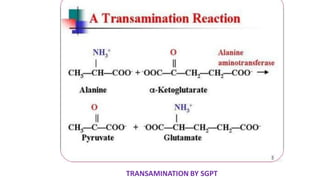
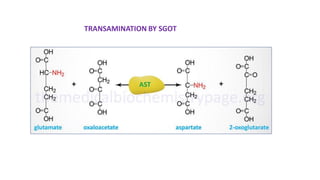
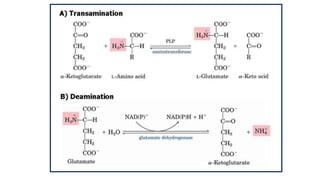
- 2. Transamination Definition : Transfer of amino group to keto acids 1. Transaminases ( amino transferase) 2. amino acids 1+ α keto acids 1↔ amino acids 2+ α keto acids 2 3. Pyridoxal phosphate –cofactor derived from vitamin B6 4. No free ammonia 5. Reversible ( catabolism /anabolism ) 6. Excess amino acids derived used for energy generation 7. Synthesis of non essential amino acids /redistribution of amino group 8. Lysine / Threonine/ Proline / hydroxyl proline exception to rule 9. Production of non essential amino acids 10 . α amino acids / δ amino acids ( Ornithine ) undergo transamination 11. Clinical significance : SGOT ↑ in AMI & SGPT ↑IN Liver diseases .
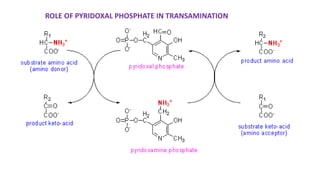
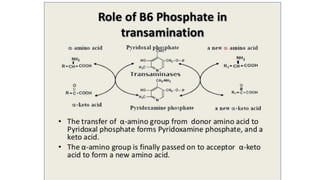
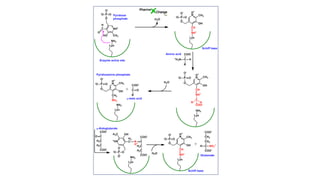
- 4. ROLE OF PYRIDOXAL PHOSPHATE IN TRANSAMINATION
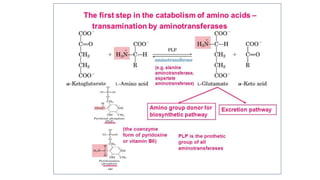
- 11. Mechanism of Transamination • CHO group of PLP forms Schiff base (1 )with Lys residue of transaminase with imine linkage Lys displaced by amino acid to form Schiff base (2 )
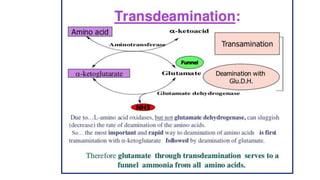
- 13. Deamination • Definition : Removal of amino group as ammonia which is utilized for urea formation & carbon skeletons are used for formation the keto acids . • Transamination & Deamination take place simultaneously.(Trans deamination )
- 14. Fate of carbon skeletons of amino acids 1. Oxidation TCA Energy 2. Synthesis of Glucose 3. Formation of lipids ( fatty acids & ketone bodies ) 4. Synthesis of non essential amino acids
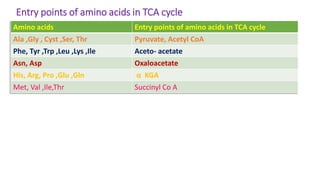
- 15. Entry points of amino acids in TCA cycle Amino acids Entry points of amino acids in TCA cycle Ala ,Gly , Cyst ,Ser, Thr Pyruvate, Acetyl CoA Phe, Tyr ,Trp ,Leu ,Lys ,Ile Aceto- acetate Asn, Asp Oxaloacetate His, Arg, Pro ,Glu ,Gln α KGA Met, Val ,Ile,Thr Succinyl Co A
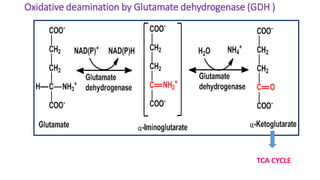
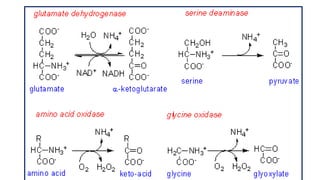
- 16. Oxidative Deamination 1. Site : kidney & Liver ( mitochondria ) 2. Catalyzed by Glutamate dehydrogenase ( GDH ) Purpose :/significance a) Ammonia utilized for Urea formation b) α keto acids for energy c) Glutamate accepts amino group from amino acids ( Transamination ) d) Glutamate –is collection center for amino group oxidative deamination
- 17. Oxidative deamination by Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH ) TCA CYCLE
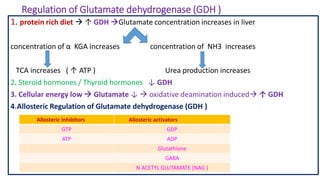
- 18. Regulation of Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH ) 1. protein rich diet ↑ GDH Glutamate concentration increases in liver concentration of α KGA increases concentration of NH3 increases TCA increases ( ↑ ATP ) Urea production increases 2. Steroid hormones / Thyroid hormones ↓ GDH 3. Cellular energy low Glutamate ↓ oxidative deamination induced ↑ GDH 4.Allosteric Regulation of Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH ) Allosteric inhibitors Allosteric activators GTP GDP ATP ADP Glutathione GABA N ACETYL GLUTAMATE (NAG )
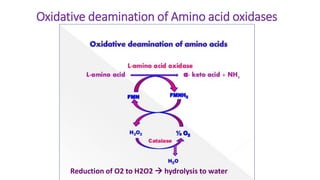
- 21. Oxidative deamination of Amino acid oxidases Reduction of O2 to H2O2 hydrolysis to water
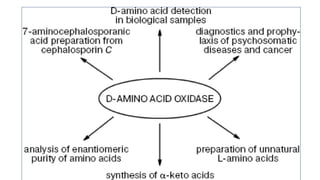
- 22. Oxidative deamination by Amino acid oxidases • Activity of L -amino acid oxidases low • Activity of D amino acid oxidase high ( liver & kidney ) • L -amino acid oxidases dose not act on Glycine & di carboxylic acids • L -amino acid oxidases dose appear to play significant role in amino acid metabolism.
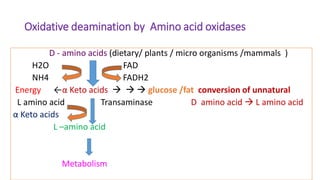
- 23. Oxidative deamination by Amino acid oxidases D - amino acids (dietary/ plants / micro organisms /mammals ) H2O FAD NH4 FADH2 Energy ←α Keto acids glucose /fat conversion of unnatural L amino acid Transaminase D amino acid L amino acid α Keto acids L –amino acid Metabolism
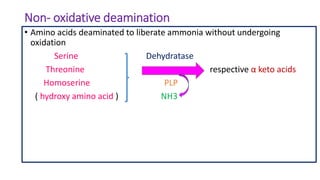
- 25. Non- oxidative deamination • Amino acids deaminated to liberate ammonia without undergoing oxidation Serine Dehydratase Threonine respective α keto acids Homoserine PLP ( hydroxy amino acid ) NH3
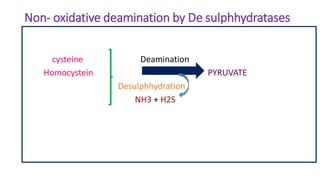
- 26. Non- oxidative deamination by De sulphhydratases cysteine Deamination Homocystein PYRUVATE Desulphhydration NH3 + H2S
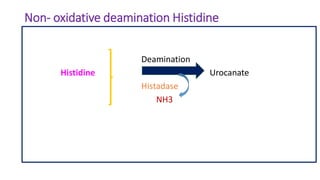
- 27. Non- oxidative deamination Histidine Deamination Histidine Urocanate Histadase NH3