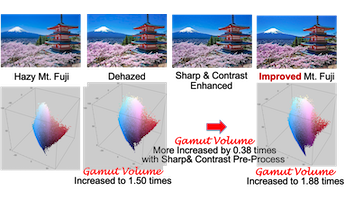
In the latter half of the 1980s, PM2.5 pollution in Beijing became a serious problem, and there were concerns about health hazards. It was expected that China's emissions must be reduced from 2013 to 2016, and the lockdown effect of Covid-19 would bring about an end, but it is still reluctant to regulate CO2 emissions. Again, in Beijing in November 2021, a visibility of 500 m or less has been observed, then road traffic is dangerous in addition to health. After that, the center of pollution has moved from India to Mongolia, and now Nepal, Qatar and Saudi Arabia. The situation is still serious in developing countries. Image restoration to remove the effects of haze and fog has been a long-standing concern of NASA, and their original Visual Servo has been put into practical use. Though the mainstream moved to the technique based on atmospheric physics. He et al.'s Dark Channel Priority (DCP) logic has had a certain effect on heavily polluted PM 2.5 scenes , but there is a limit to the restoration of detailed visibility. The observed images are affected by two spatial inhomogeneities of 1) atmospheric layer and 2) illumination. As a countermeasure, we have improved DCP process with the help of Retinex and introduced the veil coefficient as reported in CIC24. Recently, a variety of improvements in single image Dehazing, using FFA-net, BPP-net, LCA-net, or Vision-based model are in progress. However, in each case, visibility of details is still a common problem. This paper proposes an improvement in detail visibility by (1) joint sharpness-contrast preprocess and (2) adjustment in Dehaze effect with veil coefficient v. Lastly, we challenge numerical evaluation of improvement in detail visibility by the two ways of attenuation of high-frequency Fourier spectrum and the expansion rate of the color gamut.
Hiroaki Kotera, "Visibility Improvement in Air Pollution Scene by Joint Sharpness - Contrast Enhanced Dehazing" in Color and Imaging Conference, 2022, pp 85 - 91, https://doi.org/10.2352/CIC.2022.30.1.17
 Find this author on Google Scholar
Find this author on Google Scholar Find this author on PubMed
Find this author on PubMed