Desert biome project
- 1. Desert Destinations Inc. Proudly Serving Canadians since 1986 Your Agent: Tara Bosch
- 2. Biome: Hot/Dry Desert How hot can you get?
- 3. Climate: What to Expect •Dry desert climate formed by high- pressure zones that has cold air descending upon it •Very little rainfall- often less than 15cm per year •Rain usually occurs in short periods between Satellite image of the Atacama desert in South America. From long rainless periods left to right is the Pacific Ocean, Atacama desert, and the Andes mountains. By looking at the Andes mountains it can be seen •All months have that the moisture completely stops at the Atacama desert. average temperatures over 180C TRAVELERS TIP: Make sure to bring LOTS of sunscreen
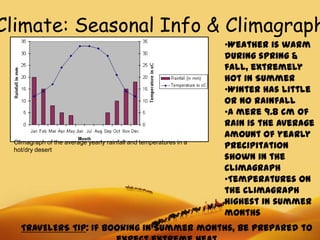
- 4. Climate: Seasonal Info & Climagraph •Weather is warm during spring & fall, extremely hot in Summer •Winter has little or no rainfall •A mere 9.8 cm of rain is the average amount of yearly Climagraph of the average yearly rainfall and temperatures in a hot/dry desert precipitation shown in the climagraph •Temperatures on the climagraph highest in summer months TRAVELERS TIP: If booking in Summer months, be prepared to
- 5. Type of Vegetation •Plants in the desert are xerophytes -> plants that have adapted to survive in a water- lacking environment •Low-down shrubs that have waxy coatings and intricate root systems exist •Leaves are packed with nutrients •Little or no organic matter due to lack of water A prickly pear cactus located in the Sonora Barrel Cactus, one of the largest desert cacti’s that can grow up to 11 ft tall TRAVELERS TIP: Hungry? Native Americans used to stew the barrel cactus to make a _ cabbage-
- 6. Vegetation: Adaptations •Plants use dew for moisture, taking it in through their leaves/stems -> ex. Cacti •At night time when temperatures drop, some plants open up their stomata to breath -> ex. Brittlebush •Plants adapt in different ways to Acacia trees in the Rajasthan Desert (India) that have lost their leaves to avoid evaporation avoid water loss -> ex. Living stones of moisture A closer plant is mainly underground to view of the escape sun’s radiation so it avoids stomata that helps evaporation some •Ability to stand extremely hot plants to breath at weather night by •Some <- What the Saguaro cactus looksgrowth plants slow down like transportin g gases in rate to conserve moisture -> ex. and out Saguaro cactus TRAVELERS TIP: Be sure to drink lots of water
- 7. Type of Soil & Global Position •Packed with nutrients- needs minimal water to be productive •Soil is shallow, rocky, and gravely with no sub-surface water •Course due to less chemical weathering •Deserts cover approx 1/5 of worlds surface •Latitude range is 15-280 south of the equator •Majority of hot/dry deserts located near the Tropic of Cancer or the Tropic of Capricorn Rocky, gravely soil that is typically found in deserts. The red color comes from the iron in the soil TRAVELERS TIP: Make sure to pack a good pair of sandals
- 8. Soil Profile Alkaline flat in the Alvord Desert, formed due to translocation. Alkaline flats contain large concentrations of salts, which is why they are often Diagram that illustrates a hot/dry deserts soil profile in comparison to other shining and white. biomes •Lack of water = small amount of vegetation = limited amount of decomposing litter -> soils lack hummus -> nutrients aren’t developed •Rate of evaporation exceeds precipitation, so translocation occurs
- 9. Soil Profile Con’t Natural vegetation regions of the world Soils of the World map, with the pale yellow representing map, with the bright yellow representing hot aridisols soil classification /dry deserts Aridisols Soil Classification: •Little hummus due to small amount of vegetation •Mineral deposits on surface of soil due to transloca •Water movement is towards the surface •Coarse sand particles are evident
- 10. Cold & Hot Deserts COLD: •Snow in the wintertime, temperature ranges from -2 to -40C •Located near the arctic part of the world •Precipitation from 15 to 26cm yearly, with snow in the HOT: winter yearrainy periods in •Warm and round, summer the spring temperature between 43.5 to 490C •Located near the tropic of The Antarctic desert, weather conditions in this cold desert capricorn & cancer can change fast & without warning •Precipitation less than 15cm yearly “What makes the desert beautiful is that somewhere it hides a well.”
- 11. A Tourist Attractions F ASIA R I C A Pyramids built by One of the fossils that ancient Egyptians in the can be found in the Gobi Sahara desert Desert USA The grand canyon located in the Mojave Desert TRAVELERS TIP: Spiders and reptiles you must be alert, because all these things you will find in a desert
- 12. BIBLIOGRAPHY •http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/de sert.htm •http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/exhibi ts/biomes/deserts.php •http://www.seafriends.org.nz/enviro/ soil/geosoil.htm •http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/exhibi ts/biomes/deserts.php#hot •http://www.thefreedictionary.c om/Humboldt+Current •http://googlesightseeing.com/m aps?p=12774&c=&t=k&hl=en&ll=- 22.755921,-64.775391&z=7 •http://ngm.nationalgeographic.c om/ngm/0308/feature3/