Gestation is the  period of time that a mammal carries her offspring, or babies, inside her body before giving birth. The length of gestation is different for each type of mammal. Larger animals usually have longer gestations than smaller animals. Human gestation, or pregnancy, lasts about nine months. An elephant’s gestation lasts about 22 months. In squirrels, gestation lasts only about six weeks.
period of time that a mammal carries her offspring, or babies, inside her body before giving birth. The length of gestation is different for each type of mammal. Larger animals usually have longer gestations than smaller animals. Human gestation, or pregnancy, lasts about nine months. An elephant’s gestation lasts about 22 months. In squirrels, gestation lasts only about six weeks.
Before birth, mammals grow inside an organ called the uterus in the mother’s belly. The uterus is a part of the body’s reproductive system. A structure called a placenta usually connects the developing baby to the uterus. The placenta brings nutrients from the mother’s body to the developing baby, or fetus.
Marsupials are mammals whose babies usually develop in a pouch after birth. Some examples are kangaroos, koalas, and opossums. Marsupials do not have true placentas. For this reason, marsupial gestation is relatively short. Even the largest type of kangaroo is born after about 40 days.
Marsupial babies are born tiny and undeveloped. Right after they are born they crawl inside a pouchlike flap of skin at the front of their mother’s body. There they continue to develop until they are ready to leave the pouch.
Placentals are mammals that have placentas during gestation. Humans, cats, dogs, deer, whales, and most other mammals are placentals. The gestation of placentals is usually longer than the gestation of marsupials. This means that the babies of placentals are born more developed than marsupial babies.
However, the babies of different placentals are born at different levels of development. Placentals also have different lengths of gestation. Horses have a gestation of about 11 months. Their babies can walk hours after birth. Chimpanzees have a gestation of about eight months. Their babies are helpless for a few months after birth.
 The period of human gestation, or pregnancy, is divided into three trimesters. Each lasts about three months.
The period of human gestation, or pregnancy, is divided into three trimesters. Each lasts about three months.
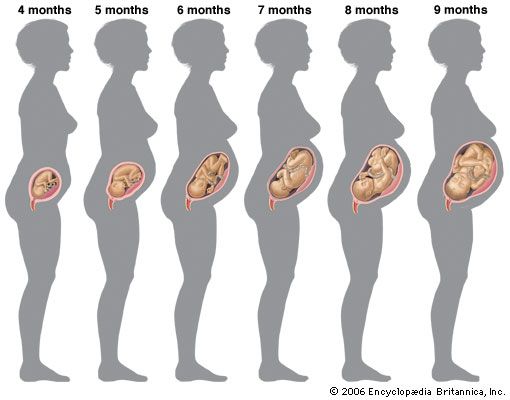 In the first trimester, the fetus develops a heartbeat and the beginnings of all the other body parts. The fetus also grows an umbilical cord, which connects it to the placenta. At three months, the fetus weighs less than 1 ounce (28 grams). In the second trimester, the fetus starts to move around in the uterus. At six months, it weighs up to 2 pounds (900 grams). In the third trimester, the baby continues to grow bigger and stronger. By the time of birth, the baby weighs about 7.5 pounds (3.5 kilograms).
In the first trimester, the fetus develops a heartbeat and the beginnings of all the other body parts. The fetus also grows an umbilical cord, which connects it to the placenta. At three months, the fetus weighs less than 1 ounce (28 grams). In the second trimester, the fetus starts to move around in the uterus. At six months, it weighs up to 2 pounds (900 grams). In the third trimester, the baby continues to grow bigger and stronger. By the time of birth, the baby weighs about 7.5 pounds (3.5 kilograms).





