Converting units powerpoints
•
39 likes•25,013 views
Powerpoint introduces conversion factors and teaches students how to convert non-metric units using the factor label method.
1 of 8






Recommended
Converting unit measures by EdTechonGC Mallett, has 24 slides with 32478 views.



Converting unit measuresEdTechonGC Mallett
24 slides•32.5K views
The document discusses various units of measurement in the metric system including units for length (meters, centimeters, millimeters), mass (kilograms, grams), capacity (liters, milliliters), area (square meters, hectares), and volume (cubic meters, liters). It provides examples for converting between metric units using multiplication or division by powers of ten. The document also briefly discusses units of time and provides examples of calculating time to complete multiple tasks.Scientific notation powerpoint by Edison Orgil, has 14 slides with 45992 views.



Scientific notation powerpointEdison Orgil
14 slides•46K views
Scientific notation is a way to write very large or small numbers as a product of a number between 1 and 10 and a power of 10. To convert a number to scientific notation, the decimal is moved to place one non-zero digit before the decimal point, and the number of places the decimal is moved determines the exponent of 10. Numbers greater than 1 have positive exponents, while numbers less than 1 have negative exponents. Converting back to standard form moves the decimal right for positive exponents and left for negative exponents by the value of the exponent.Measurement PPT by Lalaine Son, has 58 slides with 103020 views.

Measurement PPTLalaine Son
58 slides•103K views
The document discusses various units of measurement for length, volume, mass, and temperature in both the metric and imperial systems. It provides examples to convert between units and explains how to measure quantities using tools like rulers, graduated cylinders, balances, and thermometers. Key metric units include meters, centimeters, millimeters, liters, milliliters, grams, and degrees Celsius.CONVERSION OF UNITS OF MEASUREMENTS.pptx by LiezlBontilao, has 48 slides with 13719 views.

CONVERSION OF UNITS OF MEASUREMENTS.pptxLiezlBontilao
48 slides•13.7K views
CONVERSION OF UNITS OF MEASUREMENTS
Conversion of unit of Measurements for Length
1) Identify the unit you are starting with.
2) Identify the unit you want to end with.
3) Find the conversion factor/s that will convert the starting unit to ending unit. Using the fractional form the unit you want to end will be the numerator the unit to be cancelled will be the denominator.
4) Set up the Mathematical expression so that all units except the unit you want to end with, will not be cancelled.
Convert 36 inches to feet.
Solution:
Step 1: inches
Step 2 : feet
Step 3 : (1 𝑓𝑜𝑜𝑡)/(12 𝑖𝑛𝑐ℎ𝑒𝑠)
Step 4: 36 inches x (1 𝑓𝑜𝑜𝑡)/(12 𝑖𝑛𝑐ℎ𝑒𝑠) = 3 feet
Step 5: Therefore, 36 in = 3 feet
Physical Quantities--Units and Measurement--Conversion of Units by KhanSaif2, has 33 slides with 11191 views.

Physical Quantities--Units and Measurement--Conversion of UnitsKhanSaif2
33 slides•11.2K views
This presentation covers physical quantities and their types, units and their types, conversion of units and order of magnitude in a very interactive manner. I hope this presentation will be helpful for teachers as well as students.Adding Fractions With Unlike Denominators by Sarah Hallum, has 13 slides with 11017 views.

Adding Fractions With Unlike DenominatorsSarah Hallum
13 slides•11K views
To add or subtract fractions with unlike denominators:
1. Find the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators.
2. Write the fractions with this LCM as the new denominator by multiplying the numerators and denominators.
3. Add or subtract the new numerators and put over the common denominator.
4. Simplify the final fraction if possible by dividing the numerator and denominator by common factors.Oprations Of Decimal Numbers by NMSpirit , has 13 slides with 18605 views.

Oprations Of Decimal NumbersNMSpirit
13 slides•18.6K views
This document provides instructions for performing basic operations with decimals such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It explains how to align the decimals and describes the steps for each operation. Examples are provided for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing decimals. The document also covers comparing and converting fractions and decimals, with examples of how to convert a fraction to a decimal and vice versa. It concludes with contact information.Adding Subtracting Integers by Mr. M, has 46 slides with 44476 views.

Adding Subtracting IntegersMr. M
46 slides•44.5K views
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as adding numbers with the same sign and subtracting numbers with different signs. It also explains how to use a number line to demonstrate adding integers and proves that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Teaching conversion of metric units by Kevin Cummins, has 19 slides with 15466 views.

Teaching conversion of metric unitsKevin Cummins
19 slides•15.5K views
This free teaching resource is from Innovative Teaching Resources. You can access hundreds of their excellent resources here. https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Store/Innovative-Teaching-Ideas
Lesson plans and teaching Metric System by shas595, has 25 slides with 18066 views.

Metric Systemshas595
25 slides•18.1K views
This document provides information about the metric system of measurement including units of length, mass, and volume. It explains that the metric system is used in science for precise measurements and definitions. Key points include:
- The metric system uses prefixes like kilo, centi, and milli to denote powers of ten in units like meters, grams, and liters.
- Units of length are measured in meters (m) or centimeters (cm). Mass is measured in grams (g) or kilograms (kg). Volume is measured in liters (L) or milliliters (mL).
- Examples show converting between metric units using the prefixes and moving the decimal point based on powers of ten inSpeed, Distance and Time .pptx by MARYANNSISON2, has 25 slides with 6562 views.

Speed, Distance and Time .pptxMARYANNSISON2
25 slides•6.6K views
Mr. Cruz drove for 2 hours at an average speed of 80 kilometers per hour. Using the formula distance = speed x time, the distance traveled is calculated as:
Distance = Speed x Time
= 80 km/h x 2 hours
= 160 km
Therefore, the distance Mr. Cruz traveled to reach the province is 160 km.Add & Subtract Fractions by Andrea B., has 23 slides with 13165 views.

Add & Subtract FractionsAndrea B.
23 slides•13.2K views
This document provides an overview of fractions including:
- Definitions of proper, improper, and mixed numbers
- Equivalent fractions and how to identify them
- Ordering fractions with both like and unlike denominators
- Adding and subtracting fractions with both like and unlike denominators
- Examples are provided for each concept along with practice problems for students to work through
The document covers essential fraction concepts and provides clear explanations, examples, and practice problems to help students understand fractions.MEASURING LENGTH (teach) by Moira Whitehouse, has 36 slides with 38632 views.

MEASURING LENGTH (teach)Moira Whitehouse
36 slides•38.6K views
1. The document discusses the history and development of systems for measuring length and distance, from early rulers based on body parts to the modern metric system.
2. It describes how the metric system was developed using the distance from the Earth's equator to the North Pole, divided into 10 million equal parts called meters.
3. The document provides examples of measuring various lengths in millimeters and centimeters using a metric ruler, and explains how the metric units of meters, centimeters and millimeters are used to measure different distances.7. lesson 6 division of whole numbers by John Rome Aranas, has 19 slides with 8065 views.

7. lesson 6 division of whole numbersJohn Rome Aranas
19 slides•8.1K views
Division is the process of splitting a number into equal parts or groups. It can be thought of as repeated subtraction. The key terms in division are: dividend, the number being divided; divisor, the number dividing; quotient, the answer of the division equation; and remainder, any leftover amount that does not divide evenly. Any number divided by zero is undefined. Division steps include removing common zeroes, then dividing the numbers. Examples show dividing various numbers and calculating quotients and remainders. Practice problems are provided to help learners apply division concepts and skills.Dividing decimals by decimals by KristaEvans1024, has 27 slides with 4092 views.

Dividing decimals by decimalsKristaEvans1024
27 slides•4.1K views
This document contains notes and instructions for dividing decimals. It includes:
1. A review of vocabulary terms like quotient, dividend and divisor.
2. Steps for dividing decimals that include placing the decimal point in the quotient directly above the decimal point in the dividend and dividing as with whole numbers.
3. Examples of dividing decimals with answers and worked out steps shown.Proper; Improper & Mixed Number Fractions by LorenKnights, has 21 slides with 10736 views.

Proper; Improper & Mixed Number FractionsLorenKnights
21 slides•10.7K views
This document discusses different types of fractions:
- Proper fractions have a numerator less than the denominator (e.g. 1/4).
- Improper fractions have a numerator greater than or equal to the denominator (e.g. 5/3).
- Mixed numbers are a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction (e.g. 2 1/4).
The document provides examples of converting between improper fractions and mixed numbers by dividing the numerator by the denominator to get the whole number part and remainder.Viewers also liked (20)
1 Units, Measurements, & Conversions by Joseph Cadray, has 8 slides with 12611 views.

1 Units, Measurements, & ConversionsJoseph Cadray
8 slides•12.6K views
This document discusses units and measurements conversions. It explains that prefixes like centi and milli indicate fractions of base units and conversions can be done using ratios of equivalent units. For example, 1 inch is equal to 2.54 centimeters. It also notes that algebraic manipulation of units is similar to variables, where units cancel out in operations like division. Rounding may be needed in conversions to avoid exact answers. Practice problems are provided to convert between units like centimeters and inches using equivalent ratios.Ch03 4 by Rendy Robert, has 10 slides with 1097 views.

Ch03 4Rendy Robert
10 slides•1.1K views
The document discusses complex roots of the characteristic equation arising from assuming exponential solutions to a differential equation. It shows that complex roots lead to complex-valued solutions, but linear combinations of solutions can give real-valued solutions in the form of sine and cosine functions. Several examples are worked out to find the general solution of differential equations and determine the time for the solution to drop below a given value based on its graph.Solving quadratic equations by Asawari Warkad, has 23 slides with 4142 views.

Solving quadratic equationsAsawari Warkad
23 slides•4.1K views
The document discusses solving quadratic equations by factoring. It provides examples of factoring quadratic expressions and setting each factor equal to 0 to solve for the roots. Methods include identifying factors of constants, using the zero factor property, and checking solutions. It also applies these skills to word problems involving quadratic equations.Module in solving quadratic equation by aleli ariola, has 110 slides with 10941 views.

Module in solving quadratic equationaleli ariola
110 slides•10.9K views
1. The document introduces a module on solving quadratic equations for high school students.
2. It discusses different methods for solving quadratic equations, including factoring, completing the square, using the quadratic formula, and graphing.
3. It also covers complex numbers and how to solve equations containing radicals or that can be reduced to quadratic equations.Mathematics 9 Lesson 1-D: System of Equations Involving Quadratic Equations by Juan Miguel Palero, has 9 slides with 2824 views.

Mathematics 9 Lesson 1-D: System of Equations Involving Quadratic EquationsJuan Miguel Palero
9 slides•2.8K views
This powerpoint presentation discusses or talks about the topic or lesson System of Equations involving Quadratic Equations. It also discusses and explains the rules, steps and examples of System of Equations involving Quadratic EquationsGraphing quadratic equations by swartzje, has 21 slides with 19490 views.

Graphing quadratic equationsswartzje
21 slides•19.5K views
1) This document discusses how to solve quadratic equations by graphing, including identifying the terms of a quadratic equation, finding the solutions by graphing, and graphing quadratic functions.
2) The key steps for graphing a quadratic function are to find the axis of symmetry using the standard form equation, find the vertex point, and find two other points to reflect across the axis of symmetry to complete the parabolic graph.
3) An example problem walks through graphing the quadratic equation y = x^2 - 4x by first finding the roots, vertex, and axis of symmetry, and then constructing a table to plot points and graph the parabola.Quadratic Equation by itutor, has 18 slides with 42864 views.

Quadratic Equationitutor
18 slides•42.9K views
This document introduces methods for solving quadratic equations beyond factoring, including the square root property, completing the square, and the quadratic formula. It discusses how to determine the number and type of solutions based on the discriminant. The key steps are presented for solving quadratics, graphing quadratic functions as parabolas, and finding the domain and range. Piecewise-defined quadratic functions are also explained.Ppt Measurements Unit 1 by ffiala, has 62 slides with 45356 views.

Ppt Measurements Unit 1ffiala
62 slides•45.4K views
The document discusses the International System of Units (SI) which defines the standard base units used to measure physical quantities like length, mass, time, temperature, etc. It lists the seven base units - meter, kilogram, second, kelvin, mole, ampere, and candela. Derived units are defined in terms of base units, such as area being length squared. Common units outside the SI like Fahrenheit and Celsius scales for temperature are also covered.Mathematics 9 Lesson 1-D: System of Equations Involving Quadratic Equations by Juan Miguel Palero, has 9 slides with 2824 views.

Mathematics 9 Lesson 1-D: System of Equations Involving Quadratic EquationsJuan Miguel Palero
9 slides•2.8K views
Similar to Converting units powerpoints (20)
Converting Metric Units by Jd Ramirez, has 13 slides with 318 views.

Converting Metric UnitsJd Ramirez
13 slides•318 views
The document discusses converting between different units of measurement using conversion factors. It provides examples of converting between units of time, length, mass, and volume. The key steps for conversion are: 1) Write the number with original units, 2) Multiply by the conversion factor as a fraction, 3) Cancel out the original units, 4) Multiply the numbers on top and divide the numbers on bottom. Practice problems are provided to convert between units of volume like km3 to m3, cm3 to mm3, and dm3 to cm3.Scientific measurement by Kristel Manuyag, has 76 slides with 5644 views.

Scientific measurementKristel Manuyag
76 slides•5.6K views
Scientific Measurement can be summarized in 3 sentences:
Measurement involves assigning numerical values to properties of matter using standardized units. The units provide the numerical value and type of quantity being measured, with significant figures indicating the precision. Dimensional analysis allows conversion between different units by canceling unwanted units and introducing desired units using conversion factors derived from unit equality relationships.Ch. 1 lecture b by Brock Banks, has 10 slides with 246 views.

Ch. 1 lecture bBrock Banks
10 slides•246 views
1. Scientific notation is used to write very large or small numbers and involves moving the decimal point so the first non-zero digit is to the left of the decimal, with the power of 10 indicating the number of places the decimal was moved. Units of measurement and prefixes are used to represent large and small quantities.
2. Equalities show equivalent measurements between units and can be used to derive conversion factors. The factor-label method involves setting up a ratio between the given and desired units, with the unit in the numerator cancelling the unit in the denominator to give the conversion in the desired unit.
3. Examples are provided for measuring temperatures on thermometers, converting between units like hours to minutes using conversion factors2 2 unit conversions by jwallach, has 11 slides with 2412 views.

2 2 unit conversionsjwallach
11 slides•2.4K views
This document discusses unit conversions using dimensional analysis. Dimensional analysis allows one to convert between units by multiplying the original value by a conversion factor relating the two units. To perform a conversion, one identifies the given and desired units, determines the conversion factor relating those units, sets up the conversion factor as a fraction, and performs the calculation, cancelling out units. An example converts 36 inches to feet by multiplying 36 inches by the conversion factor 1 foot / 12 inches to obtain the answer of 3 feet. Dimensional analysis ensures conversions are performed correctly regardless of complexity.Measurements.ppt by warfyoropa4, has 18 slides with 26 views.

Measurements.pptwarfyoropa4
18 slides•26 views
This document discusses measurement units and conversions between metric and other systems. It covers:
- The fundamental SI units of mass, length, time, temperature and derived quantities.
- Using prefixes like kilo and centi to indicate multiples of ten in the metric system.
- Converting between metric units by moving the decimal place.
- Converting between metric and other systems like English units using conversion factors and unit cancellation.
- Applying significant figures rules to calculations to preserve measurement precision.Measurement teacher by laurengassman, has 29 slides with 823 views.

Measurement teacherlaurengassman
29 slides•823 views
1. This document provides information on units of measurement in chemistry including the SI base units and common unit prefixes.
2. It discusses the concepts of accuracy, precision, and significant figures in measurements and calculations.
3. Guidelines are given for determining the number of significant figures in calculations, measurements, and final answers involving addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.Math module 2 lesson 16 by NRWEG3, has 19 slides with 663 views.

Math module 2 lesson 16NRWEG3
19 slides•663 views
This document provides lesson materials on adding measurements using the standard algorithm. It includes fluency practice with metric units, rounding numbers, and grouping counting. An application problem asks students to add the weights of an apple and pear. Concept development has students use place value charts and the standard algorithm to add measurements by composing larger units twice, such as 158 grams and 266 grams. Partner work and a problem set provide additional practice adding measurements.Converting Units by TeacherAndrew, has 5 slides with 1179 views.

Converting UnitsTeacherAndrew
5 slides•1.2K views
This document provides instructions on how to convert between different units of measurement using conversion factors. It explains that you need to find a conversion factor that relates the initial and target units, then use that factor to perform the calculation. Two examples are shown converting feet to meters and cubic centimeters to liters. The document concludes with practice problems converting seconds to days and age in years to minutes.Recently uploaded (20)
MAT221: CALCULUS II | Transcendental Functions -Exponential and Logarithmic F... by Josophat Makawa, has 52 slides with 491 views.

MAT221: CALCULUS II | Transcendental Functions -Exponential and Logarithmic F...Josophat Makawa
52 slides•491 views
𝐓𝐢𝐭𝐥𝐞: 𝐌𝐀𝐓𝟐𝟐𝟏: 𝐂𝐚𝐥𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐮𝐬 𝐈𝐈 – 𝐓𝐫𝐚𝐧𝐬𝐜𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐥 𝐅𝐮𝐧𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐬
𝐀𝐮𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐫: 𝐉𝐨𝐬𝐨𝐩𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐌𝐚𝐤𝐚𝐰𝐚
This document provides a comprehensive exploration of transcendental functions, a fundamental topic in Calculus II. Designed for students, educators, and mathematics enthusiasts, it offers a structured approach to understanding exponential and logarithmic functions, differentiation techniques, and integral calculus.
Key topics covered include:
- The properties and applications of exponential and logarithmic functions
- Logarithmic differentiation and its use in handling complex rational functions
- Differentiation and integration of transcendental functions
- Analytical techniques such as implicit differentiation and substitution methods
- Step-by-step proofs, derivations, and worked examples
This resource is particularly valuable for undergraduate mathematics students, instructors, and researchers seeking a well-organized reference on transcendental functions. With clear explanations, mathematical rigor, and illustrative examples, it enhances conceptual understanding and problem-solving skills in calculus.
𝐖𝐡𝐞𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐫 𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐝 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐜𝐨𝐮𝐫𝐬𝐞𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐤, 𝐞𝐱𝐚𝐦 𝐩𝐫𝐞𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧, 𝐨𝐫 𝐚𝐝𝐯𝐚𝐧𝐜𝐞𝐝 𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐥 𝐬𝐭𝐮𝐝𝐢𝐞𝐬, 𝐭𝐡𝐢𝐬 𝐝𝐨𝐜𝐮𝐦𝐞𝐧𝐭 𝐬𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐞𝐬 𝐚𝐬 𝐚𝐧 𝐞𝐬𝐬𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐢𝐚𝐥 𝐠𝐮𝐢𝐝𝐞 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐦𝐚𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐧𝐬𝐜𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐥 𝐟𝐮𝐧𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐬.
myFutureNC's 2025 Educational Attainment report by ethomas14, has 24 slides with 1326 views.

myFutureNC's 2025 Educational Attainment reportethomas14
24 slides•1.3K views
North Carolina's 2025 State of Educational Attainment report published by myFutureNC.BBA 204 UNIT 1 MM DR KANCHAN KUMARI.pptx by Dr. Kanchan Kumari, has 14 slides with 74 views.

BBA 204 UNIT 1 MM DR KANCHAN KUMARI.pptxDr. Kanchan Kumari
14 slides•74 views
Study material for Management StudentsThe PLA Beyond Borders: Chinese Military Operations in Regional and Global Co... by Dadang Solihin, has 371 slides with 176 views.

The PLA Beyond Borders: Chinese Military Operations in Regional and Global Co...Dadang Solihin
371 slides•176 views
Buku The PLA Beyond Borders: Chinese Military Operations in Regional and Global Context diedit oleh Joel Wuthnow, Arthur S. Ding, Phillip C. Saunders, Andrew Scobell, dan Andrew N.D. Yang, merupakan karya komprehensif yang membahas operasi militer China di luar batas wilayahnya, termasuk dalam konteks regional dan global.
Buku ini terdiri dari 12 bab yang dibagi menjadi dua bagian utama: bagian pertama membahas faktor-faktor pendukung (enablers) yang memungkinkan operasi militer China, sementara bagian kedua fokus pada teori dan praktik operasi militer China.
Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ... by EduSkills OECD, has 8 slides with 170 views.

Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...EduSkills OECD
8 slides•170 views
Hannah Borhan, Research Assistant, OECD Education and Skills Directorate and Pietro Gagliardi, Policy Analyst, OECD Public Governance Directorate present at the OECD webinar 'From classroom to community engagement: Promoting active citizenship among young people" on 25 February 2025. You can find the recording of the webinar on the website https://oecdedutoday.com/webinars/
RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper (MMV Exam MCQ) by SONU HEETSON, has 17 slides with 241 views.

RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper (MMV Exam MCQ)SONU HEETSON
17 slides•241 views
RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper. MMV MCQ PDF Free Download for Railway Assistant Loco Pilot Exam.CMS letter to U.S. Representatives about House budget by Mebane Rash, has 2 slides with 2319 views.

CMS letter to U.S. Representatives about House budgetMebane Rash
2 slides•2.3K views
Medicaid and school mealsMAT221: CALCULUS II | Transcendental Functions -Exponential and Logarithmic F... by Josophat Makawa, has 52 slides with 491 views.

MAT221: CALCULUS II | Transcendental Functions -Exponential and Logarithmic F...Josophat Makawa
52 slides•491 views
The PLA Beyond Borders: Chinese Military Operations in Regional and Global Co... by Dadang Solihin, has 371 slides with 176 views.

The PLA Beyond Borders: Chinese Military Operations in Regional and Global Co...Dadang Solihin
371 slides•176 views
Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ... by EduSkills OECD, has 8 slides with 170 views.

Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...EduSkills OECD
8 slides•170 views
Converting units powerpoints
- 1. Converting Units
- 2. Why do we need to convert? Sometimes, we aren’t able to make a measurement in the units we want to use. In Chemistry and Physics, we use equations to solve problems. These equations only work when certain units are used. In your everyday life, you might need to convert units. For example, maybe you want to compare prices of products at the grocery store. Unless the volume of each product is listed in the same unit, we won’t be able to compare prices.
- 3. Conversion Factors When we convert units, we use conversion factors. Conversion factors are relationships between units that we know to be true. Some examples: 12 inches = 1 foot 1 minute = 60 seconds 16 ounces = 1 lb 24 hours = 1 day
- 4. Steps to converting units: Write the number (with units) that you want to convert. Multiply it by a conversion factor, written as a fraction. Make sure the old units cancel. Multiply all the numbers on the top and divide by the numbers on the bottom.
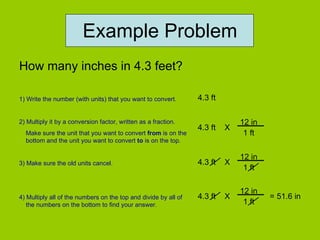
- 5. Example Problem How many inches in 4.3 feet? 1) Write the number (with units) that you want to convert. 2) Multiply it by a conversion factor, written as a fraction. Make sure the unit that you want to convert from is on the bottom and the unit you want to convert to is on the top. 3) Make sure the old units cancel. 4) Multiply all of the numbers on the top and divide by all of the numbers on the bottom to find your answer. 4.3 ft 4.3 ft X 12 in 1 ft 4.3 ft X 12 in 1 ft 4.3 ft X 12 in 1 ft = 51.6 in
- 6. Another Example 1) Write the number (with units) that you want to convert. 2) Multiply it by a conversion factor, written as a fraction. Make sure the unit that you want to convert from is on the bottom and the unit you want to convert to is on the top. 3) Make sure the old units cancel. 4) Multiply all of the numbers on the top and divide by all of the numbers on the bottom to find your answer. Convert 52.8 hours to days. 52.8 hrs 52.8 hrs X 1 day 24 hrs 52.8 hrs X 1 day 24 hrs 52.8 hrs X 1 day 24 hrs = 2.2 days
- 7. What if there are two units to change? 3.45 m/min = ___________ ft/s We need to change meters to feet. (1 meter = 3.281 feet) We also need to change minutes to seconds. (1 minute = 60 seconds) Choose one unit to change first. Then, multiply by a second fraction to change the other. Notice: The original number was written with minutes on the bottom. The only units which didn’t cancel were the units we wanted to convert to. We arrived at the answer by multiplying 3.45 X 3.281 and dividing by 60. 3.45 m min X 3.281 ft 1 m X 1 min 60 s = 0.189 ft/s
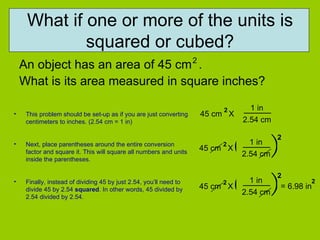
- 8. What if one or more of the units is squared or cubed? An object has an area of 45 cm . What is its area measured in square inches? 2 This problem should be set-up as if you are just converting centimeters to inches. (2.54 cm = 1 in) Next, place parentheses around the entire conversion factor and square it. This will square all numbers and units inside the parentheses. Finally, instead of dividing 45 by just 2.54, you’ll need to divide 45 by 2.54 squared . In other words, 45 divided by 2.54 divided by 2.54. 45 cm X 2 1 in 2.54 cm 45 cm X 2 1 in 2.54 cm ( ) 2 45 cm X 2 1 in 2.54 cm ( ) 2 = 6.98 in 2