Phosphorus triiodide
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
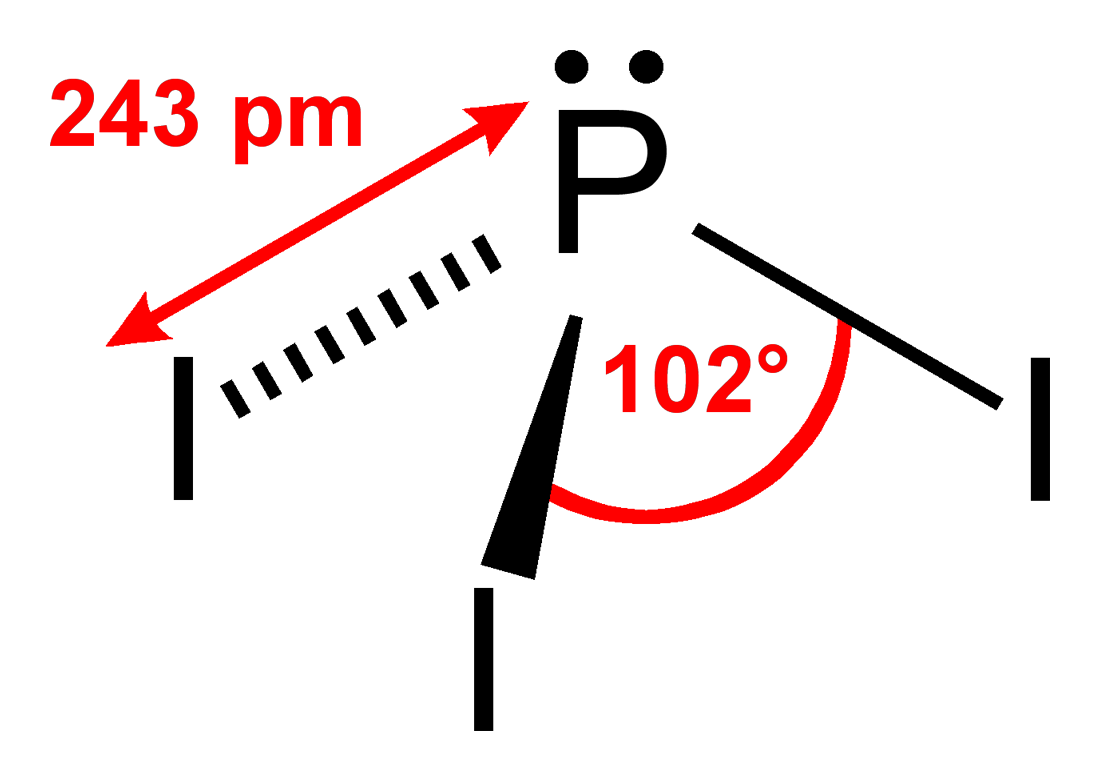
Phosphorus triiodide (PI3) is an inorganic compound with the formula PI3. A red solid, it is too unstable to be stored for long periods of time; it is, nevertheless, commercially available.[2] It is widely used in organic chemistry for converting alcohols to alkyl iodides and also serves as a powerful reducing agent.
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Phosphorus triiodide Phosphorus(III) iodide | |
| Other names
Triiodophosphine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.302 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| PI3 | |
| Molar mass | 411.68717 g/mol |
| Appearance | dark red solid |
| Density | 4.18 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 61.2 °C (142.2 °F; 334.3 K) |
| Boiling point | 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) (decomposes) |
| Decomposes | |
| Structure | |
| Trigonal pyramidal | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H314, H335 | |
| P260, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | non-flammable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Properties
Although PI3 is a pyramidal molecule, it has only a small molecular dipole because each P-I bond has almost no bond dipole moment. The P-I bond is also weak; PI3 is much less stable than PBr3 and PCl3, with a standard enthalpy of formation for PI3 of only −46 kJ/ mol (solid). The phosphorus atom has an NMR chemical shift of 178 ppm (downfield of H3PO4).
Reactions
Phosphorus triiodide reacts vigorously with water, producing phosphorous acid (H3PO3) and hydroiodic acid (HI), along with smaller amounts of phosphine and various P-P-containing compounds. Alcohols likewise form alkyl iodides, this providing the main use for PI3.
PI3 is also a powerful reducing agent and deoxygenating agent. It reduces sulfoxides to sulfides, even at −78 °C.[3] Meanwhile, heating a 1-iodobutane solution of PI3 with red phosphorus causes reduction to P2I4.
Preparation
The usual method or preparation is by the union of the elements, often by addition of iodine to a solution of white phosphorus in carbon disulfide:
- P4 + 6 I2 → 4 PI3
Alternatively, PCl3 may be converted to PI3 by the action of hydrogen iodide or certain metal iodides.
Uses
Phosphorus triiodide is commonly used in the laboratory for the conversion of primary or secondary alcohols to alkyl iodides.[4] The alcohol is frequently used as the solvent, on top of being the reactant. Often the PI3 is made in situ by the reaction of red phosphorus with iodine in the presence of the alcohol; for example, the conversion of methanol to give iodomethane:[5]
- PI3 + 3 CH
3OH → 3 CH
3I + " H
3PO
3"
These alkyl iodides are useful compounds for nucleophilic substitution reactions, and for the preparation of Grignard reagents.
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.