User:Hgrobe/platetectonics
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Plate Tectonics
- Licence: CC-by (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)
- Citation: hannes.grobe@awi.de (2012) - unless an explicit citation is given.
- see also
- Animated reconstruction of plate tectonics - PALEOMAP Project, Scotese 2003, http://www.scotese.com
- Plate tectonics and geologic reconstructions - PLATES Project, http://www.ig.utexas.edu/research/projects/plates/
- Age of the lithosphere for Google Earth - http://nachon.free.fr/GE/Welcome.html
- Seismic Monitor betrieben von Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology (IRIS), Washington, USA, zeigt die aktuellen Erdbeben auf der Erde.
Die Erde
[edit]-
Die Erde ist annähernd eine Kugel (mittlerer Radius = 6370 km). Der schalenförmig Aufbau besteht aus (1) innerer fester Kern, (2) äußerer flüssiger Kern, (3) unterer Mantel, (4) oberer Mantel, (5) Erdkruste. Die "Schalen" unterscheiden sich in der chemischen Zusammensetzung und in den physikalischen Eigenschaften.
-
Diagrammatic section through the earth (Gringer (2012), Wikipedia
-
Konvektionszellen im Erdmantel bewegen die Krustenplatten. So verändert sich das Bild der Erdoberfläche im Verlauf von Millionen Jahren ständig.
-
Die Erdkruste besteht aus ozeanischer und aus kontinentaler Kruste.
-
Die Kruste besteht aus 7 großen und vielen kleinen Platten die sich mit einer Geschwindigkeit von 1-20 cm/Jahr bewegen (Plattentektonik).
-
Die Reibung an den Plattengrenzen erzeugt Erdbeben.
-
Erdbeben entstehen bis in eine Tiefe von max. 700 km. In diesem Bereich ist die Kruste spröde genug um brechen zu können.
-
Simulation der Konvektion im Mantel
-
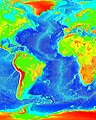
Age of the oceanic lithosphere, Müller et al. (2008) doi:10.1029/2007GC001743
-
The six stages in the life of an ocean can be named as (examples in brackets): (1) embryonic - African Rift Valley, (2) juvenile - Red Sea, (3) mature - Atlantic, (4) declining - Pacific, (5) terminal - Mediterranean Sea, (6) suturing - Himalaya
-
The drift of continents apart and together continues throughout earth history and will continue in the future. The process is called the Wilson cycle after the geophysicist John Tuzo Wilson.
Mid ocean ridge
[edit]-
Map of the Atlantic (Schott 1912-1940)
-
The Atlantic ocean floor in 1980 (NOAA/NGDC 2006) http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/image/2minrelief.html
-
Birth of an ocean: Continental crust breaks apart due to the onset of convection in the earth mantle below
Tectonic
[edit]-
Submarine vulcano in Bransfield Strait, Antarctica; Bransfield Strait is the back arc basin of an island chain
-
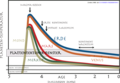
Cooling of planets after birth, only the earth remains in the plate tectonic window and thus has sufficient heat for convection to keep plate tectonic running
-
Comparing the ages of the crusts of the inner planets indicates Earth having the jungest crust. Due to plate tectonics, crust is recycled and renewed throughout geological time.
-
Section through Bransfield Strait (Antarctic Peninsula) as an example for a subduction zone with back-arc basind.
- Movie of lava flows on West Mata Volcano (35 sec.), filmed by ROV Jason in a depth of 1200 m in the Pacific Ocean between Fiji, Tonga and Samoa; Courtesy of National Science Foundation and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (2009) - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q7ignzZaYNU
Seismic
[edit]-
Seismic array used to investigate the geophysical structure of the ocean floor.
-
Diagram of the principle of a marine geophysical seismic survey
-
Air gun in the lab of a research vessel in service
-
Air gun array prepared on deck of a vessel for deployment
-
Streamer on winch
-
Seismometer at the German geophysical observatory in the Antarctic
-
An den Plattengrenzen bauen sich Spannungen auf. Wir ein bestimmter Grenzwert erreicht, entladen sich die Spannungen in Form von Erdbeben. Die erzeugten Wellen können den gesamten Erdkörper durchlaufen. Eine Aufzeichnung erfolgt mit Seismometern.
Ore deposits
[edit]-
Erzbergwerk Rammelsberg, Goslar, Harz (world heritage) - mine of exhalative ores for 1000 years (Photo: Norbert Kaiser)
-
Melierterz from Rammelsberg (15 cm Ø)
-
Hydrothermal circulation at a MOR (mid ocean ridge)
-
Sedimentary ore deposit from the Red Sea