isolation precautions and use of PPE.pptx
- 2. ISOLATION Definition: Isolation is the separation of a patient from a contact with others in order to control the spread of an infectious or communicable disease.
- 3. NEED FOR ISOLATION • Isolation aimed controlling and preventing the spread of infection • Isolation precautions are designed to minimize the transmission of infection in the hospital by using updated and skilled technology • Isolation helps to protect patients, family members, visitors and health care workers from the spread of inefction.
- 4. MODES/TYPES OF ISOLATION 1. Strict isolation: It is used to prevent the transmission of all highly communicable disease that are spread by both contact and airborne routes of transmission. Eg. Chickenpox, Rabies 2. Respiratory isolation: Used to prevent transmission of organisms by means of droplets that are sneezed or breathed into the environment
- 5. 3. Protective isolation: Used to prevent contact between potentially pathogenic micro- organism and uninfected persons who have seriously impaired resistance. Eg. Leukemia, who are on certain therapeutic regimens
- 6. 4. Enteric isolation: Used to control diseases that can be transmitted through direct or indirect oral contact with infected feces or contaminated articles. Transmission of infection depends on ingestion of the pathogens. Eg. Dysentry, Hepatitis. 5. Wound and skin isolation: Used to prevent spread of infection found in infected wounds and contaminated articles. Eg. Herpes, Impetigo and ringworm.
- 7. 6. Blood Isolation: Used to prevent acquisition of infection by patients and personnel from contact with blood or items contaminated with blood. Eg. Hep B, HIV 7. Discharge isolation: a) Secretion precautions lesion: it is used to prevent acquisition of infection by personnel and patients from direct contact with wounds and secretion contaminated articles. Eg Conjunctivitis, Gonorrhea and Syphilis.
- 8. b) Secretion precautions oral: Used to prevent acquisition of infection by personnel from direct contact with oral secretions. Eg. Herpes, Areolas and Scarlet fever. c) Excretion precautions: Used to prevent acquisition of infection by personnel and patients from direct contact with fecal excretions. Eg. Poliomyelitis and Staphylococcal poisoning.
- 9. STANDARD PRECAUTIONS Standard precautions are a set of infection control practices used to prevent the transmission of diseases that can be acquired by contact with blood, body fluids, non intact skin and mucous membranes.
- 10. These measures should be followed when providing care to or handling: • All individuals whether they appear infectious/symptomatic or not • All specimen whether they appear infectious or not • All needles and sharps whether they appear infectious or not.
- 11. Universal precautions was a term used in the past to refer to the infection control practices to avoid contact with a patient’s blood and other potentially infectious materials by means of wearing nonporous articles such as PPE kits. Now it is replaced by the word Standard Precautions.
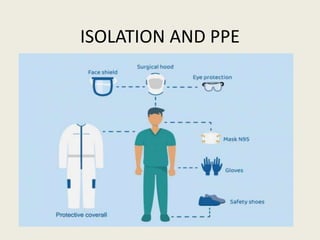
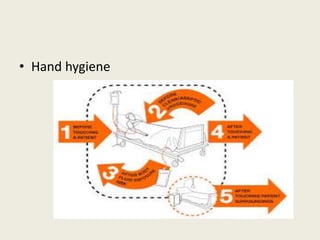
- 12. Standard precautions are indicated while handling all patients, specimen and sharps. Components of standard precautions include: • Hand hygiene • No touch technique • Use of gloves to avoid contact with blood, body fluid, secretion etc • Use of mask, gown, shoes, eye glasses etc.
- 13. • Sharp handling carefully • Spoilage cleaning. Eg. Spills of infectious materials immediately • Disinfection of linen, equipment used by patient. They must be sterilized or discarded between each patient use • Ensure appropriate biomedical waste separation and disposal
- 14. • Patients should be confined to restricted area • If required nasal carriers must be treated with mupirocin.
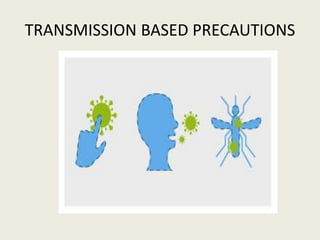
- 16. Transmission based precautions also called specific precautions are a set of infection control practices that should be followed over and above the standard precautions. Accordingly there are three types of transmission based precautions: • Contact precautions • Droplet precautions • Airborne precautions
- 17. CONTACT PRECAUTIONS Contact precautions should be followed when there is definitive or suspected evidence of certain infectious agents that are transmitted by direct or indirect contact during patient care.
- 18. INFECTION CONTROL MEASURES ( CONTACT) The following should be applied in addition to other standard precaution measures.
- 19. • Hand hygiene
- 20. • Personal protective equipment
- 21. • Equipment: single used equipment must be used, if not possible then it must be cleaned and dried before use.
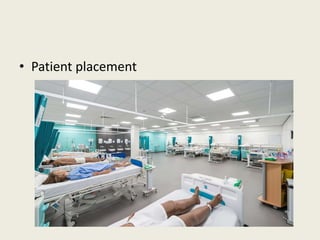
- 22. • Patient placement: single isolation room with a bathroom facility is preferred. If not possible Cohorting may be carried out in various ways. • Transfer of patients: Patients movement should be limited only to medically necessary purposes. • Disinfection of rooms: Patients rooms must be frequently cleaned and disinfected adequately focusing on frequently touched surfaces and equipments in the immediate vicinity of the patients.
- 24. It is a large particles >5 µm in size and it is generated by sneezing, coughing and talking. It only travel shorter distance (<3 feet).
- 25. INFECTION CONTROL MEASURES ( DROPLET) • Hand hygiene • PPE: Health care workers should wear surgical mask when in close contact with patients. • Respiratory hygiene/coughing etiquettes
- 27. • Transfer of patients: Transfer of patient must be avoided unless on certain circumstances and when transfer the following precautions must be taken: Patient wears surgical mask Patient follows respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette HCW transporting the patient should wear surgical mask, gloves, gown and protective eyewear.
- 28. • Disinfection of the rooms
- 30. CONTROL MEASURES • PPE • Patient placement: patients should be placed in airborne infection isolation room ( AIIR). Its components are: adequate ventilation, ultraviolet germicidal irradiation and filtration. • Ventilation: Natural ventilation, mechanical ventilation
- 31. • Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation
- 32. • Filtration : must be done through exhaust fan or through HEPA ( high efficiency particulate air) • In Transfer of patients they must be wear surgical mask and follow cough and respiratory hygiene etiquettes. All skin lesion must be covered. The HCW must wear N95 Respirator and other PPE as indicated.
- 33. • Visitors and staffs: Entry of visitors and staff should be restricted or they should wear PPE before entry into room.