The_scramble_for_africa
- 1. ““The Scramble for Africa”The Scramble for Africa”
- 2. Africa Today: Shaped by Its History “The Scramble for Africa”
- 3. The Seeds are Planted • The Portuguese began the first colonies in Africa in the 1400s. • In 1659, the Dutch founded the Cape Colony on Africa’s southern tip in 1659. • In the 1600s, France founded the colony of Saint Louis in today’s Senegal. • The British started to colonize Africa in the 1700s.
- 4. 1800s rubber imperialism When most European nations ended slavery in the early______, they shifted their focus to trading goods such as gold, ivory, and____________. Soon after,the European powers divided up most of Africa. They used ______________to keep power. This is a policy of taking over other countries’ government’s trade, and culture.
- 5. From Trading to Controlling • After the slave trade was abolished in West Africa, Europeans continued to come to Africa in search of resources for their factories in Europe. • Originally, Europeans traded with Africans for the resources they needed. However, Europeans would eventually begin to colonize, or take over, land and resources in Africa. • Before 1880, Europe had colonized only 5% of Africa, mainly along the western coast.
- 6. The Scramble Begins • Beginning in the 1880s, the colonization of Africa rapidly increased. • Several factors led to the colonization boom. – The Industrial Revolution led European countries to hunt for raw materials needed to develop products. – Methods of transportation improved. – Several European countries became engaged in a growing colonial rivalry with each other. – Europeans began signing treaties with African tribal leaders. • The carving up of Africa by Europeans became known as the “Scramble for Africa.”
- 7. Reasons for Colonialism • Despite Europeans involvement in the Slave Trade Europeans usually relied on Africans to trade slaves instead of colonizing the continent. • By the 1880s every major nation in the world had abolished the institution of slavery. • Europeans found a new interest in Africa. • Africa is a continent of vast wealth.
- 8. “The Scramble for Africa” • In order to avoid armed conflict with each other, leaders of several European countries met at the Berlin Conference in 1885. • At the conference, rules were created to determine how European countries could claim African land. • They agreed to carve up Africa into vast empires, ignoring the rights of the African people already living in these areas. • By 1900, most of Africa had been colonized by the Europeans. Only Liberia and the Empire of Ethiopia remained independent.
- 9. In 1884 at the request of Portugal, German chancellor Otto von Bismark called together the major western powers of the world to negotiate questions and end confusion over the control of Africa. Bismark appreciated the opportunity to expand Germany's sphere of influence over Africa and desired to force Germany's rivals to struggle with one another for territory. At the time of the conference, 80% of Africa remained under traditional and local control. The Berlin ConferenceThe Berlin Conference
- 10. "The Berlin Conference was Africa's undoing in more ways than one. The colonial powers superimposed their domains on the African continent. By the time independence returned to Africa in 1950, the realm had acquired a legacy of political fragmentation that could neither be eliminated nor made to operate satisfactorily."* The Berlin ConferenceThe Berlin Conference
- 11. The _______controlled much of East Africa. Large numbers of Europeans settled in Kenya. But most colonial rulers used African deputies to control the countries. Many deputies were traditional chiefs. They often favored their own peoples. This caused conflict between ethnic groups. British
- 12. Colonialism • Colonialism is forced control of one nation by another nation. • Beginning in the early 19th Century, Europeans aggressively tried to establish colonies in Africa. • Colony is when a nation establishes a government under its rule in a foreign territory. • Imperialism is empire building. Expansion occurs when one state is more powerful than are the obstacles to expansion. European civilization experienced a period of unprecedented rapid expansion around the globe during the last third of the nineteenth century.
- 13. What type of Political boundaries existed before the Berlin Conference in 1885?
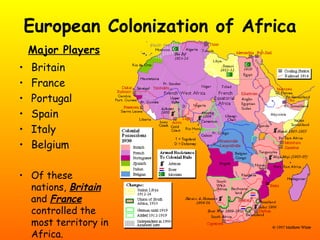
- 14. European Colonization of Africa Major Players • Britain • France • Portugal • Spain • Italy • Belgium • Of these nations, Britain and France controlled the most territory in Africa.
- 15. Positive European Reasons for Colonialism 1. Colonies provided Europe with strategic military and economic advantages. 2. Europe received minerals and other natural resources (diamonds, gold, cotton, ivory, and other natural resources) which fed the Industrial Revolution 3. Europeans had access to cheap labor 4. Open up new trading markets for European goods. 5. Spread Christianity throughout the continent.
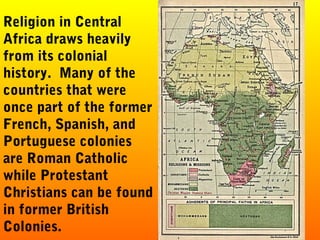
- 16. Religion in Central Africa draws heavily from its colonial history. Many of the countries that were once part of the former French, Spanish, and Portuguese colonies are Roman Catholic while Protestant Christians can be found in former British Colonies.
- 17. Impact of Colonialism Positive Effects on Africa • Schools and hospitals built. • Economy was improved by new governments. • Roads and railroads were built. • Health was improved (Health systems, etc…) • Berlin Conference set a specific date for the end of the slave trade. • New technology elevated the standard of
- 18. Impact of Colonial Period/ Partitioning of AfricaImpact of Colonial Period/ Partitioning of Africa Negative Effects for AfricaNegative Effects for Africa Conflicts broke out between tribes that were once friendly. African tribes lost control of their own countries. Land was confiscated for farms for the European colonies. Wars, revolts, and protests were common. Starvation and disease became widespread. “NEW BORDERS” were drawn that separated families and tribes.
- 19. The Scramble’s Legacy • The scramble for Africa caused lasting harm. – Europeans took the best land by force. – African farmers were forced to grow cash crops like cocoa and coffee, causing there to be a shortage of food in many areas of Africa. – Africans were forced to work under terrible conditions on plantations, railways, and logging. – In order to gain power, Europeans encouraged Africans to fight against each other. – New political boundaries caused ethnic groups to clash. – This has led to ethnic and political unrest in Africa today.
- 20. France Britian Belgium Some of the Central African countries became rich from trading with the Europeans. But they were all weakened in time… Why? Name the European colonial powers. Spain Germany Portugal