Tony Evers facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Tony Evers
|
|
|---|---|

Evers in 2022
|
|
| 46th Governor of Wisconsin | |
| Assumed office January 7, 2019 |
|
| Lieutenant | Mandela Barnes Sara Rodriguez |
| Preceded by | Scott Walker |
| 26th Superintendent of Public Instruction of Wisconsin | |
| In office July 6, 2009 – January 7, 2019 |
|
| Governor | Jim Doyle Scott Walker |
| Preceded by | Elizabeth Burmaster |
| Succeeded by | Carolyn Stanford Taylor |
| Personal details | |
| Born |
Anthony Steven Evers
November 5, 1951 Plymouth, Wisconsin, U.S. |
| Political party | Democratic |
| Spouse | Kathy Evers |
| Children | 3 |
| Residence | Governor's Mansion |
| Education | University of Wisconsin, Madison (BA, MA, PhD) |
| Signature | 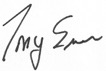 |
| Website | |
Anthony Steven Evers (/ivɜːrs/ EE-vurs, born November 5, 1951) is an American educator and politician serving as the 46th governor of Wisconsin since 2019. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as Wisconsin's Superintendent of Public Instruction from 2009 to 2019.
Born and raised in Plymouth, Wisconsin, Evers was educated at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, eventually receiving a Ph.D. After working as a teacher for several years, he became a school administrator, serving as a principal, until he assumed the office of district superintendent. Evers first ran for Superintendent of Public Instruction in 1993 and again in 2001, losing both elections. Evers was instead appointed deputy superintendent, a position he served in from 2001 to 2009. In 2009, he ran for Superintendent of Public Instruction again, this time winning. He was reelected twice, in 2013 and 2017.
On August 23, 2017, Evers announced his candidacy for governor of Wisconsin, challenging two-term Republican incumbent Scott Walker. Walker was seen as a vulnerable incumbent and had been criticized for his education policies. Evers won the Democratic primary in August 2018. Former state representative Mandela Barnes won the primary for the lieutenant governorship, becoming Evers's running mate. The pair defeated the Scott Walker-Rebecca Kleefisch ticket in the 2018 election. Evers was reelected by a larger margin in 2022.
Evers is known for his frequent use of his veto power, which is significantly greater for Wisconsin governors than for those of other U.S. states, due to his opposition to the vast majority of the Republican-controlled Wisconsin Legislature's agenda. He has used his veto power more frequently than any governor in Wisconsin history, and has used line-item veto power to rewrite Republican-authored bills.
Contents
Early life and career
Evers was born in 1951 in Plymouth, Wisconsin, the son of Jean (Gorrow) and Raymond Evers, a physician. His first job was "as a kid, scraping mold off of cheese" in Plymouth. As a young adult, Evers worked as a caregiver in a nursing home. He attended Plymouth High School. He earned bachelor's (1973), master's (1976), and doctoral degrees (1986) in educational leadership from the University of Wisconsin–Madison. He began his professional career as a teacher and media coordinator in the Tomah school district. From 1979 to 1980 he was principal of Tomah Elementary School, and from 1980 to 1984 he was principal of Tomah High School. From 1984 to 1988 Evers was superintendent of the Oakfield school district, and from 1988 to 1992 he was superintendent of the Verona school district. From 1992 to 2001 he was administrator of the Cooperative Education Service Agency (CESA) in Oshkosh.
Department of Public Instruction (2001–2019)
Evers first ran for state superintendent, a nonpartisan post, in 1993 and was defeated by John Benson. In 2001, he ran again and finished third in the primary to Elizabeth Burmaster. After her election, Burmaster appointed Evers deputy superintendent, a position he held until Burmaster was appointed president of Nicolet College. Evers served as president of the Council of Chief State School Officers and from 2001 to 2009 was Wisconsin's Deputy Superintendent of Public Instruction.
State Superintendent
Evers then ran again in 2009, this time winning. He defeated Rose Fernandez in the general election. In April 2013 Evers defeated Don Pridemore and won reelection. In 2017 Evers defeated Republican candidate Lowell Holtz, a former Beloit superintendent, with about 70% of the vote.
In 2009 Evers used government email accounts for fundraising purposes. He and another government employee were fined $250 each for soliciting campaign donations during work hours.
In October 2018, a divided federal appeals court found that Evers had violated neither the U.S. Constitution's Free Exercise Clause nor its Establishment Clause when he denied busing to an independent Catholic school because there was a nearby archdiocesan school.
Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA)
In March 2016, the United States Department of Education announced that Evers had been selected to serve on the Negotiated Rulemaking Committee for Title 1, Part A, of the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA). The committee was charged with drafting proposed regulations for two areas of ESSA.

Funding formula proposal
Evers proposed the "Fair Funding for Our Future" school finance reform plan. The plan sought to address some of the challenges with the Wisconsin school funding system and proposed changes to ensure equity and transparency in the quality of Wisconsin schools. Wisconsin Governor Scott Walker never included Evers's plan in his proposed state budgets, citing the cost.
Relations with tribal nations
As superintendent, Evers worked with the Great Lakes Inter-Tribal Council and federally recognized tribal nations in Wisconsin to begin an MOU process with each tribal nation to outline the working partnership the state seeks to establish and grow with each sovereign nation.
Sparsity aid
Sparsity aid was enacted in Wisconsin based on recommendations from Evers's Rural Schools Advisory Council. The council stressed that declining enrollment and escalating fixed costs put added pressure on small, sparsely populated districts. Since it was implemented, hundreds of school districts have benefitted from sparsity aid.
Student mental health
In 2017, Evers secured increased state investment in order to increase the number of trained professionals in schools and more funding for mental health training and cross-sector collaboration.
Governor of Wisconsin (2019–present)
Elections
2018
On August 23, 2017, Evers announced that he would seek the Democratic nomination for governor of Wisconsin in 2018. He cited his 2017 reelection as state superintendent with over 70% of the vote, as well as his criticism of Governor Walker, as key reasons for deciding to run. Evers launched his first campaign advertisement against Walker on August 28, 2017. Evers won the eight-candidate Democratic primary on August 14, 2018. On November 6, 2018, Evers narrowly defeated Walker in the general election.
2022
Evers sought reelection in 2022. His 2018 running mate, Lieutenant Governor Mandela Barnes, instead chose to run for United States Senate. In the August 2022 Democratic Primary, Evers was unopposed and Brookfield-area state representative Sara Rodriguez was nominated as his running mate. Evers and Rodriguez prevailed in the 2022 general election, defeating the Republican ticket of Tim Michels and Roger Roth.
Tenure

Republican efforts to restrict gubernatorial power
Since his election as governor, Republicans in the legislature and state supreme court have used their positions in partisan attempts to usurp powers from Evers and executive departments. This began just weeks after his election—before he took office—when the Republican-controlled legislature met in a lame-duck session and passed legislation to reduce the powers of the incoming governor and attorney general. The laws targeted Evers's authority over economic development issues, required his administration to rewrite thousands of government documents, and required the attorney general to get legislative approval before settling lawsuits. The legislature also enacted legislation to restrict voting rights, including limits on early voting in Wisconsin and restrictions on the use of student identification cards as acceptable voter identification. Walker signed all the legislation into law over Evers's objections. The move was "widely criticized as a power play" and challenged as unconstitutional in four lawsuits variously filed by Evers, other Wisconsin Democrats, and labor unions. The changes to Wisconsin voting laws were struck down by a federal district court, but later restored by the U.S. Seventh Circuit.
In addition, Walker made 82 appointments to state positions that the legislature rushed to confirm. In March 2019—shortly after the start of Evers's first term—a judge ruled that this process violated the constitution. At that time, Evers reappointed 67 of the 82 lame-duck appointees, but replaced 15 of those Walker appointed. Evers's appointments were endorsed by a Wisconsin Court of Appeals decision in April, but later that month the Wisconsin Supreme Court reinstated the 15 Walker appointees, and ultimately ruled that the legislature's actions in the lame-duck session had not been unconstitutional.
The Wisconsin Supreme Court also endorsed most of the lame-duck laws the legislature adopted, defeating lawsuits brought by the League of Women Voters and Service Employees International Union. The lawsuits largely hinged on the constitutionality of the legislature holding such votes in "extraordinary sessions"—special sessions not called by the governor. Such sessions are not explicitly authorized by the constitution or state law, so litigants contended that the acts of such sessions are not constitutional. The Wisconsin Supreme Court rejected those arguments.
Late in Evers's first term, many Walker appointees refused to leave office when their terms expired. Evers appointed replacements, but Senate Republicans did not act on the appointments. Evers challenged the holdovers in state court, and the Wisconsin Supreme Court held that appointees whose terms had expired could remain in their positions indefinitely so long as the Senate refused to confirm a replacement. The Senate also wielded the confirmation power to punish Evers appointees. The Senate has so far rejected 21 appointees since Evers took office; in the 40 years before Evers's term, the Senate had only rejected four nominees.
In Evers's second term, Republicans sought to enact constitutional amendments to further limit the governor's powers. In 2024, Wisconsin voters will be asked to vote on two amendments that would limit the governor's control over state spending. One would invalidate any spending decisions made by the governor or other agency that was not explicitly appropriated by legislation. The other would require legislative approval for usage of any federal funds sent to the state. The manner of holding these referenda—at the primary in August—is also unique; every other constitutional amendment in Wisconsin history has been voted on at a general election.
First term
In February 2019, Evers withdrew Wisconsin National Guard forces from the border with Mexico, where President Donald Trump had called for a "national emergency". Evers said, "There is simply not ample evidence to support the president's contention that there exists a national security crisis at our Southwestern border. Therefore, there is no justification for the ongoing presence of Wisconsin National Guard personnel at the border."
.....
On March 12, 2020, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Evers declared a public health emergency in the state. The next day, he ordered all schools in the state to close by March 18, with no possibility of reopening until at least April 6. On March 17, Evers instituted a statewide ban on public gatherings of more than 10 people, following an advisory from the federal government. This was expanded to a statewide "safer at home" on March 25, originally set to expire on April 25, with people allowed to leave their homes only for essential business and exercise. A poll conducted between March 24 and 29 gave Evers an approval rating of 65%, up 14% in one month, and also showed that 76% of voters approved of his handling of the pandemic.
On April 6, Evers issued an executive order to delay the state's April 7 presidential primary, as well as other coinciding elections. The move came in response to inaction by legislative Republicans to delay or otherwise modify the in-person election despite the widely perceived risk of worsening the spread of the virus if the election went ahead as planned. Evers had said on April 2 that he had no legal authority to issue such an order, and Republican leaders in the legislature used his own words against him when challenging the order in court. A conservative majority on the Wisconsin Supreme Court blocked the executive order just hours after it was issued on April 6, and the election took place as scheduled on April 7.
On April 16, Evers ordered an extension of the statewide lockdown to May 26, and mandated all schools in the state to remain closed through the end of the academic year. The legislature promptly sued to block the order, and the Wisconsin Supreme Court's conservative majority ultimately struck it down on May 13, following the expiration of Evers's initial state of emergency. Evers responded to the suit by accusing legislative Republicans of a "power grab", and said they cared more about political power than people's lives. Republicans have called the extension an "abuse of power".
On April 20, Evers announced a recovery plan called the "Badger Bounce Back", laying out details of his plan for reopening Wisconsin's economy gradually as the pandemic subsides. The plan called for daily death tolls from the virus to drop for 14 continuous days before "phase one" could be initiated.
On July 30, Evers issued a statewide mask mandate in a new attempt to curb the increasing spread of the virus, declaring a new state of emergency in order to do so. As with prior actions Evers took to tackle the pandemic, Republicans promptly sued, arguing that he had overstepped his power. This was despite the fact that Republicans in the legislature had the power to simply terminate the new state of emergency by a majority vote. No attempt was made at this until February 2021, when Evers countered by issuing another state of emergency.
On August 24, 2020, Evers deployed the Wisconsin National Guard to Kenosha following riots that occurred in the aftermath of the shooting of Jacob Blake. Looting, damage and destruction to vehicles, businesses and public facilities such as some local schools, the Dinosaur Discovery Museum and a public library were reported in Kenosha during the unrest. He also issued a statement denouncing the excessive use of force by police and invoking the names of African Americans killed by law enforcement. Evers said, "While we do not have all of the details yet, what we know for certain is that he is not the first Black man or person to have been shot or injured or mercilessly killed at the hands of individuals in law enforcement in our state or our country."
Evers also responded to the shooting by calling Wisconsin state lawmakers into a special session to pass legislation addressing police brutality.
On March 31, 2021, the Wisconsin Supreme Court struck down Evers's mask mandate in a 4–3 ruling, split along conservative-liberal ideological lines, with the court ruling against Evers's argument that the changing nature of the pandemic justified multiple states of emergency.
On April 30, 2021, Evers sought $1.6 billion in federal funds to expanded access to Wisconsin's Medicaid program. ..... Republicans in the state legislature blocked all the proposals.
Second term
After Evers's reelection in 2022, the legislature had to come to terms with Evers over the languishing issue of revenue for local governments. The problem had been created by two items in Scott Walker's 2011 "budget reforms": first, the formula for sharing state tax revenue to local governments had been adjusted to artificially create a state budget surplus by slowly starving municipalities. Second, local governments had been restricted from raising their own revenue through new sales taxes. After a decade under the Walker policies, local revenue was becoming a statewide crisis as shared revenue to municipalities had fallen considerably as a percentage of the revenue collected. Municipalities of all sizes were struggling to make their budgets, with many threatening deep cuts to police and other vital services.
Evers and the legislature managed to compromise on shared revenue in 2023 Wisconsin Act 12, revising the formula to give an average boost of about 36% to the shared revenue for each municipality. Municipalities were also granted additional flexibility to raise new revenue through sales taxes.
Evers also secured another victory for local government funding in the 2023 budget through use of his line-item veto. Wisconsin has one of the most extensive line-item veto powers in the country, with governors enabled to delete specific words in order to change the meaning of a sentence or whole section of law. By striking a few words, Evers increased the limit under which school districts could request additional tax levee by referenda. In that budget, he also vetoed an income tax cut for the top two brackets of Wisconsin earners, and vetoed an attempt to condense Wisconsin's four income tax brackets into three.
Later that year, Evers and the legislature also compromised on a funding package for American Family Field, as the Milwaukee Brewers and Major League Baseball had begun threatening that Milwaukee could lose the team if improvements were not made to the stadium.
Possibly the most important development of Evers's second term was the election of Janet Protasiewicz as justice of the Wisconsin Supreme Court, giving liberals a majority on the court for the first time since 2008. This led to Evers's long-sought abolition of the 2011 legislative gerrymander, creating the possibility that the 2024 legislative elections could produce a legislature that approximately reflects the popular vote.
Political positions
Evers has said his top priorities are improving the Wisconsin public school system, making health care more affordable and fixing Wisconsin's roads and bridges.
Education
Evers supports directing more funding towards K-12 education and would like to work with Republicans to do more to help underperforming schools. He would like to expand Pre-K education to all students and continue the freeze of the in-state tuition price for higher education.
Gerrymandering
..... In January 2020, he created a nonpartisan redistricting commission by executive order with the intent of drawing an alternative map proposal for post-2020 census redistricting to counter the proposal the Republican-controlled legislature has said it will put forward if the issue ends up in the state's court system, as it has under past periods of divided government in Wisconsin.
Gun control
Evers strongly supports universal background checks for gun purchases. He has also supported an extreme risk protection order act, commonly known as a "red flag law", which would permit loved ones or police to petition to have an individual's guns taken away if a judge deems them a risk to themselves or others.
Health care
Evers has said that Scott Walker's decisions regarding health care in Wisconsin led to higher insurance premiums for residents. He has pointed out that Minnesota accepted a Medicaid expansion and has been more proactive about healthcare overall, resulting in 47% lower insurance premiums than Wisconsin's. Evers supports legislation that would protect residents from being charged higher costs for health insurance due to old age or preexisting conditions. He also supports allowing children to stay on their parents' health insurance plans until the age of 26. He plans to remove Wisconsin from a national lawsuit that seeks to overturn the Affordable Care Act.
Immigration
Evers supports permitting undocumented immigrants living in Wisconsin to obtain driver's licenses, and has called this position "common sense".
In December 2019, in response to Trump's executive order requiring states' consent for refugee resettlement, Evers sent the administration a letter stating that Wisconsin would accept refugees, calling them "part of the fabric of [the] state", and criticizing Trump's refugee policies as "overly cumbersome and inappropriate". In February 2020, Evers sent U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo a letter to asking him to halt negotiations with the government of Laos regarding deportations of Wisconsin's Hmong refugee population, who had previously been protected from deportation due to a long record of human rights violations in Laos.
Income tax
During the 2018 campaign, Evers proposed to cut income tax by 10% for Wisconsin residents who earn less than $100,000 per year. He also pledged not to raise taxes, saying, "I'm planning to raise no taxes." But Evers's first budget proposal in 2019 increased taxes by $1.3 billion, an amount he called "small." PolitiFact rated this change of position a "full flop." His second budget proposed a $1 billion tax increase. Evers fulfilled his proposal to cut income taxes by 10%, which was funded by raising taxes on manufacturers and farmers with a turnover of over $300,000 per year.
LGBT rights
In June 2019, Evers issued an executive order to fly the rainbow flag at Wisconsin's Capitol Building for Pride month, making it the first time the rainbow flag had ever flown above the capitol.
Roads
Evers has cited studies showing that Wisconsin has some of the nation's worst roads. He ran for governor on a promise to focus on improving roads and bridges, and has said he is open to imposing a gas tax to fund the projects.
Personal life
Evers is married to his high-school sweetheart, Kathy. They have three adult children and nine grandchildren. Evers had esophageal cancer before undergoing intensive surgery in 2008.
Electoral history
Superintendent of Public Instruction (2001)
| Wisconsin Superintendent of Public Instruction Election, 2001 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
| Nonpartisan Primary, February 20, 2001 | |||||
| Nonpartisan politician | Linda Cross | 58,258 | 23.18% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | Elizabeth Burmaster | 55,327 | 22.01% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | Tony Evers | 45,575 | 18.13% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | Jonathan Barry | 36,135 | 14.38% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | Tom Balistreri | 33,531 | 13.34% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | Dean Gagnon | 15,261 | 6.07% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | Julie Theis | 6,783 | 2.70% | ||
| Scattering | 458 | 0.18% | |||
| Total votes | 251,328 | 100.0% | |||
Superintendent of Public Instruction (2009, 2013, 2017)
| Wisconsin Superintendent of Public Instruction Election, 2009 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
| Nonpartisan Primary, February 17, 2009 | |||||
| Nonpartisan politician | Tony Evers | 89,883 | 34.99% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | Rose Fernandez | 79,757 | 31.04% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | Van Mobley | 34,940 | 13.60% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | Todd Price | 28,927 | 11.26% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | Lowell Holtz | 22,373 | 8.71% | ||
| Scattering | 1,431 | 0.18% | +0.06% | ||
| Total votes | 256,909 | 100.0% | +7.89% | ||
| General Election, April 7, 2009 | |||||
| Nonpartisan politician | Tony Evers | 439,248 | 57.14% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | Rose Fernandez | 328,511 | 42.74% | ||
| Scattering | 905 | 0.12% | +0.02% | ||
| Total votes | 768,664 | 100.0% | +6.22% | ||
| Wisconsin Superintendent of Public Instruction Election, 2013 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
| General Election, April 2, 2013 | |||||
| Nonpartisan politician | Tony Evers (incumbent) | 487,030 | 61.15% | +4.01% | |
| Nonpartisan politician | Don Pridemore | 308,050 | 38.67% | ||
| Scattering | 1,431 | 0.18% | +0.06% | ||
| Plurality | 178,980 | 22.47% | |||
| Total votes | 796,511 | 100.0% | +3.62% | ||
| Wisconsin Superintendent of Public Instruction Election, 2017 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
| Nonpartisan Primary, February 21, 2017 | |||||
| Nonpartisan politician | Tony Evers (incumbent) | 255,552 | 69.43% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | Lowell E. Holtz | 84,398 | 22.93% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | John Humphries | 27,066 | 7.35% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | Rick Melcher (Write-in) | 377 | 0.10% | ||
| Scattering | 703 | 0.19% | |||
| Total votes | 368,096 | 100.0% | |||
| General Election, April 4, 2017 | |||||
| Nonpartisan politician | Tony Evers (incumbent) | 494,793 | 69.86% | +7.71% | |
| Nonpartisan politician | Lowell E. Holtz | 212,504 | 30.00% | ||
| Nonpartisan politician | Rick Melcher | 62 | 0.01% | ||
| Scattering | 930 | 0.13% | -0.04% | ||
| Plurality | 282,289 | 39.86% | +17.39% | ||
| Total votes | 708,289 | 100.0% | -11.08% | ||
Wisconsin Governor (2018, 2022)
| Wisconsin Gubernatorial Election, 2018 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
| Democratic Party Primary, August 14, 2018 | |||||
| Democratic | Tony Evers | 225,082 | 41.77% | ||
| Democratic | Mahlon Mitchell | 87,926 | 16.32% | ||
| Democratic | Kelda Roys | 69,086 | 12.82% | ||
| Democratic | Kathleen Vinehout | 44,168 | 8.20% | ||
| Democratic | Mike McCabe | 39,885 | 7.40% | ||
| Democratic | Matt Flynn | 31,580 | 5.86% | ||
| Democratic | Paul Soglin | 28,158 | 5.23% | ||
| Democratic | Andy Gronik | 6,627 | 1.23% | ||
| Democratic | Dana Wachs | 4,216 | 0.78% | ||
| Democratic | Josh Pade | 1,908 | 0.35% | ||
| Write-ins | 221 | 0.04% | |||
| Total votes | 537,719 | 100.0% | +72.29% | ||
| General Election, November 6, 2018 | |||||
| Democratic | Tony Evers | 1,324,307 | 49.54% | +2.95% | |
| Republican | Scott Walker (incumbent) | 1,295,080 | 48.44% | -3.82% | |
| Libertarian | Phil Anderson | 20,255 | 0.76% | N/A | |
| Independent | Maggie Turnbull | 18,884 | 0.71% | N/A | |
| Green | Michael White | 11,087 | 0.41% | N/A | |
| Independent | Arnie Enz | 2,745 | 0.10% | N/A | |
| Write-ins | 980 | 0.04% | -0.02% | ||
| Total votes | 2,673,308 | 100.0% | +10.91% | ||
| Democratic gain from Republican | |||||
| Wisconsin Gubernatorial Election, 2022 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
| General Election, November 8, 2022 | |||||
| Democratic | Tony Evers (incumbent) | 1,358,774 | 51.15% | +1.61% | |
| Republican | Tim Michels | 1,268,535 | 47.75% | -0.69% | |
| Independent | Joan Ellis Beglinger | 27,198 | 1.02% | N/A | |
| Write-ins | 1,983 | 0.04% | +0.04 | ||
| Democrat hold | |||||
See also
 In Spanish: Tony Evers para niños
In Spanish: Tony Evers para niños
 In Spanish: Tony Evers para niños
In Spanish: Tony Evers para niños
- Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction
- List of superintendents of public instruction of Wisconsin


