Pathology of Hepatitis
- 1. Never offer the devil a ride.He will always want to be in the driving seat…!BK
- 2. 2CPC 4.2.2George, 62 year old farmer from Tully, presents to his GP with fatigue. His wife has asked him to consult you as his eyes look a bit yellow'. Fatigue: Progressing 2wk. Unable to get out. nausea : no vomiting/haematemesis : no Anorexia, wt loss: yes thinks lost a bit of weight. bowel habit : constipated, stool pale, no blood.
- 3. 3CPC 4.2.2Fever: no Bleeding/bruising : no cough/dyspnoea : noprevious episodes : 2 x episodes fatigue last 2 years; first attack preceeded by 2 weeks of fever. saw GP - blood tests : 'showed liver not working so well'. then felt better and has not been to see GP since. This time he feels much worse. other PMH of note? 'never sees doc'; has never been in hospital; no regular medication no OTC/herbal remedies SH : married; 3 adult children. Moved to Australia from Greece 26 years ago. Banana farmer
- 4. 4Laboratory Investigations:FBC: Hb 13.8 g/dl, PCV 45%; WBC 7000/mm3, 70% N, 25% L; Platelets 200,000/mm3 Blood film: Normocytic, normochromic cells Bilirubin: Total serum Bilirubin = 98 μmol/l, (Direct 67)Liver enzymes: Aspartate amino transferase (AST) = 62 U/l Alanine amino transferase (ALT) = 110 U/l Alkaline Phosphatase = 116 U/I Serum Protein: Total protein = 61 g/l, Albumin = 20 g/l, Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HbsAg): Positive
- 5. 5Differential Diagnosis:Viral fever -? Yellow fever, Relapsing fever, Dengue, Ebola, Leptospirosis (common in Tully) - ?Hepatitis – Acute / Chronic - ?Chronic Hepatitis B – why chronic?History & presentation in Hep. A & C ?Other causes of Jaundice?Alcoholic liver disease ?Toxins, chemical, Reyes syndrome?Anemia - ?Malignancy - ?
- 7. 7Pathology of HepatitisViral & AlcoholicDr. Venkatesh M. Shashidhar.Assoc.Prof & Head of Pathology
- 8. 81.5 kg, wedge shape4 lobes, Right, left, (Caudate, Quadrate)Double blood supplyHepatic arteriesPortal – Venous bloodNormal
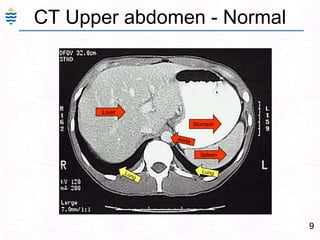
- 9. 9CT Upper abdomen - NormalLiverStomachAortaSpleenLungLung
- 10. Normal Liver - InfantMuch larger, both lobes, below costal margin – palpable*
- 11. 11Normal Liver
- 12. 12Normal Liver – MicroscopyAcinus – showing zones 1, 2 & 3.Central VeinBlood FlowPortal Triad
- 13. 13Structure of Liver LobulePortal Triad: Art, Vein, BD
- 14. 14Acinus LobuleFunctional Anatomic3Zone 1 – Toxin damage. Zone 3 – Ischemic damage
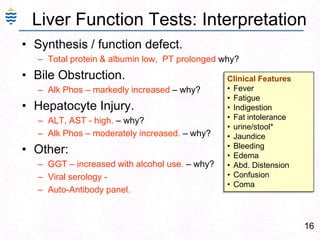
- 19. Obstruction to bile excretion.16Liver Function Tests: InterpretationSynthesis / function defect.Total protein & albumin low, PT prolonged why?Bile Obstruction.Alk Phos – markedly increased – why?Hepatocyte Injury.ALT, AST - high. – why?Alk Phos – moderately increased. – why?Other:GGT – increased with alcohol use. – why?Viral serology - Auto-Antibody panel. Clinical FeaturesFever
- 20. Fatigue
- 21. Indigestion
- 22. Fat intolerance
- 23. urine/stool*
- 24. Jaundice
- 25. Bleeding
- 26. Edema
- 27. Abd. Distension
- 28. Confusion
- 29. Coma17Clinical Features - PathogenesisHypoalbuminemia
- 30. Hyperammonemia
- 31. Hypoglycemia
- 32. Palmarerythema
- 33. Spider angiomas
- 34. Hypogonadism
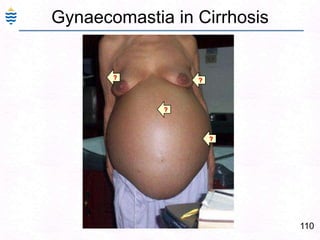
- 35. Gynecomastia
- 36. Weight loss
- 37. Muscle wasting
- 38. Ascites
- 39. Splenomegaly
- 41. Hemorrhoids
- 43. Complications of Hepatic Failure
- 44. Coagulopathy
- 46. Hepatorenal syndromeDecreased Albumin synthesisHepatorenal syndrome
- 47. Jaundice in liver failure18
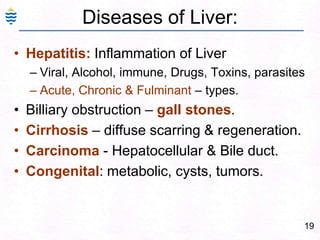
- 48. 19Diseases of Liver:Hepatitis: Inflammation of LiverViral, Alcohol, immune, Drugs, Toxins, parasitesAcute, Chronic & Fulminant – types.Billiary obstruction – gall stones.Cirrhosis – diffuse scarring & regeneration.Carcinoma - Hepatocellular & Bile duct.Congenital: metabolic, cysts, tumors.
- 49. Viral Hepatitis:
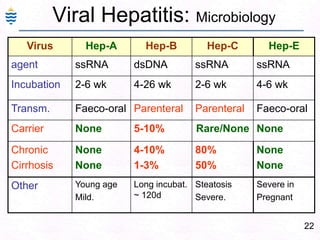
- 50. 21Viral Hepatitis: IntroductionViral Hepatitis:Specific – Heptitis B, C, D (serum),A, ENon-Specific - Many viruses CMV, EBV, etc.Acute, Chronic (CPH, CAH), Fulminant.Specific viral hepatitis important cause of morbidity & mortality.Horizontal transmission – Blood.. Sex.Vertical transmission – Mother to fetus.Hepatitis Cirrhosis Hepatic Ca. (not in A/E)
- 52. 23Hepatitis A'faecal-oral' spread, Travel / exposure. Relatively short incubation period (2-6wk)Epidemics common, may be sporadic. Direct cytopathic virus (immune in B & C)No carrier state – prolonged immunity.Usually mild illness, full recovery usual.Rarely – severe or fulminant.IgM Ab is diagnostic. (no IgG tests).
- 53. 24Viral Hepatitis A: Serology
- 54. 25Hepatitis BSpread by blood, Sex & vertical.Relatively long incubation period (4-26wk)liver damage by antiviral immune reaction carrier state exists.Relatively serious infection – chronic, Complications: cirrhosis, carcinoma.Diagnosis: Viral serology (HBsAg)
- 55. 26Viral Hepatitis B: SerologySequence of serologic markers for hepatitis B viral hepatitis demonstrating (A) acute infection with resolution and (B) progression to chronic infection.
- 56. 27Pathogenesis of Hepatitis A & B:
- 57. 28History Hep B Virus:In 1965 - Dr. Blumberg who was studying haemophilia, found an antibody in two patients which reacted against an antigen from an Australian Aborigine. Later the antigen was found in patients with serum type hepatitis and was initially designated "Australia Antigen". Later proved to be hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg). Dr. Blumberg was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1976.
- 58. 29Pathogenesis:Ingestion / inoculationReplication - ViremiaLiver – major site replication.Cellular immune response.Apoptosis, necrosis of hepatocytes.Inflammation - Hepatitis Bridging Hepatocyte necrosis (Central vein, portal triad)Fibrosis – patchy/bridgingCirrhosis – extensive fibrosis with loss of archetecture & regenerating nodules.Liver Failure, Coma, Carcinoma..
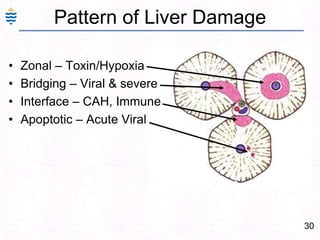
- 59. 30Pattern of Liver DamageZonal – Toxin/HypoxiaBridging – Viral & severeInterface – CAH, ImmuneApoptotic – Acute Viral
- 60. 31Spectrum of Viral Hepatitis:Carrier state / Asymptomatic phaseAcute hepatitis – fever, icterus.Chronic Hepatitis – non specific.Chronic Persistent Hepatitis (CPH)Chronic Active Hepatitis (CAH)Fulminant hepatitis – massive necrosisCirrhosis – total fibrosis.Hepatocellular Carcinoma
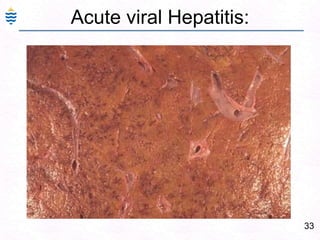
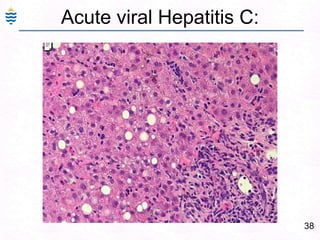
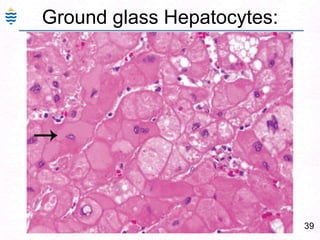
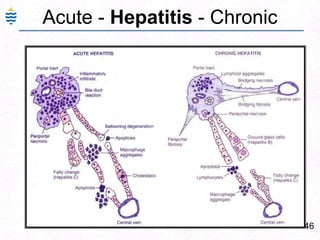
- 61. 32Acute Hepatitis:Swelling and ApoptosisPiecemeal or Bridging, panacinar necrosisDiffuse Inflammation – lymphocytes, Macrophages.Ground glass hepatocytes – HBVMild fatty change – HCV.Portal inflammation and Cholestasis
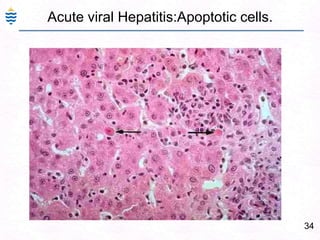
- 63. 34Acute viral Hepatitis:Apoptotic cells.
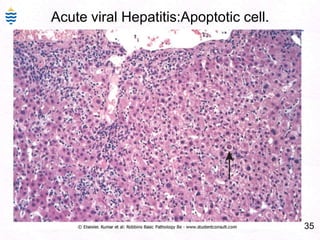
- 64. 35Acute viral Hepatitis:Apoptotic cell.
- 67. 38Acute viral Hepatitis C:
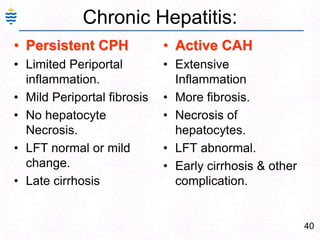
- 69. 40Chronic Hepatitis:Persistent CPHLimited Periportal inflammation. Mild Periportal fibrosisNo hepatocyte Necrosis.LFT normal or mild change.Late cirrhosis Active CAHExtensive Inflammation More fibrosis.Necrosis of hepatocytes.LFT abnormal.Early cirrhosis & other complication.
- 70. 41Liver Biopsy – viral Hepatitis-C
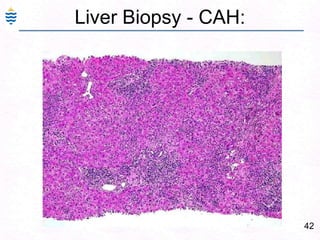
- 71. 42Liver Biopsy - CAH:
- 72. 43Chronic Active viral Hepatitis:
- 74. 45Liver Biopsy – CPH:InflammationNo Necrosis
- 75. 46Acute - Hepatitis - Chronic
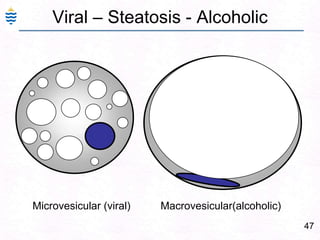
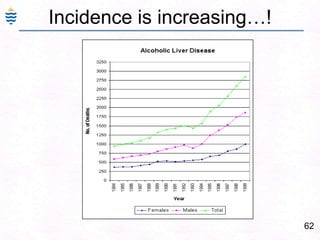
- 76. 47Viral – Steatosis - AlcoholicMicrovesicular (viral) Macrovesicular(alcoholic)
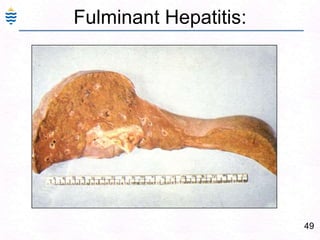
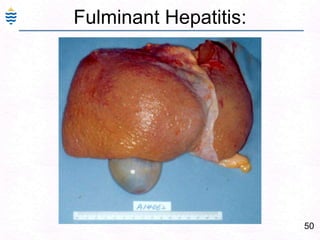
- 77. 48Fulminant Hepatitis:Hepatic failure with in 2-3 weeks.Reactivation of chronic or acute hepatitisMassive necrosis, shrinkage, wrinkledCollapsed reticulin networkOnly portal tracts visibleLittle or massive inflammation – timeMore than a week – regenerative activityComplete recovery – or - cirrhosis.
- 82. 53Clinical Spectrum of HBV inf:
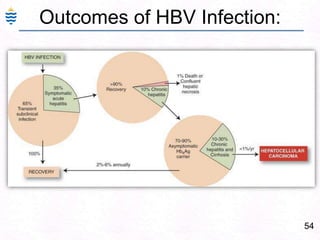
- 83. 54Outcomes of HBV Infection:
- 84. “Nearly all men can stand adversity, but if you want to test a man's character, give him power”— Abraham Lincoln
- 86. 57Viral Hepatitis C: Serology
- 87. Hepatitis B – Lab result interpret
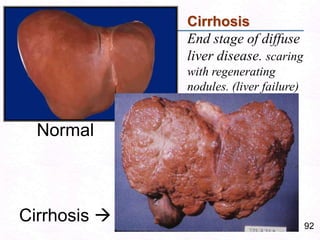
- 88. 59Cirrhosis End stage of diffuse liver disease. scaring with regenerating nodules. (liver failure)Normal Cirrhosis
- 89. The past has gone and future you cannot see.The present, when you can do something, that is the Gift (Present) with which you can make your future & past memorable.- Sai Baba"The past, the present and the future are really one: they are today."-Harriet Beecher Stowe
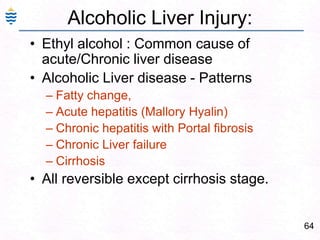
- 93. 64Alcoholic Liver Injury:Ethyl alcohol : Common cause of acute/Chronic liver diseaseAlcoholic Liver disease - PatternsFatty change, Acute hepatitis (Mallory Hyalin)Chronic hepatitis with Portal fibrosis Chronic Liver failureCirrhosisAll reversible except cirrhosis stage.
- 94. 65Alcoholic Liver Injury: PathogenesisAcetaldehyde – metabolite – hepatotoxicDiversion of metabolism to alcohol Fat storage – fatty change. Cell swelling..Rupture Fat necrosis severe inflammation fibrosis.Alcohol stimulates collagen synthesisInflammation, Portal bridging fibrosisMicronodular cirrhosis.
- 95. 66Alcoholic Liver DamageIto Cells
- 96. 67Alcoholic Liver Injury: PathogenesisDiversion of fat metabolism to alcohol – fat storage.Acetaldehyde – hepatotoxic – denatures ProteinsIncreased peripheral release of fatty acids.Alcohol stimulates collagen synthesisMutant ALDH2 gene with low activity enzyme is observed in Caucasians but is found in some 40% of Orientals (autosomal dominant).Acetaldehyde
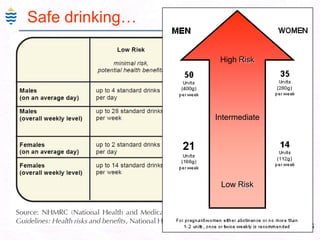
- 98. 69Risk of Alcohol injury1 Unit = 10ml = 8gm
- 100. 71Alcohol Toxicity:
- 105. Diffuse fatty liver - un-enhanced CT.NormalHamer O W et al. Radiographics 2006;26:1637-1653©2006 by Radiological Society of North America
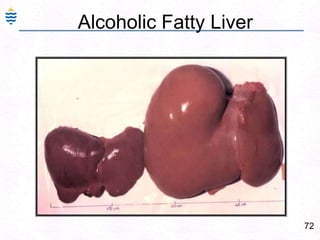
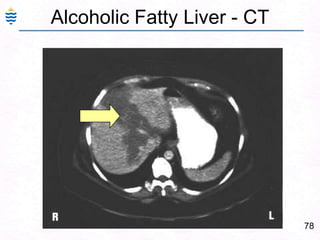
- 106. 77Alcoholic Fatty Liver - CT
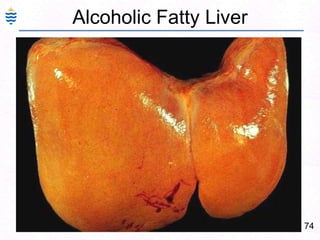
- 107. 78Alcoholic Fatty Liver - CT
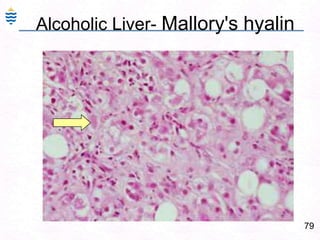
- 108. 79Alcoholic Liver- Mallory's hyalin
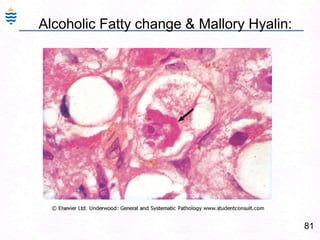
- 110. 81Alcoholic Fatty change & Mallory Hyalin:
- 112. 83Alcoholic Fatty Liver - collagen stain
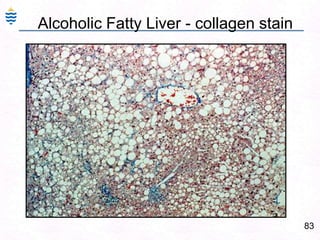
- 114. 85Alcoholic Fatty Liver - collagen stain
- 115. Alcoholic Hepatitis:86Centrilobular necrosis. Ballooned degenerating hepatocytes (BC) Mallory bodies (MB) Many Neutrophils, few lymphocytes & Macrophages.
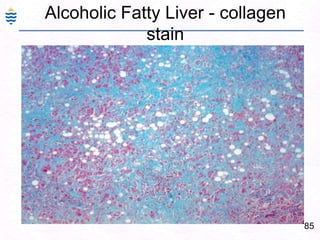
- 116. The central vein(or terminal hepatic venule (THV), is encased in connective tissue (C) (central sclerosis). Fat-laden hepatocytes (F) are evident in the lobule. The portal tract displays moderate chronic inflammation.87Alcoholic Liver Injury: ComplicationsPancreatitis – Acute or Chronic. Due to ischemic damage to pancreas.Alcoholic hepatitis – similar to viral hepatitis.Fulminant hepatitisAlcoholic Cirrhosis – Micronodular.Alcohol & Medical studentshttp://www.m-c-a.org.uk/about_us/about_mca
- 117. Drug Induced Zonal Hepatitis:88Autopsy specimen in a case of acetaminophen overdose.
- 118. Prominent hemorrhagic necrosis of the centrilobular zones of all liver lobules.
- 119. greater activity of drug-metabolizing enzymes in the central zones.
- 120. Other agents that produce such injury are carbon tetrachloride, acetaminophen, toxins of the mushroom Amanita phalloides.
- 121. Patients either die in acute hepatic failure or recover without sequelae.Reye Syndrome:89Acute disease of children
- 122. Microvesicular steatosis, hepatic failure, and encephalopathy.
- 123. Cerebral edema and fat accumulation are reported in the brain.
- 124. The symptoms usually begin after a febrile illness, commonly influenza or varicella infection, and are said to correlate with the administration of aspirin,
- 126. Uncommon, possibly as a result of decreasing use of aspirin in children.Toxemia of Pregnancy:90Hypertension, proteinuria, edema and coagulation abnormalities (pre-eclampsia) and convulsions and coma (eclampsia).
- 127. HELLP syndrome (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelet count) can also occur in pre-eclamptic women.
- 128. Patchy hemorrhages over capsule
- 130. Fibrin thrombi in portal vessels.
- 131. Hepatocellular necrosis.91Pathology of Cirrhosis
- 132. 92Cirrhosis End stage of diffuse liver disease. scaring with regenerating nodules. (liver failure)Normal Cirrhosis
- 133. 93Post hepatitis Liver CirrhosisShrunken, irregular nodularity, (macro nodular) fibrous septa.
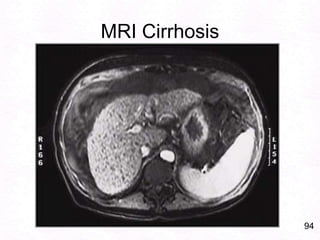
- 134. 94MRI Cirrhosis
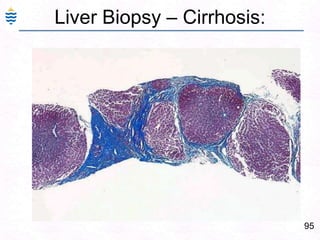
- 135. 95Liver Biopsy – Cirrhosis:
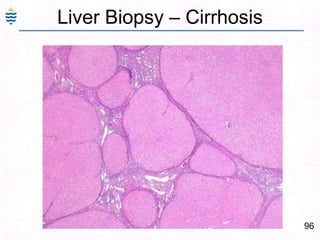
- 136. 96Liver Biopsy – Cirrhosis
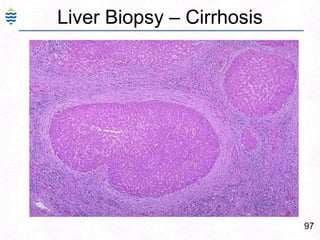
- 137. 97Liver Biopsy – Cirrhosis
- 138. 98IntroductionCirrhosis is common end result of many chronic liver disorders.Diffuse scarring of liver – follows hepatocellular necrosis of hepatitis.Inflammtion – healing with fibrosis - Regeneration of remaining hepatocytes form regenerating nodules.Loss of normal architecture & function.
- 139. 99Etiology of CirrhosisAlcoholic liver disease 60-70%Viral hepatitis 10%Biliary disease 5-10%Primary hemochromatosis 5%Cryptogenic cirrhosis 10-15%Wilson’s, 1AT def rare
- 142. 102Pathogenesis:Hepatocyte injury leading to necrosis.Alcohol, virus, drugs, toxins, genetic etc..Chronic inflammation - (hepatitis).Bridging fibrosis.Regeneration of remaining hepatocytes Proliferate as round nodules.Loss of vascular arrangement results in regenerating hepatocytes ineffective.
- 144. 104Pathogenesis of Ascitis:Hepatorenal Syndrome
- 145. 105Cirrhosis – Portal hypertensionCirrhosis-obstructionPortal hypertensionSplenomegalytransudation - Ascites
- 146. 106Causes of Portal Hypertension:
- 148. 108Cirrhosis:
- 151. 111Ascitis in congenital Cirrhosis
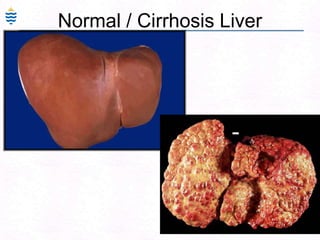
- 152. 112Normal / Cirrhosis Liver
- 154. 114Biliary Cirrhosis
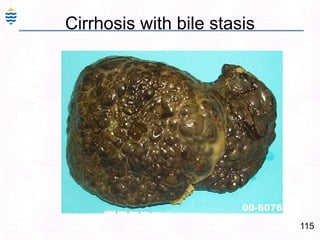
- 155. 115Cirrhosis with bile stasis
- 156. 116Cirrhosis with bile stasis
- 157. 117Primary Biliary Cirrhosis - Micronodular
- 158. 118Liver Biopsy – Cirrhosis
- 159. 119Palmar erythema & Spider nevi? Pathogenesis
- 162. 122Nutmeg Liver:Chronic Passive Congestion – Heart failure.Venous stasis - right atrium - hypoperfusion retrograde congestion – IVC & SVC.Central zone (Zone-3) – congestion and necrosis.Hemorrhage – RBCs in zone-3 - Mottled appearance (nutmeg).Symptoms are similar to those of chronic hepatitis - Ascites, distended abdomen, ankle edema, Hepatic encephalopathy, confusion.
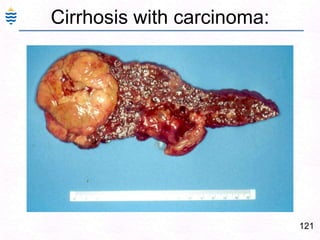
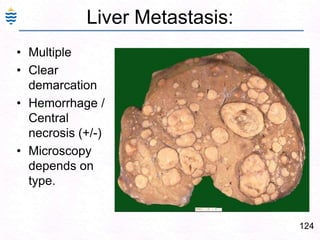
- 164. 124Liver Metastasis:MultipleClear demarcationHemorrhage / Central necrosis (+/-)Microscopy depends on type.
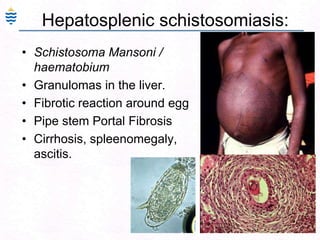
- 166. 126Hepatosplenic schistosomiasis:Schistosoma Mansoni / haematobiumGranulomas in the liver.Fibrotic reaction around egg Pipe stem Portal FibrosisCirrhosis, spleenomegaly, ascitis.
- 167. 127Hepatosplenic schistosomiasis:Schistosoma Mansoni / haematobiumGranulomas in the liver.Fibrotic reaction around egg Pipe stem Portal FibrosisCirrhosis, spleenomegaly, ascitis.
- 168. "It's not the will to win, but the will to prepare to win that makes the difference."Bear Bryant1913-1983, Football Coach
- 169. 129CPC-2.2– HBS–HepatitisBasic science - Core Learning Issues: anatomy and histology of the liver & Spleen Portal circulation.Liver Functions & Bilirubin metabolism (RBC, Hb)Viral Hepatitis – epidemiology,virology.Pathology Core Learning Issues: Pathology of liver, Hepatitis. Causes, types, gross & microscopic morphology. Jaundice – clinical and pathological typesAcholuric, obstructive, hemolytic, hepatic.Laboratory investigations. Pathology of cirrhosis & its complications.
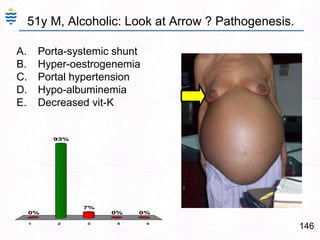
- 170. 13051y M, Alcoholic: Look at Arrow ? Pathogenesis.Porta-systemic shuntHyper-oestrogenemiaPortal hypertensionHypo-albuminemiaDecreased vit-K
- 171. Pathogenesis - typical of which virus?HAVHBVHCVHDVNon Specific
- 172. 42y M, alcoholic, recurrent fatigue. Liver biopsy. ? DiagnosisAcute HepatitisChronic Active hepatitis.Chronic Persistant hepatitis.Fulminant Hepatitis.Cirrhosis.
- 173. A 42year travelling salesperson has routine medical test for insurance. Following initial testing he was advised liver biopsy. This is a image of his Liver Biopsy. What is the most likely diagnosis?Acute Viral HepatitisAlcoholic hepatitis.Chronic viral Hepatitis. Post viral cirrhosis.Alcoholic Cirrhosis.
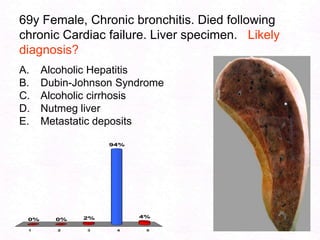
- 174. 69y Female, Chronic bronchitis. Died following chronic Cardiac failure. Liver specimen. Likely diagnosis?Alcoholic Hepatitis Dubin-Johnson SyndromeAlcoholic cirrhosisNutmeg liverMetastatic deposits
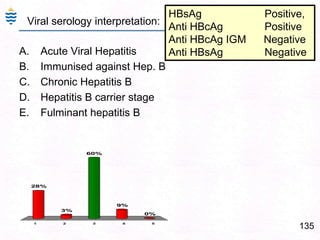
- 175. 135HBsAg Positive, Anti HBcAg PositiveAnti HBcAg IGM NegativeAnti HBsAg NegativeViral serology interpretation:Acute Viral HepatitisImmunised against Hep. BChronic Hepatitis BHepatitis B carrier stageFulminant hepatitis B
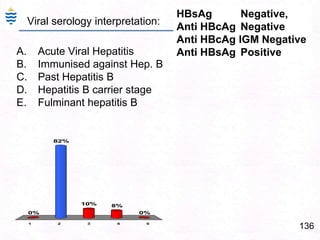
- 176. 136HBsAg Negative, Anti HBcAg NegativeAnti HBcAg IGM NegativeAnti HBsAg PositiveViral serology interpretation:Acute Viral HepatitisImmunised against Hep. BPast Hepatitis BHepatitis B carrier stageFulminant hepatitis B
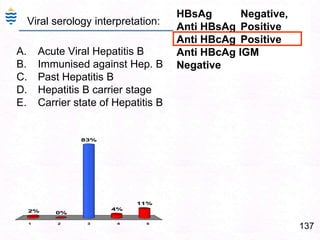
- 177. 137HBsAg Negative, Anti HBsAg PositiveAnti HBcAg PositiveAnti HBcAg IGM NegativeViral serology interpretation:Acute Viral Hepatitis BImmunised against Hep. BPast Hepatitis BHepatitis B carrier stageCarrier state of Hepatitis B
- 178. 138Protein (Total) 59 g/LAlbumin 30 g/LGlobulin 29 g/LBilirubin (Total) 27 μmol/LALP 71 U/LGGT 523 U/LALT 79 U/LAST 151 U/LLab Investigations interpretation:Alcoholic Liver diseaseAcute Viral Hepatitis.Past Hepatitis BHepatitis B carrier stageCarrier state of Hepatitis B
- 179. 139Lab Investigations interpretation: Urea 5.8 mmol/LCreatinine 80 μmol/LProtein (Total) 66 g/L Albumin 35 g/LGlobulin 31 g/LBilirubin (Total) 192 μmol/LBilirubin (Conj.) 130 μmol/LALP 203 U/LGGT 470 U/LALT 6055 U/LAST 4860 U/LAlcoholic Liver diseasePast Hepatitis BAcute Viral Hepatitis.Hepatitis B carrier stageCarrier state of Hepatitis B
- 180. 28y M, alcoholic, homosexual icterus and fever. Liver biopsy. ? diagnosisAcute viral hepatitisHemolytic anemiaChronic persistent hepatitisAlcoholic fatty liver.Alcoholic Hepatits.
- 181. 62 year Male, malaise, lethargy since 2 years. Liver mildly enlarged. No jaundice. Liver function tests normal. Image from liver biopsy. Most likely diagnosis? Alcoholic fatty liver. Acute viral hepatitis.Fulminant hepatitis.Chronic viral hepatitis.Alcoholic Cirrhosis.
- 182. 34y M, icterus and fever. Liver biopsy. ? diagnosisAcute HepatitisChronic Persistent Hepatitis.Chronic active HepatitisFulminant HepatitisCirrhosis
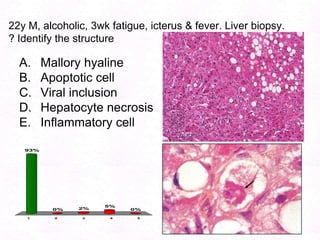
- 183. 22y M, alcoholic, 3wk fatigue, icterus & fever. Liver biopsy. ? Identify the structureMallory hyalineApoptotic cellViral inclusionHepatocyte necrosisInflammatory cell
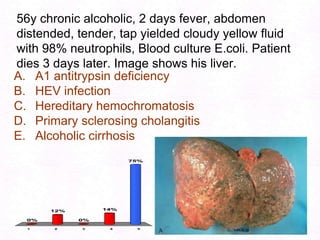
- 184. 56y chronic alcoholic, 2 days fever, abdomen distended, tender, tap yielded cloudy yellow fluid with 98% neutrophils, Blood culture E.coli. Patient dies 3 days later. Image shows his liver.A1 antitrypsin deficiencyHEV infectionHereditary hemochromatosisPrimary sclerosing cholangitisAlcoholic cirrhosis
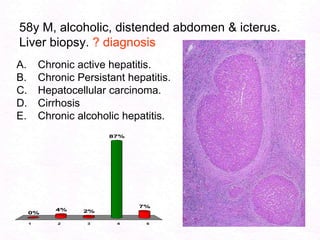
- 185. 58y M, alcoholic, distended abdomen & icterus. Liver biopsy. ? diagnosisChronic active hepatitis.Chronic Persistant hepatitis.Hepatocellular carcinoma.CirrhosisChronic alcoholic hepatitis.
- 186. 14651y M, Alcoholic: Look at Arrow ? Pathogenesis.Porta-systemic shuntHyper-oestrogenemiaPortal hypertensionHypo-albuminemiaDecreased vit-K
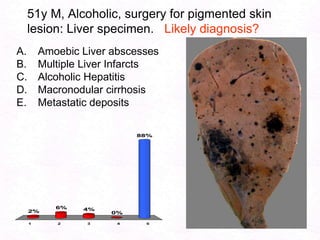
- 187. 51y M, Alcoholic, surgery for pigmented skin lesion: Liver specimen. Likely diagnosis?Amoebic Liver abscessesMultiple Liver InfarctsAlcoholic HepatitisMacronodular cirrhosisMetastatic deposits
- 188. 59y Male, Alcoholic, presents with fatigue, anorexia. Normal liver function tests. Liver specimen. Likely diagnosis?Dubin-Johnson SyndromeAlcoholic cirrhosisAlcoholic HepatitisFatty LiverMetastatic deposits
- 189. 22y M, alcoholic, 3wk fatigue, icterus & fever. Liver biopsy. ? Identify the structureMallory hyalineApoptotic cellViral inclusionHepatocyte necrosisInflammatory cell
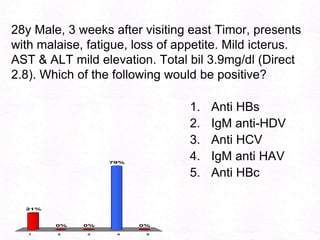
- 190. 28y Male, 3 weeks after visiting east Timor, presents with malaise, fatigue, loss of appetite. Mild icterus. AST & ALT mild elevation. Total bil 3.9mg/dl (Direct 2.8). Which of the following would be positive?Anti HBsIgM anti-HDVAnti HCVIgM anti HAVAnti HBc
- 191. 28y Male, 3 weeks after visiting east Timor, presents with malaise, fatigue, loss of appetite. Mild icterus. AST & ALT mild elevation. Total bil 3.9mg/dl (Direct 2.8). Which of the following would be positive?Anti HBsIgM anti-HDVAnti HCVIgM anti HAVAnti HBc
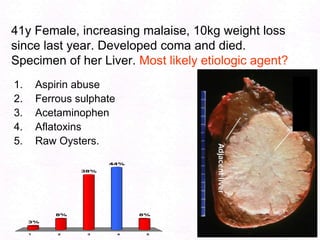
- 192. 41y Female, increasing malaise, 10kg weight loss since last year. Developed coma and died. Specimen of her Liver. Most likely etiologic agent?Aspirin abuseFerrous sulphateAcetaminophenAflatoxinsRaw Oysters.
- 193. A 48y man referred following high ALT in health screening. HCV immunoassay +ve. Past h/o appendectomy 10 years ago. Examination is normal. Which of the following tests would determine if he has Chronic HCV infection?Repeat EIA for anti HCV Ab.Recombinant immunoblot assay (RIBA)Alpha-fetoprotein levels.HCV RNA test.Direct, indirect & total bilirubin assay.
- 194. 154Learn from the mistakes of others. You can't live long enough to make them all yourself…!61% of 5th year students exceeded ‘sensible’ limitsDrugs and alcohol were taken mainly for pleasure and were perceived as a normal part of life for many students… Capability of advising patients…?http://www.lycaeum.org/research/researchpdfs/1996_webb_1.pdf
- 195. 155CPC-2.2– Major Pathology CLI:Pathology of Acute & Chronic Liver injury. Hepatitis – Causes, Types, Pathophysiology, Gross & Microscopic Pathology. Complications. Common types: Viral (Specific & Non specific), Alcoholic & Drug induced. Pathophysiology of Jaundice, Clinical & Pathological types. Pathology of cirrhosis – Classification, morphology & Complications. Pathology of Alcoholic Liver disease – Pathophysiology, types & complications.
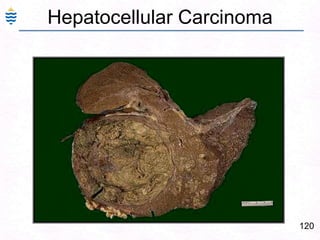
- 196. 156CPC-2.2– Minor Pathology CLI:Hemosiderosis & Hemochromatosis. Pathogenesis of Hepatic coma, Liver failure. Primary Biliary cirrhosis. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver cysts & tumours – adenoma, hyperplasia & cancer.Amoebic liver abscess & Hydatid disease of liver.Congenital liver disorders – enzyme disorders.
- 198. 158Case # 2 - ? Diagnosis60yr Male, 8 month slowly developing weakness, mild icterus. PE: Mild Abdominal tenderness, No organomegaly. Mild Scleral icterus.Labs: ALT: 52 (N= 8-33 U/L) AST: 58 (N= 4-36 U/L) Alk Phos: 150 (N= 20-130 u/L) Bilirubin 3.9 (N= 0.1-1.2 mg/dL) (direct 1.8) T Protein 4.8 (N= 6.0-7.8 g/dL) Albumin 2.5 (N= 3.2-4.5 g/dl) PT = 16 sec (N= 11-14.7 sec ) Differential diagnosis?What further investigations?
- 199. 159Diagnosis pathway:ALT: 52AST: 58 Alk Phos: 150Bilirubin 3.9 (direct 1.8)Jaundice?Mild increase, Mixed (combined)Synthesis?Total protein, albumin – Low & PT abnormal. Obstruction & Bilirubin Clearance ?Alk Phos is up a bit – but not high – some obstruction.Hepatocyte Direct Injury:ALT & AST are up a bit, but not dramatically.Discussion:Chronic Mild compromise - chronic Active hepatitis. (In CPH LFT will be normal)
- 200. 16028y Male, 3 weeks after visiting east Timor, presents with malaise, fatigue, loss of appetite. Mild icterus. AST & ALT mild elevation. Total bil 3.9mg/dl (Direct 2.8). Which of the following would be positive?