Harriet Tubman

 Harriet Tubman Statue (Sep 3, 2010)
Harriet Tubman Statue (Sep 3, 2010)by Jim Henderson
National Women's History Museum
Character, Courage and Commitment
As a conductor on the Underground Railroad, Harriet Tubman made several trips into slave-holding states, leading dozens of individuals to freedom in the North. During the Civil War, she further risked her life and safety to work first as a nurse and then as a spy for the Union Army. Afterwards, she became an outspoken advocate for African American and women's rights, insisting that all be afforded dignity, treated with respect and granted equality.
 Harriet Tubman Statue (Sep 3, 2010)
Harriet Tubman Statue (Sep 3, 2010)by Jim Henderson
National Women's History Museum
Araminta Ross was born in Dorchester County, Maryland in or around 1822 on Anthony Thompson's plantation. Araminta grew up to be known as Harriet Tubman. By 1840, Harriet, her mother and several siblings had been relocated from a plantation in Bucktown back to Thompson's farm.
The young girl would grow up to become one of the most celebrated figures of her time. Her legacy of steadfast courage and commitment to justice would endure more than 100 years after her death.
Today, no trace of Tubman's birthplace remains. Though, a historical marker notes the location.
Cambridge, Maryland. Dorchester County. Site of Harriet Tubman's birth
 Sweet potato planting, Hopkinson's Plantation
Sweet potato planting, Hopkinson's Plantationby Henry P. Moore
National Women's History Museum
Tubman worked as a field hand for many years -following the oxen loading and unloading wood and carrying heavy burdens -all along developing great strength and determination.Later, she was hired out to perform housework and child care where the plantation mistress proved capricious and cruel, employing frequent beatings for the most minor of offenses.
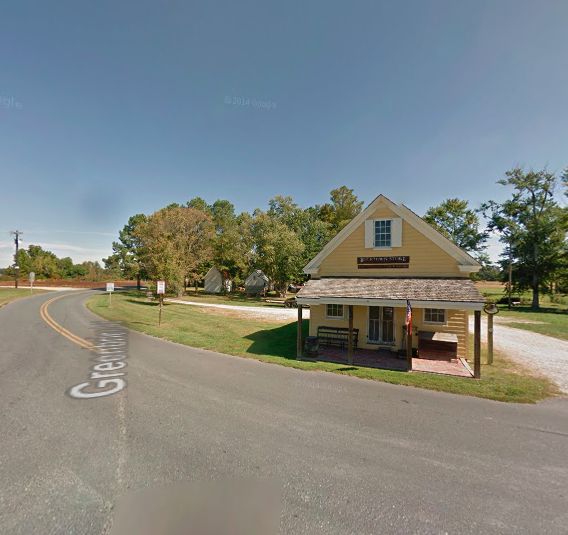

The Bucktown Village store still stands in Bucktown, Maryland. It was here that 12-year-old slave Araminta Ross was shopping with the plantation cook when an overseer entered, pursuing an escaped slave. The overseer ordered Araminta to assist with tying the man up, which she refused to do. As the escaping slave bolted for the door, the overseer swept up a two-pound scale weight up from the counter and threw it after him. The weight missed its mark, hitting Araminta instead. The blow knocked her unconscious.
It was not her first experience with the violence of slavery, but it would have the most lasting effect as she suffered from severe headaches for the rest of her life.
Bucktown Village Store historic site, Cambridge, Maryland.
 Harriet Tubman Quotation
Harriet Tubman QuotationHarriet Tubman
National Women's History Museum
Tubman worked as a field hand for many years -following the oxen loading and unloading wood and carrying heavy burdens -all along developing great strength and determination.Later, she was hired out to perform housework and child care where the plantation mistress proved capricious and cruel, employing frequent beatings for the most minor of offenses.
 A drawing of Harriet Tubman called "Moses" (1934-1935)
A drawing of Harriet Tubman called "Moses" (1934-1935)by Bernarda Bryson
National Women's History Museum
Araminta married a free black named John Tubman in 1844, taking his last name. She changed her first name, adopting her mother's name, becoming Harriet. In 1849, worried that she and the other slaves on the plantation where she lived were going to be sold, Tubman decided to run away. Her husband refused to go with her, so she set out with her two brothers. Her brothers turned back, but Tubman persevered to freedom, settling in Philadelphia.
Tubman could not be happy in freedom knowing that her relatives and friends remained enslaved. She made the dangerous decision to return to Maryland to secure their freedom as well.
 Harriet Tubman Quotation (Apr 20, 2016)
Harriet Tubman Quotation (Apr 20, 2016)Harriet Tubman
National Women's History Museum

Linchester Mill was the hub of Underground Railroad activity in the area. Whites and blacks, free and enslaved, had regular contact here at the general store or the post office. Free and enslaved African Americans worked side-by-side, providing a constant flow of information and support to freedom seekers. Quakers and free blacks who lived near the mill secretly helped fleeing slaves pass through the area.
The mill dam created a spot to cross Hunting Creek. Such crossing points helped freedom seekers avoid unwanted attention.
Linchester Mill historic site, Preston, Maryland.
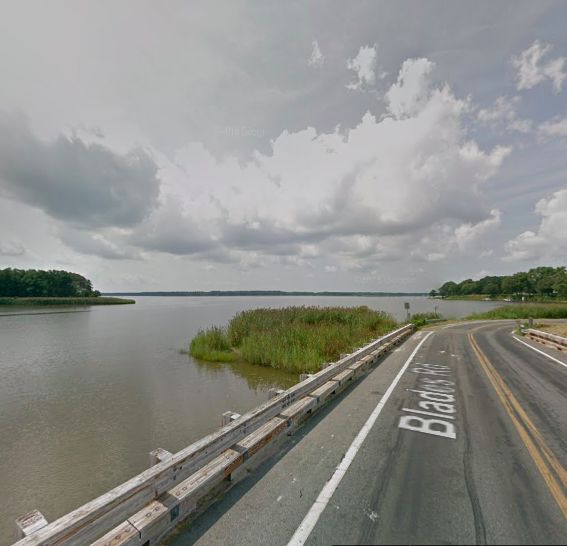

Harriet Tubman’s parents were active in the Underground Railroad, and she most likely made her first escape from their home near Choptank Landing.
On Christmas Day 1854, Tubman led her three brothers to freedom from nearby Poplar Neck. Robert, Ben and Henry, as well as several others, hid in a corn crib until dark, when they could begin their journey north.
At nightfall, Harriet safely led them on their journey towards freedom, traveling through Delaware, Pennsylvania, and across upstate New York to St. Catharines, Ontario, Canada.
Choptank River, Preston, Maryland, near site of Tubman's parents' home.

The forests, marshes, and waterways that characterized Tubman's home territory are largely unchanged from the time that she made her home in Dorchester County.
Knowledge of the terrain was vital to survival while hiding and trying to flee. Tubman and others had to successfully navigate the land and waterways, trap and forage for food, and hide from their pursuers. Understanding the tides, knowing how to find food and fresh water, and following the North Star were all skills that later proved vital as she guided her charges north along the Underground Railroad to freedom.
Blackwater National Wildlife Refuge, Cambridge, Maryland
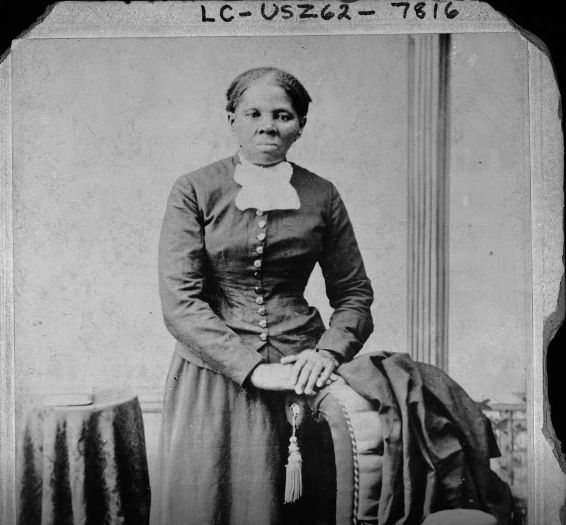 Harriet Tubman
Harriet TubmanNational Women's History Museum
As part of the Underground Railroad network, Tubman successfully employed a variety of escape and evasion methods to help aid fleeing slaves. Disguise was a favorite. If it was announced that a group of male slaves had bolted from a plantation, she dressed the fugitives as women for the trip north.
On another occasion, Tubman came dangerously close to being identified during a stopover at a train depot. To confuse her pursuers, she quickly purchased a ticket for the southbound train, correctly believing, that as it turned out, few would expect an “outlaw” of her notoriety to venture further into Dixie in such a public manner. For one of her more brazen missions, she convinced a light-skinned fugitive to pose as a white master transporting a group of slaves to a town further up the road.
For all the recriminations directed at her by displeased plantation owners throughout the South, Tubman was never caught and never lost a “passenger.”
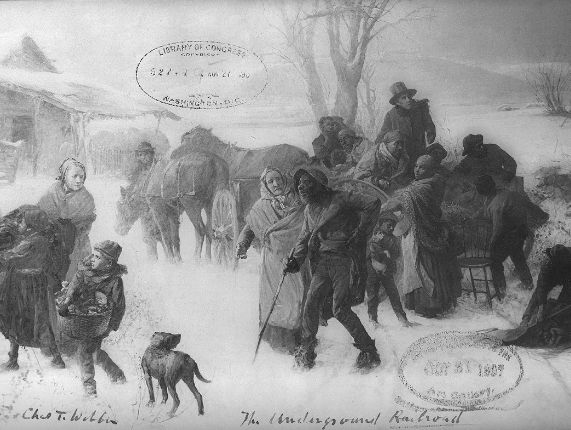 The Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroadby Chas T. Webber
National Women's History Museum
Moving “passengers” along the Underground Railroad, Tubman became very familiar with the different towns and transportation routes characterizing the South. This information proved extremely valuable to Federal military commanders after the Civil War began in 1861.
Poorly drawn and outdated maps, coupled with soldiers who had little knowledge of the United States beyond their own village, made individuals like Tubman vitally important to the Union war effort. Utilizing the extensive knowledge of the South she had obtained while working for the Underground Railroad, Tubman was able to provide accurate intelligence data to Northern troops.
Tubman also served as a spy, seeking and delivering intelligence from behind enemy lines. At the war's conclusion, she was granted a military pension of $20 per month, the first African American woman to receive one.
 Harriet Tubman
Harriet TubmanNational Women's History Museum
After the war, Tubman retired to a piece of land on the outskirts of Auburn, New York where she lived surrounded by family. She cared for her parents and other relatives, becoming a stalwart of the community. She was famous in her own lifetime for her accomplishments, was sought after as a speaker, and collaborated on a biography of her life story.
Tubman died in 1913 and was buried with military honors at Fort Hill Cemetery in Auburn, New York.

Tubman's legacy lives on in the hearts and spirit of every American. She has been honored with monuments and statues, schools bear her name, and thousands of Americans daily travel along Harriet Tubman roads, streets, and avenues.
Harriet Tubman Elementary School, Washington, DC.
 Harriet Tubman (2012)
Harriet Tubman (2012)National Women's History Museum
Tubman has been honored on a United States postage stamp.
 MLK Jr. Barack Obama and Malcolm X (2010)
MLK Jr. Barack Obama and Malcolm X (2010)National Women's History Museum
She has been celebrated as an enduring Civil Rights icon by contemporary artists and activists.
In April 2016, the US Treasury announced that she would become the first American woman pictured on currency in over 100 years.
Soon, Tubman will take her place in history on the new twenty dollar bill.
 Quote Describing Harriet Tubman as Inspiration (Apr 21, 2016)
Quote Describing Harriet Tubman as Inspiration (Apr 21, 2016)National Women's History Museum
