Verbs in English
Contents
Are you just starting to learn English? Or maybe you're an advanced learner looking to improve? By mastering verbs, you can easily give your English more action, as well as make your sentences more interesting. In this article, you'll find verb definition and many useful references to get started!
What is a Verb?
Verbs are among the most important parts of any language, and English verbs are no exception. The definition of a verb is “a word that we use to talk about actions, events, or states.” This can include physical actions (such as “run” or “swim”), mental activities (such as “think” or “believe”), or even emotional responses (such as “laugh” or “cry”).
There are many different types of verbs, each with their unique characteristics and uses. For instance, action verbs are typically used to describe physical actions. In contrast, linking verbs help connect the subject of a sentence to other information, such as an adjective or noun. Modal verbs are used to express possibility, necessity, and obligation.
Verb meaning can be tricky to navigate, so let's start with the types you'll find in sentences!
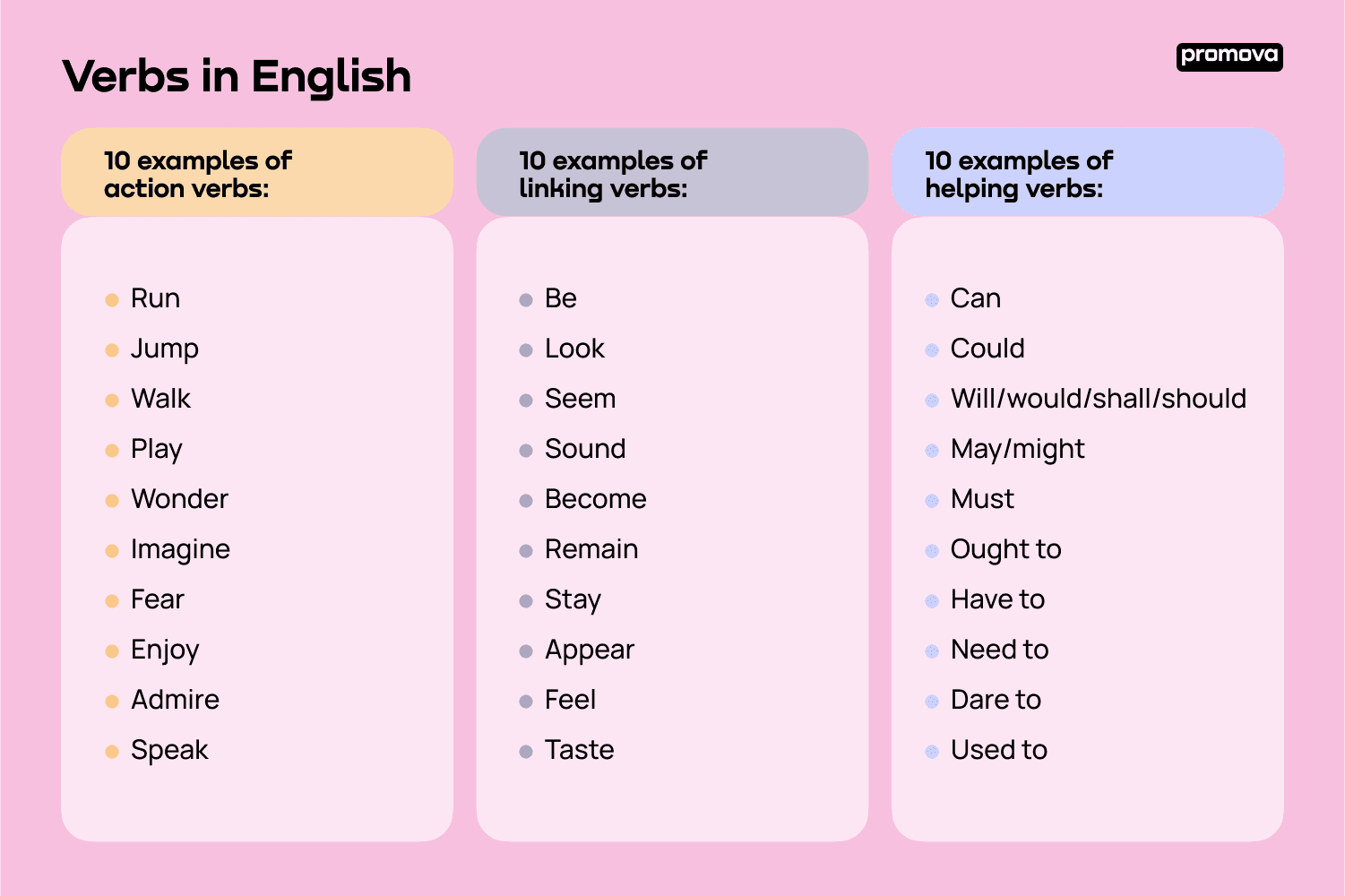
3 Types of Verbs in English
There are 3 different kinds of verbs: action verbs, linking verbs, and helping (auxiliary) verbs. See all these types of verbs with examples below:
Action Verbs
Action verbs are a common type of verbs, always describing an action someone or something is doing. Action verbs are verbs that show us what someone is doing, have done, will do, or can do. Main verb examples include “run,” “jump,” “walk,” and “play.”
Action verbs are a great way to inject life into your sentences. Not only can they be used to describe physical activities, but they can also be used to talk about mental and emotional states. For instance, verbs like “wonder,” “imagine,” or “fear” can be used to describe a person's mental state, while verbs like “enjoy” or “admire” can be used to describe emotional responses.
Action verbs are a great way to add life and energy to your writing. They can be used in any tense, from the present simple (“I walk”) to the future perfect continuous (“I will have been walking”). You can also use them with adverbs or adjectives for added impact. For example, “He ran quickly across the field,” or “She smiled sadly at him.”
10 examples of action verbs:
- Run
- Jump
- Walk
- Play
- Wonder
- Imagine
- Fear
- Enjoy
- Admire
- Speak
Linking Verbs
Linking verbs are verbs that connect the subject of a sentence to other information, such as an adjective or noun. This type of verb is also known as a “state-of-being verb” because it does not describe any action but rather expresses a state of being. It can be used to express physical attributes (such as “be” or “look”), mental states (such as “seem”), or emotions (such as “sound”).
One common mistake that English learners often make is using linking verbs like “look“ or “seem“ incorrectly as if they were action verbs. For example, saying “I look the phone” or “I seem at my friend” is incorrect because these verbs do not express direct actions. Instead, linking verbs like “look“ or “seem“ connect the subject to a description or state of being. The correct usage would be, “I look at the phone” (where “look“ requires the preposition "at") or “She seems tired” (where “seems“ links the subject to an adjective, “tired“). These verbs describe states or conditions, not direct actions.
Other examples of linking verbs include verbs like “become,” which is often used to describe change over time; verbs like “remain” and “stay,” which are often used when talking about a location or place; and verbs like “seem” and “appear,” which are often used to talk about one's emotional state.
10 examples of linking verbs:
- Be
- Look
- Seem
- Sound
- Become
- Remain
- Stay
- Appear
- Feel
- Taste
Helping Verbs
Helping verbs are an important part of the English language and can be used to express possibility, necessity, and obligation. They modify other verbs in a sentence by expressing how likely something is to happen or how necessary it is for something to occur. Examples of these verbs include “can,” “could,” “will,” “would,” “shall,” and “should.” By using these verbs correctly, you can make your sentences more precise and accurate.
Unlike verbs like “run” or “jump,” which describe actions rooted in reality, helping verbs often express possibilities or probabilities. For instance, verbs like “may” and “might” can be used to talk about things that may happen in the future, verbs like “could” and “would” can be used to describe things that are possibly true in the present or past, verbs like “must” and “shall” can be used in formal writing to express obligation, and verbs like “should” can be used to talk about desirable behavior.
Using helping verbs correctly can help you to communicate more effectively, allowing you to say exactly what you mean. For example, if you want to say that something is possible or likely to happen, you could use verbs like “may” and “might”; if you wanted to express obligation or desirability, verbs like “must” or “should” would be more appropriate.
10 examples of helping verbs:
- Can
- Could
- Will/would/shall/should
- May/might
- Must
- Ought to
- Have to
- Need to
- Dare to
- Used to
8
Using Verbs in Sentences
When using verbs in sentences, it is important to pay attention to verb tense and verb form. Verb tense refers to when an action occurred (past, present, future), while verb form refers to the verb itself (action verb, linking verb, helping verb).
- I ran quickly away from the scary situation
- She smiles at me and nods to the beat with the music.
- We have been walking for hours, our feet growing increasingly sore with each step.
- He must have seen the look on my face because he nodded back.
- I tried to come to school yesterday, but things got in the way.
As you can see, verbs can also tell you when that action happened, like in the past, present, or future. This is verb tense. When using verbs in sentences, it's important to pay attention to verb tense and verb form. Examples of verb tenses above are "ran" (past), "smiles" (present), "have been walking" (present perfect), and "tried" (past).
Let's get into verb grammar in more detail now!
Verbs in the Present
Present Simple
The present simple verb tense is among the most commonly used verb tenses in English, and it is used to express actions that happen regularly, habits, or general truths. It consists of a verb in its base form (e.g., “I jump”) or with an auxiliary verb such as “do” (e.g., “I do jump”). The present simple can be used for both affirmative statements ("He jumps") and negative statements ("He does not jump").
For example, "She speaks Spanish" indicates a habitual action, while "The sun rises every morning" expresses a universal truth about nature. Other common uses for the present simple include giving instructions, making predictions, and expressing wishes or desires.
Present Continuous
The present continuous verb tense helps talk about things happening now. It includes verbs ending in "-ing," like “jumping.” For example, "I am jumping" means you are jumping now.
Other common uses of the present continuous verb tense include describing ongoing plans or actions ("We are jumping because it's fun"), expressing your feelings at the moment ("I am feeling nervous"), and indicating a change in state or status ("He is becoming more confident").
Present Perfect
The present perfect verb tense helps us talk about things that occurred in the past but are still connected to the present. It usually includes a verb ending with "-ed" or an auxiliary verb like "have." For example, "She has spoken Spanish for years" shows something that started in the past and continues in the present.
Other common uses of the present perfect verb tense include talking about finished actions ("I have jumped"), ongoing past experiences ("I have been jumping for hours"), and past events that still affect us in the present ("I have been jumpy all day").
Verbs in the Past
Past Simple
The past simple verb tense helps us talk about things that happened in the past. To use it, we add "-ed" to the verb (like "jumped") or use an auxiliary verb like "had." For example, "I jumped over the fence" means you did this action in the past. You can also use it for finished actions like "I had jumped over a million fences".
Other common uses of the past simple verb tense include talking about major events in our lives ("I jumped over a fence when I was 5 years old") and expressing what we did in the past, even if it's not relevant to the present ("I have jumped over many different fences, but I don't do it anymore").
Past Continuous
The past continuous verb tense is used to talk about actions that were happening in the past. It usually has a verb ending with "-ing," like "jumping." For example, "I was jumping" means you were jumping at some point in the past. You can also use it for things that had been happening for a while, like "I had been jumping for hours".
Other common uses of the past continuous verb tense include describing ongoing plans or actions that happened in the past, expressing your feelings during a certain time, and indicating a change in state or status from something that happened before.
Past Perfect
The past perfect verb tense is used to talk about events that happened before a particular point in the past. It usually includes a verb ending with "-ed" or an auxiliary verb like "had." For example, "She had spoken Spanish for years" shows something that started and ended in the past.
The past perfect verb tense can be used for talking about finished actions ("I had jumped"), ongoing experiences that ended at some point in the past ("I had been jumping for hours"), as well as expressing what we did in the past, even if it's not relevant to the present anymore ("I have jumped over many different fences, but I don't do it anymore"). Additionally, you can use it to indicate a change in state or status from something that happened before ("He had become more confident").
Verbs in the Future
Future Simple
The future simple verb tense is used to talk about things that will happen. It describes actions that will happen, and it often uses “will” followed by the base form of the verb (e.g., “will jump,” “will speak”)." For example, you can say “I will jump” to mean that you are going to jump in the future. You can also use it for things that will be happening for a while, like “I will have been jumping for hours.”
Other common uses of the future verb tense include talking about things we plan to do (“I will jump tomorrow“), expressing our feelings about something that will happen in the future (“I am excited to run tomorrow“), and indicating a change in state or status from something that will happen before (“He will become more confident“).
Future Continuous
The future continuous verb tense helps us talk about things that will be happening in the future. For example, you can say "I will be jumping" to mean that you are going to be jumping in the future. You can also use it for things that will go on for a while, like "I will have been jumping for hours."
Other common uses of the future verb tense include talking about what we expect to happen in the future ("I am expecting to jump tomorrow"), expressing our feelings about something that will happen in the future ("I am looking forward to jumping tomorrow") and indicating a change in state or status from something that will happen before ("He is expected to become more confident").
Future Perfect
The future perfect verb tense helps us talk about events that will have happened before a particular point in the future. It usually includes a verb ending with “-ed” or an auxiliary verb like “will have.” For example, "She will have spoken Spanish for years" shows something that will start and end in the future.
The future perfect verb tense can be used for talking about finished actions ("I will have jumped"), ongoing experiences that will end at some point in the future ("I will have been jumping for hours") as well as expressing what we expect to happen before a particular point in the future ("I think she will have become more confident").
Summary
Verbs are essential for expressing yourself in English and can be used to talk about the past, present, and future. We discussed verbs examples from each verb tense, including the past simple, past continuous, past perfect, future simple, future continuous, and future perfect verb tenses.
From talking about finished actions ("I had jumped") to ongoing experiences that will end at some point in the future ("I will have been jumping for hours"), verbs are versatile tools that allow us to communicate our thoughts more effectively. With practice and a better understanding of verb usage, you can confidently express your ideas!


Comments