Latest Blogs
Winter Lung Health: How Dry, Cold Air Impacts Your Airways
As the temperature drops and winter sets in, the dry, frigid air can take a toll on your respiratory system. Winter lung health is a critical concern for many people, especially those with pre-existing conditions like asthma or COPD. Understanding how cold weather affects your airways is crucial for maintaining optimal lung health in winter. In this article, we'll explore the impact of winter on your lungs, common respiratory issues, and provide practical winter lung health tips to help you breathe easier during the colder months. Understanding the Impact of Winter on Your Airways The cold, dry air of winter can have several adverse effects on your respiratory system. When you breathe in this air, it can dry out the mucous membranes in your nose and throat, reducing their ability to filter out irritants, dust, and germs. This makes you more susceptible to winter respiratory infections like colds, flu, and sinusitis. Additionally, cold air can cause the airways to narrow and become irritated, leading to coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. This is particularly problematic for people with asthma or COPD, as their airways are already sensitive and inflamed. Common Winter Lung Issues Several respiratory problems are more prevalent during the winter months. Here are some of the most common ones: Asthma: Cold air is a known trigger for asthma flare-ups. The dry, frigid air can irritate the airways, causing them to swell and produce excess mucus. This can lead to coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing. Bronchitis: Both acute and chronic bronchitis can worsen in winter. The cold air can irritate the bronchial tubes, causing inflammation and increased mucus production. Symptoms may include a persistent cough, chest congestion, and shortness of breath. Pneumonia: While pneumonia is caused by a viral or bacterial infection, cold weather can exacerbate symptoms. Breathing in cold air can irritate the lungs, leading to inflammation and fluid buildup. Signs of pneumonia include fever, chills, cough with mucus, and difficulty breathing. COPD: People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) are particularly vulnerable in winter. The cold air can cause the airways to constrict, making it harder to breathe. COPD flare-ups are more common during this season, leading to increased coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Tips to Protect Your Lungs in Winter Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to safeguard your lungs and promote optimal winter respiratory health. Here are some practical winter lung health tips: Use a humidifier: Dry indoor air can irritate your airways. Using a humidifier to maintain a humidity level between 30 and 50% can help keep your nasal passages and throat moist. Just be sure to clean the humidifier regularly to prevent mould growth. Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps thin out mucus, making it easier to clear from your lungs. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water per day. Wear a scarf over your mouth and nose: When going outside in cold weather, cover your mouth and nose with a scarf or cold weather mask. This helps warm and humidify the air you breathe in, reducing irritation to your airways. Avoid sudden temperature changes: Going from a warm, humid environment to a cold, dry one can shock your lungs. Try to gradually transition between temperatures to minimise the impact on your airways. Exercise indoors: While outdoor exercise is great, frigid air can trigger respiratory symptoms. During the winter months, consider exercising indoors where the air is warmer and more humid. Role of Nutrition in Lung Health During Winter What you eat can also play a role in supporting your winter lung health. Certain foods are particularly beneficial for respiratory wellness: Apples: Rich in antioxidants and flavonoids, apples can help reduce inflammation in the lungs and protect against oxidative stress. Leafy greens: Vegetables like spinach, kale, and collard greens are packed with vitamins and minerals that support lung function. They also contain chlorophyll, which helps oxygenate the blood. Fatty fish: Cold-water fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids. These healthy fats have anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce lung inflammation and improve airway function. Ginger: This spicy root has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Ginger may help relax the airways, reduce lung damage, and improve breathing. Conclusion Winter can be a challenging time for respiratory health, but understanding how cold, dry air impacts your airways is the first step in protecting your lungs. By implementing practical winter lung health tips, nourishing your body with lung-supportive foods, and working with your healthcare provider to manage any underlying conditions, you can breathe easier all season long. At Metropolis Healthcare, we're committed to providing accurate diagnostic testing and personalised care to support your respiratory wellness. If you have concerns about your lung health this winter, our team of experts is here to help. From at-home sample collection to advanced laboratory analysis, we offer convenient, reliable services to keep you informed and empowered on your health journey. FAQs Can cold air permanently damage your lungs? While cold air itself doesn't typically cause permanent lung damage, repeated exposure can worsen existing respiratory conditions like asthma and COPD. Over time, this can lead to long-term complications if not properly managed. Why does breathing cold air hurt my chest? Breathing in cold, dry air can irritate the airways and cause them to narrow. This can lead to coughing, wheezing, and a feeling of tightness or pain in the chest. The discomfort is usually temporary and subsides once you're back in a warmer environment. How can I protect my lungs in cold weather? Some key winter lung health tips include using a humidifier, staying hydrated, covering your mouth and nose outside, avoiding sudden temperature changes, and exercising indoors. Additionally, eating a lung-healthy diet and managing any existing respiratory conditions can help safeguard your lungs in winter. When to see a doctor? If you experience severe or worsening respiratory symptoms like shortness of breath, wheezing, or a persistent cough, it's important to consult your doctor. People with pre-existing lung conditions like asthma or COPD should work closely with their healthcare provider to manage flare-ups and adjust medications as needed during the winter months. As the temperature drops and winter sets in, the dry, frigid air can take a toll on your respiratory system. Winter lung health is a critical concern for many people, especially those with pre-existing conditions like asthma or COPD. Understanding how cold weather affects your airways is crucial for maintaining optimal lung health in winter. In this article, we'll explore the impact of winter on your lungs, common respiratory issues, and provide practical winter lung health tips to help you breathe easier during the colder months. Understanding the Impact of Winter on Your Airways The cold, dry air of winter can have several adverse effects on your respiratory system. When you breathe in this air, it can dry out the mucous membranes in your nose and throat, reducing their ability to filter out irritants, dust, and germs. This makes you more susceptible to winter respiratory infections like colds, flu, and sinusitis. Additionally, cold air can cause the airways to narrow and become irritated, leading to coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. This is particularly problematic for people with asthma or COPD, as their airways are already sensitive and inflamed. Common Winter Lung Issues Several respiratory problems are more prevalent during the winter months. Here are some of the most common ones: Asthma: Cold air is a known trigger for asthma flare-ups. The dry, frigid air can irritate the airways, causing them to swell and produce excess mucus. This can lead to coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing. Bronchitis: Both acute and chronic bronchitis can worsen in winter. The cold air can irritate the bronchial tubes, causing inflammation and increased mucus production. Symptoms may include a persistent cough, chest congestion, and shortness of breath. Pneumonia: While pneumonia is caused by a viral or bacterial infection, cold weather can exacerbate symptoms. Breathing in cold air can irritate the lungs, leading to inflammation and fluid buildup. Signs of pneumonia include fever, chills, cough with mucus, and difficulty breathing. COPD: People with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) are particularly vulnerable in winter. The cold air can cause the airways to constrict, making it harder to breathe. COPD flare-ups are more common during this season, leading to increased coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Tips to Protect Your Lungs in Winter Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to safeguard your lungs and promote optimal winter respiratory health. Here are some practical winter lung health tips: Use a humidifier: Dry indoor air can irritate your airways. Using a humidifier to maintain a humidity level between 30 and 50% can help keep your nasal passages and throat moist. Just be sure to clean the humidifier regularly to prevent mould growth. Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps thin out mucus, making it easier to clear from your lungs. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water per day. Wear a scarf over your mouth and nose: When going outside in cold weather, cover your mouth and nose with a scarf or cold weather mask. This helps warm and humidify the air you breathe in, reducing irritation to your airways. Avoid sudden temperature changes: Going from a warm, humid environment to a cold, dry one can shock your lungs. Try to gradually transition between temperatures to minimise the impact on your airways. Exercise indoors: While outdoor exercise is great, frigid air can trigger respiratory symptoms. During the winter months, consider exercising indoors where the air is warmer and more humid. Role of Nutrition in Lung Health During Winter What you eat can also play a role in supporting your winter lung health. Certain foods are particularly beneficial for respiratory wellness: Apples: Rich in antioxidants and flavonoids, apples can help reduce inflammation in the lungs and protect against oxidative stress. Leafy greens: Vegetables like spinach, kale, and collard greens are packed with vitamins and minerals that support lung function. They also contain chlorophyll, which helps oxygenate the blood. Fatty fish: Cold-water fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids. These healthy fats have anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce lung inflammation and improve airway function. Ginger: This spicy root has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Ginger may help relax the airways, reduce lung damage, and improve breathing. Conclusion Winter can be a challenging time for respiratory health, but understanding how cold, dry air impacts your airways is the first step in protecting your lungs. By implementing practical winter lung health tips, nourishing your body with lung-supportive foods, and working with your healthcare provider to manage any underlying conditions, you can breathe easier all season long. At Metropolis Healthcare, we're committed to providing accurate diagnostic testing and personalised care to support your respiratory wellness. If you have concerns about your lung health this winter, our team of experts is here to help. From at-home sample collection to advanced laboratory analysis, we offer convenient, reliable services to keep you informed and empowered on your health journey. FAQs Can cold air permanently damage your lungs? While cold air itself doesn't typically cause permanent lung damage, repeated exposure can worsen existing respiratory conditions like asthma and COPD. Over time, this can lead to long-term complications if not properly managed. Why does breathing cold air hurt my chest? Breathing in cold, dry air can irritate the airways and cause them to narrow. This can lead to coughing, wheezing, and a feeling of tightness or pain in the chest. The discomfort is usually temporary and subsides once you're back in a warmer environment. How can I protect my lungs in cold weather? Some key winter lung health tips include using a humidifier, staying hydrated, covering your mouth and nose outside, avoiding sudden temperature changes, and exercising indoors. Additionally, eating a lung-healthy diet and managing any existing respiratory conditions can help safeguard your lungs in winter. When to see a doctor? If you experience severe or worsening respiratory symptoms like shortness of breath, wheezing, or a persistent cough, it's important to consult your doctor. People with pre-existing lung conditions like asthma or COPD should work closely with their healthcare provider to manage flare-ups and adjust medications as needed during the winter months.
Folate vs Folic Acid: What's the Difference and Why It Matters
Folate and folic acid are two terms which are often used interchangeably when referring to vitamin B9, an essential nutrient for human health. However, while both play similar roles in the body, there are some key differences between folate and folic acid that are important to understand. This article delves into the key distinctions between folate and folic acid, their respective health benefits, and why getting enough of this vitamin is crucial for everyone, especially women who are pregnant or planning to conceive. What Are Folate and Folic Acid? Before diving into the folate vs. folic acid comparison, let's first define each: Folate is the naturally occurring form of vitamin B9 found in various plant and animal foods. Good sources include leafy green vegetables, citrus fruits, beans, and liver. Folic acid is the synthetic form of vitamin B9 used in supplements and added to fortified foods like breakfast cereals, breads, and pastas. It is more shelf-stable and bioavailable compared to natural folate. Both folate and folic acid are converted in the body to the metabolically active form called levomefolic acid or 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF). This is the form that can be used by cells for critical functions like DNA synthesis, red blood cell production, and homocysteine metabolism. Key Differences Between Folate and Folic Acid While folate and folic acid ultimately serve the same purpose in the body, there are some notable differences between folate and folic acid: Source: Folate is naturally present in foods, while folic acid is an artificially produced compound. Bioavailability: Folic acid is more readily absorbed and bioavailable compared to food folate. The body converts about 85% of folic acid into the active form, versus only 50% of folate from natural sources. Tolerance: Some people have a genetic variation (MTHFR polymorphism) that reduces their ability to convert folic acid to the active form. For them, high doses of folic acid may actually be harmful. Natural folate does not pose this risk. Fortification: Many countries, including India, have mandatory or voluntary folic acid fortification of certain foods to help prevent birth defects. Natural folate is not used for fortification. Understanding these key differences between folate and folic acid can help you make informed choices about the best sources of vitamin B9 for your individual needs. Health Benefits of Folate and Folic Acid Folate The health benefits of getting enough natural folate from your diet include: Supporting red blood cell production and preventing folate-deficiency anemia Reducing the risk of certain cancers, including colorectal cancer Promoting brain health and lowering the risk of depression and dementia Helping to regulate homocysteine levels, an amino acid linked to heart disease Folic Acid Folic acid supplementation is particularly important in certain situations: Pregnancy: Adequate folic acid intake (400-800 mcg/day) starting at least one month before conception and continuing through the first trimester significantly reduces the risk of neural tube birth defects like spina bifida and anencephaly. This is why folic acid vs folate during pregnancy is an important consideration. Folate deficiency: People with digestive disorders, alcoholism, or eating disorders that impair folate absorption may benefit from folic acid supplements to prevent deficiency. Medication interactions: Some drugs like methotrexate and anti-epileptic medications can interfere with folate metabolism. Folic acid supplements may be recommended to counteract these effects. Why Does the Difference Matter? You may be wondering, with all the similarities in function, does the whole folate vs. folic acid debate really matter? In most cases, both forms can fulfil your vitamin B9 requirements. However, there are some important reasons to understand the distinction: If you have the MTHFR gene variation, you may do better with natural folate or a special form of folic acid (L-methylfolate) to avoid any negative effects from unmetabolized folic acid buildup. Focusing on folate-rich foods helps ensure you're also getting other vital nutrients, fibre, and antioxidants for overall health. A balanced diet is always preferable to relying solely on supplements. Being aware of the differences between folate and folic acid allows you to make educated choices about supplements and fortified foods, especially during pregnancy when folic acid vs. folate intake is critical. What Is the Healthiest Source of Vitamin B9? The optimal approach to getting enough vitamin B9 is to include both natural folate and folic acid in your diet. Regularly eat a variety of folate-rich foods like spinach, asparagus, Brussels sprouts, avocados, oranges, beans, and lentils. Aim for at least 400 mcg DFE (dietary folate equivalents) per day. If you are pregnant, trying to conceive, or have a higher risk of deficiency, add a folic acid supplement of 400-800 mcg per day. Look for a multivitamin or B-complex formula with folic acid. Choose fortified foods like breakfast cereals and breads to boost your folic acid intake, unless you need to limit your consumption due to MTHFR gene variations. The combination of dietary folate and folic acid supplementation, tailored to your individual needs, is the best way to reap the full spectrum of vitamin B9 benefits. When and Why to Use Folic Acid Supplements Folic acid supplements are recommended in the following scenarios: Pregnancy: All women of reproductive age should take 400 mcg of folic acid daily and increase to 600-800 mcg during pregnancy to reduce the risk of neural tube defects. Start supplementing at least one month before trying to conceive. Folate deficiency: If you have been diagnosed with folate deficiency based on a blood test, your doctor may prescribe folic acid supplements to replenish your stores and prevent complications like anaemia. Digestive disorders: Conditions like coeliac disease, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and chronic diarrhoea can impair folate absorption. Folic acid supplements may be necessary to maintain adequate levels. Medications: Certain medications can interfere with folate metabolism or increase the risk of deficiency. These include methotrexate, sulfasalazine, triamterene, and some anti-seizure drugs. Folic acid supplementation may be advised to offset these effects. Conclusion The folate vs. folic acid question doesn't have a one-size-fits-all answer. Both forms of vitamin B9 offer important health benefits, but the key is to tailor your intake based on your age, sex, health status, and reproductive goals. For personalised guidance on optimising your folate levels, consider consulting with Metropolis Healthcare. Their expert team offers comprehensive nutrition assessments and testing to help you make informed decisions about your diet and supplement needs. With a commitment to patient education and preventive care, Metropolis is your trusted partner in navigating the sometimes confusing world of vitamins for better health. FAQs Is folate better than folic acid? Neither form is necessarily "better." Both effectively raise vitamin B9 levels, but there are differences between folate and folic acid in terms of bioavailability and potential risks for certain individuals. The healthiest approach is usually to get a mix of both natural folate and folic acid, unless you have a specific condition that warrants avoiding folic acid. Can I get enough folate from my diet? It is possible to meet your daily folate needs through a diet alone by regularly consuming a wide variety of plant foods like leafy greens, legumes, and citrus fruits. However, many people may still fall short, especially pregnant women who have higher requirements. Afolic acid supplement provides a reliable way to ensure adequate intake. What happens if I take too much folic acid? Folic acid is generally safe and well-tolerated in the recommended doses. Excess folic acid is excreted in the urine. However, very high doses (above 1,000 mcg per day) may cause side effects like abdominal cramps, diarrhoea, and skin reactions in some people. There are also concerns that excess folic acid could mask vitamin B12 deficiency or increase the risk of certain cancers, but more research is needed. It's best to consult your healthcare provider about the appropriate dosage for your needs.
Guillain Barre Syndrome: Symptoms, Causes & Diagnosis
Imagine waking up one day with a tingling sensation in your toes and fingers. Within a few days, you find it difficult to walk, struggle with double vision, and even have trouble breathing. These frightening symptoms could point to Guillain Barre syndrome (GBS), a rare but serious autoimmune disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system. GBS syndrome occurs when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy nerve cells, leading to muscle weakness, numbness, and, in severe cases, paralysis. Learning about Guillain Barre disease symptoms, types, causes, and diagnosis is crucial for early detection and timely treatment. In this article, we'll provide a comprehensive overview of GBS to help you understand this complex condition better. What is Guillain-Barre Syndrome? Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS), also known as GBS syndrome, is a rare but serious neurological disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the peripheral nerves. This leads to symptoms like muscle weakness, tingling, and, in severe cases, paralysis. Guillain Barre disease symptoms often start in the feet and legs, spreading upward to the arms and upper body. Although the condition is rare, affecting approximately 1 in 100,000 people annually, Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS) can occur in individuals of any age, with a slightly higher prevalence in adult males. While the exact Guillain Barré syndrome cause is not fully understood, it is often triggered by an infection, such as a respiratory illness or stomach flu. This has led some to link the condition to a potential GBS virus, though no specific virus exclusively causes it. Occasionally, GBS disease symptoms may also arise after surgery or vaccination. Rapid progression of Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS) makes early recognition and treatment critical. Treatment of GBS syndrome typically includes immunotherapy, such as intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) or plasmapheresis, to reduce the immune attack on nerves. Physical therapy may also aid in recovery. While most people recover, the severity of symptoms and recovery time can vary. What are The Latest Updates On Guillain Barre syndrome? In 2023, the FDA required manufacturers to include warnings about a possible increased risk of Guillain Barre syndrome (GBS) in the prescribing information for two respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccines: Abrysvo (Pfizer) and Arexvy (GlaxoSmithKline). Postmarketing observational studies suggested a higher likelihood of GBS syndrome occurring within 42 days of vaccination, especially in individuals aged 65 and older. While these findings raised concerns, the available evidence remains insufficient to confirm a direct causal relationship between these vaccines and GBS. Guillain Barre syndrome definition usually includes a rare neurological disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the peripheral nerves, leading to symptoms such as muscle weakness, tingling, and, in severe cases, paralysis. Guillain Barre disease symptoms often progress rapidly, making early detection critical. Although the exact Guillain Barré syndrome cause is unclear, it is often triggered by infections and, in rare cases, vaccines or surgeries. The FDA's actions underscore the importance of continued monitoring and transparency regarding potential vaccine-related risks. Healthcare providers must inform patients about the potential risks, including the possibility of GBS virus association, and encourage reporting of any suspected cases. Early recognition and treatment of GBS syndrome, such as immunotherapy and supportive care, can significantly improve patient outcomes. Guillain Barre Syndrome Types There are several types of GBS syndrome, each with distinct characteristics: Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP): This is the most common form of GBS in North America and Europe. It is characterised by muscle weakness starting in the lower body and spreading upward. Miller Fisher Syndrome (MFS): Less common in the U.S. but more prevalent in Asia. It is characterised by paralysis of the eyes, unsteady gait, and coordination problems. Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy (AMAN) and Acute Motor-Sensory Axonal Neuropathy (AMSAN): More common in China, Japan, and Mexico. It is often characterised by more severe and prolonged symptoms. Symptoms of Guillain Barre Syndrome The symptoms of Guillain Barre syndrome (GBS), an autoimmune nerve disorder, can vary significantly depending on its type and severity. This condition primarily affects the peripheral nervous system and often progresses quickly. Common GBS disease symptoms include: Muscle weakness or paralysis, typically starting in the lower body and progressing upward. Coordination and balance problems, which can make walking or climbing stairs difficult. Eye movement issues, such as double vision or the inability to move the eyes. Facial weakness, leading to difficulties with speaking, chewing, or swallowing. Severe pain, often described as aching, shooting, or cramping, which is usually worse at night. Autonomic dysfunction, which may include rapid heart rate, abnormal blood pressure, and breathing difficulties. Bladder and bowel control issues, which can further complicate daily functioning. In most cases, individuals with GBS experience their most severe symptoms within two weeks of onset. Severe forms of this peripheral neuropathy can be life-threatening if critical functions like breathing are affected. If you or someone you know exhibits these symptoms, immediate medical attention is essential. Early diagnosis and treatment of GBS syndrome, including therapies like intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) or plasmapheresis, can significantly reduce complications and improve recovery outcomes. Causes and Risk Factors of GBS The exact Guillain Barré syndrome cause is not fully understood, but it is believed to be triggered when the immune system mistakenly attacks the peripheral nerves, often following a viral or bacterial infection. Common infections linked to GBS include influenza, the Zika virus, and Campylobacter jejuni, a bacterium often found in undercooked poultry. In rare cases, GBS syndrome may also be triggered by certain vaccines or surgeries. Risk factors for developing GBS include: People over 50 years old are at higher risk GBS is slightly more common in men than in women Recent infections, particularly respiratory or gastrointestinal illnesses Certain vaccinations, though the risk is very low, with an estimated 1-2 cases per million doses Previous history of GBS, which may increase the likelihood of recurrence It is important to note that while these factors can increase the risk, GBS syndrome can affect individuals of any age or health status. If you notice symptoms such as muscle weakness, numbness, or tingling, consult a healthcare professional promptly for an accurate diagnosis and timely treatment. Diagnosis of Guillain-Barré Syndrome Diagnosing Guillain Barré syndrome (GBS) involves a combination of clinical evaluation and specialised tests to confirm the condition. GBS, an autoimmune nerve disorder, occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the peripheral nerves, leading to muscle weakness, numbness, or tingling. The diagnostic process typically begins with a detailed physical exam, during which your doctor will check for muscle weakness, reflex changes, and sensory issues. They may also review your medical history, including any recent infections or vaccinations. To confirm a GBS syndrome diagnosis, your doctor may recommend the following tests: Lumbar puncture (spinal tap): Analyses cerebrospinal fluid for elevated protein levels, a hallmark of GBS Electromyography (EMG): Evaluates the electrical activity of muscles to detect nerve damage Nerve conduction studies: Measure how quickly electrical signals travel through the nerves In some cases, blood tests may be performed to rule out other conditions that mimic GBS symptoms. Early and accurate diagnosis of this peripheral neuropathy is essential to begin timely treatment, minimise complications, and improve recovery outcomes. Treatment Options for GBS While there's no cure for Guillain Barré syndrome (GBS), treatment focuses on managing symptoms, preventing complications, and supporting recovery. GBS, an autoimmune nerve disorder, often progresses rapidly, making early intervention crucial. The two primary treatment options are: Plasma exchange (plasmapheresis): This procedure removes harmful antibodies from the blood, reducing inflammation and nerve damage. It is most effective when initiated within the first week of symptom onset. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG): High doses of healthy antibodies are infused intravenously to block the damaging antibodies responsible for GBS. IVIG is as effective as plasma exchange and is often preferred due to its simpler administration. In addition to these treatments, supportive care plays a vital role, including: Monitoring breathing and providing ventilator support if respiratory muscles are affected Pain management with appropriate medications Physical therapy to maintain muscle strength and flexibility Occupational therapy to adapt daily activities during recovery Emotional support or counseling to address the psychological impact of GBS. Most individuals with GBS require hospitalisation for close monitoring and care. With timely and effective treatment, many patients begin to recover within weeks, though some may experience lingering weakness or sensory issues that require ongoing rehabilitation. Recovery and Life Expectancy The recovery journey after Guillain Barre syndrome varies for each person. While some may recover fully within a few months, others may have ongoing symptoms for years. Generally, the chances of a good recovery are higher if: You're younger than 50 Symptoms began 3 weeks or less before treatment You didn't need a ventilator You started recovering within 2-4 weeks of symptom onset Studies show that about 70% of patients recover fully, while 30% may have some residual weakness. Less than 5% experience a relapse or recurrence of GBS. Although the recovery process can be slow and challenging, staying committed to your treatment plan and maintaining a positive outlook can make a significant difference. Conclusion Facing a Guillain Barré syndrome diagnosis can be overwhelming, but remember that with proper medical care and support, most people recover well. Stay vigilant about any signs of muscle weakness or numbness, and don't hesitate to consult your doctor if you have concerns. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to minimising complications and improving outcomes. If you need reliable diagnostic services, consider Metropolis Healthcare. With a network of advanced labs across India, Metropolis offers accurate testing and personalised care. Their team of experienced phlebotomists provide convenient home sample collection, and reports are delivered online for easy access. Take charge of your health today! FAQs 1. What is The First Symptom For GBS? Guillain Barre syndrome symptoms usually start with weakness or tingling in the legs, spreading to the arms and upper body. These sensations can develop rapidly over hours to weeks. 2. Who is More Likely to Get Guillain-Barré Syndrome? While Guillain Barre syndrome can affect anyone, certain factors increase the risk: Age: Individuals aged 50 and above are at higher risk Gender: GBS affects slightly more men than women Recent infections: About 66% of Guillain Barre syndrome patients report diarrhoea or respiratory illness weeks before symptoms appear Other triggers: Viral infections, rare cases of vaccination, and surgery may also precede Guillain Barre syndrome. 3. How Do I Take Care Of Myself if I Have Guillain-Barré Syndrome? If you're diagnosed with Guillain Barre syndrome, prompt treatment is essential: Hospitalisation: Guillain Barre syndrome often requires hospital care to monitor progression and manage complications Early interventions: Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) or plasma exchange can improve short-term outcomes Supportive care: This includes respiratory support, physical therapy, and watching for issues like lung infections Rehabilitation: Physiotherapy helps regain strength and mobility during recovery 4. What is The Life Expectancy For Someone With Guillain-Barré Syndrome? Most people with Guillain Barre syndrome can expect a normal lifespan after recovery. However, the acute phase carries a small risk of death (<2%) due to severe complications. Residual effects are common, but many individuals recover fully with time and proper care. 5. How Long Do GBS Symptoms Last? Guillain Barre syndrome symptoms vary in duration. Recovery often begins 2-3 weeks after onset, but can take weeks to years. Some people may have lasting nerve damage. 6. How to Confirm GBS? Diagnosing Guillain Barre syndrome involves several key tests: Symmetric symptoms and quick onset are hallmarks. Loss of reflexes is a common sign. Spinal tap shows high CSF protein in GBS. EMG and nerve conduction studies assess nerve function.
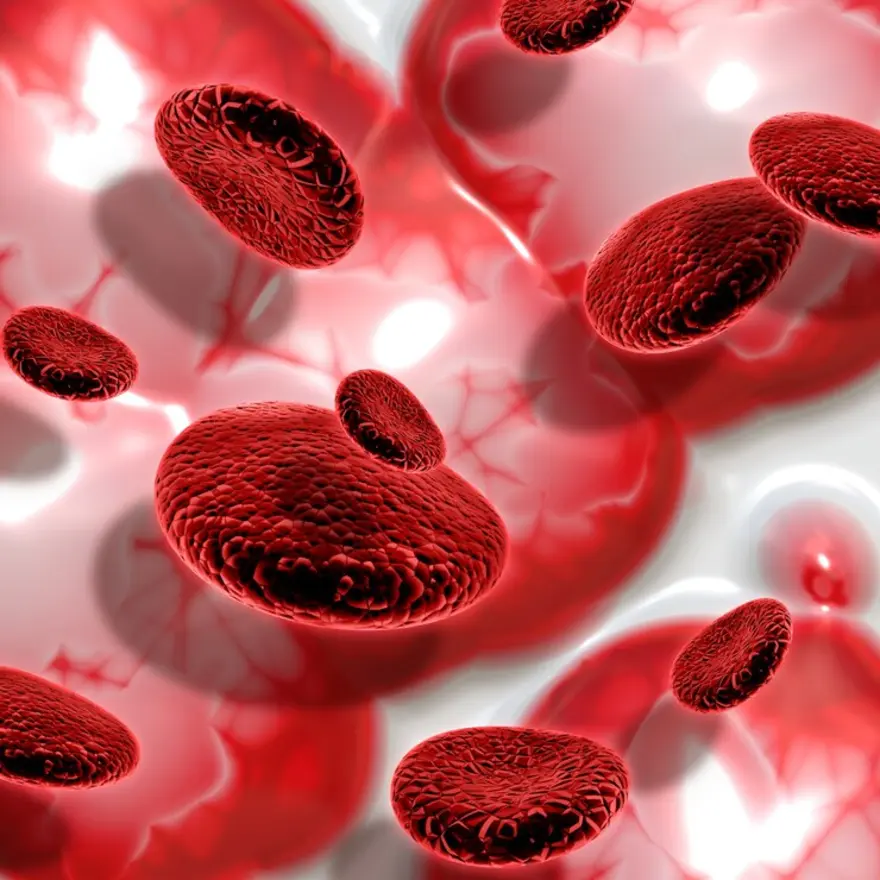
Qartemi: India’s Revolutionary CAR T Therapy for Blood Cancer
In a significant breakthrough for blood cancer treatment in India, Immuneel Therapeutics has launched Qartemi, a revolutionary CAR T-cell therapy specifically designed for adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (B-NHL). This innovative blood cancer therapy harnesses the power of the patient's own immune system to fight cancer, offering new hope to those who have exhausted conventional treatment options. With approximately 120,000 new cases and over 70,000 deaths annually from leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma in India, the burden of blood cancers is substantial. The Qartemi drug marks a crucial step towards making advanced, life-saving treatments more accessible to Indian patients, shifting the paradigm towards a cure for blood cancer. What is Qartemi, and how does it utilise CAR-T therapy? Qartemi is India's first globally benchmarked CAR T-cell treatment specifically designed for adult B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. This innovative therapy, seen as a significant step towards a cure for blood cancer, involves genetically modifying the patient's own T cells to recognise and attack cancer cells. Here's a step-by-step overview of how the Qartemi drug works: T Cell Extraction: The patient's T cells, a type of white blood cell crucial for immune response, are collected from their blood. Genetic Modification: These T cells are then genetically engineered in a laboratory to express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) on their surface. This CAR is specifically designed to target a protein called CD19, which is found on the surface of B-cell lymphoma cells. CAR T-Cell Expansion: The genetically modified CAR T cells are multiplied in the lab to create millions of cancer-fighting cells. Reinfusion: The expanded CAR T cells are then infused back into the patient's bloodstream, where they seek out and destroy the cancer cells expressing the CD19 antigen. Significance of Qartemi in India The launch of the Qartemi drug holds immense significance for India, given the country's growing burden of blood cancers. Consider these alarming statistics: India witnesses approximately 120,000 new cases and over 70,000 deaths annually due to blood cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. Approximately 40,000 new cases of non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) are diagnosed in India each year. Access to advanced cancer treatments remains a significant challenge for many Indian patients due to financial constraints and limited availability. The Qartemi drug addresses these challenges by providing a globally benchmarked CAR T cancer treatment at a significantly more accessible price compared to international alternatives. Developed and manufactured indigenously by Immuneel Therapeutics, Qartemi ensures that Indian patients have access to cutting-edge, life-saving therapies right here at home. Qartemi Approval by CDSCO Qartemi has been rigorously evaluated and approved by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), India's apex regulatory body for pharmaceuticals and medical devices. This approval follows the successful completion of the IMAGINE trial, which demonstrated the safety and efficacy of Qartemi in treating adult patients with B-NHL. The IMAGINE trial, conducted across multiple hospitals in India, including Narayana Hospital, Apollo Cancer Hospital, and PGIMER, showed impressive results: An overall response rate (ORR) of 83.3% at Day+90, setting a new benchmark for CAR T-cell therapy in India. No patients required ICU admissions or developed neurotoxicity, indicating a favorable safety profile similar to other approved CAR T-cell therapies. The CDSCO's approval of Qartemi based on these positive clinical trial outcomes marks a significant step forward in bringing this revolutionary treatment to patients in need. How Qartemi Works To understand how Qartemi works, let's take a closer look at the science behind CAR T-cell immunotherapy: T Cell Extraction: The process begins by collecting T cells, a type of white blood cell essential for immune response, from the patient's blood through a procedure called leukapheresis. Genetic Modification: The extracted T cells are sent to a specialised laboratory, where they undergo genetic engineering. Using a harmless virus as a vehicle, the T cells are modified to express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) on their surface. This CAR is specifically designed to recognise and bind to the CD19 antigen found on B-cell lymphoma cells. CAR T-Cell Expansion: The genetically modified CAR T cells are then multiplied in the laboratory to create millions of cancer-fighting cells. This expansion process ensures that there are enough CAR T cells to mount a strong immune response against the cancer. Reinfusion: Once the CAR T cells have been expanded, they are infused back into the patient's bloodstream. The infusion process is similar to a standard blood transfusion and typically takes less than an hour. Cancer Cell Destruction: After reinfusion, the CAR T cells circulate throughout the patient's body, seeking out and binding to the CD19 antigen on the surface of B-cell lymphoma cells. Upon binding, the CAR T cells become activated and release cytotoxic molecules that destroy the cancer cells. Ongoing Surveillance: One of the remarkable features of CAR T-cell therapy is that the modified T-cells can persist in the patient's body for months or even years after the initial treatment. These long-lasting CAR T cells continue to monitor for any remaining or recurring cancer cells, providing ongoing protection against relapse. Benefits of Qartemi Qartemi offers several significant benefits for patients battling B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: High Efficacy: The IMAGINE trial demonstrated an impressive overall response rate of 83.3% at Day+90, indicating that Qartemi is highly effective in treating adult B-NHL patients who have exhausted other treatment options. Favorable Safety Profile: Unlike some other cancer treatments, Qartemi has shown a favorable safety profile, with no patients in the IMAGINE trial requiring ICU admissions or developing neurotoxicity. Personalised Treatment: Qartemi is a personalised therapy that uses the patient's own immune cells to fight cancer. This tailored approach ensures that the treatment is specific to each individual patient, potentially reducing the risk of side effects and improving outcomes. Accessibility: Developed and manufactured in India, Qartemi is priced significantly lower than global CAR-T cell treatment alternatives. This affordability makes the treatment more accessible to Indian patients who may otherwise struggle to afford such advanced therapies. Eligibility for Qartemi Treatment To be eligible for Qartemi treatment, patients must meet certain criteria: Diagnosis of relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL) after exhausting other treatment options. Adequate organ function and overall health status to tolerate the treatment process. No active infections or severe comorbidities that could compromise the immune system. Willingness and ability to comply with the treatment protocol and follow-up requirements. Patients interested in exploring Qartemi as a treatment option should consult with their oncologist or haematologist to determine their eligibility and discuss the potential risks and benefits of the therapy. Cost and Accessibility One of the most remarkable aspects of Qartemi is its affordability. While similar blood cancer therapy abroad cost between $600,000 and $700,000, Qartemi is priced significantly lower, ranging from Rs 35 lakh to Rs 50 lakh. By combining world-class CAR-T therapy with indigenous manufacturing, Immuneel Therapeutics has taken a significant step toward making this advanced treatment more accessible to Indian patients. However, challenges persist. CAR T cancer treatment is not yet covered by insurance in India, making it financially burdensome for many patients. Additionally, the treatment requires hospitalisation, adding to the overall cost and complexity. Despite these hurdles, Qartemi marks an important advancement in the quest for a widely accessible cure for blood cancer, offering hope to thousands of patients across the country. Side Effects and Risks As with any advanced medical treatment, Qartemi comes with potential side effects and risks. Some of the most common ones include: Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS): Patients may experience high fever, chills, trouble breathing, severe nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, dizziness, headaches, fast heartbeat, and muscle or joint pain. Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS): Symptoms can include headaches, changes in consciousness, confusion, agitation, seizures, tremors, trouble speaking and understanding, and loss of balance. Other serious side effects: These may include allergic reactions, abnormal mineral levels in the blood, weakened immune system, low blood cell counts, and an increased risk of developing another type of blood cancer. What Role Will Qartemi Play in Shaping the Future of CAR-T Therapy in India? Qartemi is set to revolutionise cancer treatment in India by offering a highly effective yet affordable CAR T cancer treatment option. Its approval and availability mark a significant milestone in making advanced cancer therapies accessible to a broader population. By partnering with leading hospitals across the country, Immuneel Therapeutics aims to expand access to this life-saving treatment. This collaboration will help build the necessary expertise and facilities to administer CAR-T therapy safely and effectively. As more patients benefit from Qartemi and similar treatments, it will likely spur further research and development in the field of T-cell immunotherapy in India. This could lead to the development of CAR T cells targeting other types of cancers, potentially offering hope to even more patients. Conclusion While it's not a magic cure for blood cancer, Qartemi is a powerful tool in the hands of skilled oncologists. As with any medical treatment, it's essential to consult with a trusted healthcare provider to determine if Qartemi is the right choice for you or your loved one. If you're considering Qartemi or need to monitor your health during treatment, Metropolis Healthcare can be your trusted partner. With a wide network of diagnostic labs across India, Metropolis offers accurate pathology testing and health check-up services. Their team of qualified technicians can collect blood samples from the comfort of your home, with reports conveniently shared online. By delivering reliable results and personalised care, Metropolis empowers you to prioritise your health throughout your cancer journey. FAQs What is Qartemi? Qartemi is India's first affordable CAR T cell treatment for adult B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (B-NHL). It is a personalised T-cell immunotherapy that involves extracting a patient's T-cells, genetically modifying them to target cancer cells, and reinfusing these modified cells into the patient. Which types of cancer can Qartemi treat? Qartemi is specifically designed to treat adult B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (B-NHL), particularly in cases where the disease has relapsed or is at an advanced stage. Who is eligible for Qartemi therapy? Qartemi's blood cancer therapy is eligible for adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Eligibility involves a comprehensive medical evaluation to ensure the patient can tolerate the treatment and has no contraindications. What is the cost of Qartemi therapy in India? Qartemi's blood cancer therapy in India is priced significantly lower than similar CAR T cancer treatments abroad, which typically cost between ₹5 crore and ₹6 crore. In comparison, Qartemi is available for ₹35 lakh to ₹50 lakh, making it approximately one-tenth the cost. This affordability reflects Immuneel Therapeutics' commitment to making advanced cancer therapies more accessible to patients in India. Are there any risks or side effects of Qartemi therapy? Yes, Qartemi therapy can have several side effects and risks, similar to other CAR-T therapies. These include cytokine release syndrome (CRS), immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS), allergic reactions, abnormal mineral levels, weakened immune system, low blood cell counts, and an increased risk of developing another blood cancer. How long does Qartemi therapy take? The duration of Qartemi therapy can vary, but it generally involves several steps, including T cell collection, chimeric antigen receptor modification, and infusion. Patients typically need close monitoring for several weeks after the treatment due to the potential for serious side effects. Is CAR-T therapy available in all hospitals in India? No. Qartemi is currently offered by select leading hospitals in India that have the necessary expertise and facilities. These include Narayana Hospital, Apollo Cancer Hospital, PGIMER, Manipal Hospitals, Apollo Hospitals, CMC Vellore, RGCIRC Delhi, and SGPGI Lucknow, among others.
Benefits of Walnuts During Pregnancy: Nutritional Value and Health Advantages
Introduction Walnuts are a nutritious and versatile nut that can be a valuable addition to a healthy diet, especially during pregnancy. Packed with essential nutrients, walnuts offer numerous health benefits for both the mother and the developing fetus. In fact, studies show that consuming walnuts during pregnancy can support foetal brain development and reduce the risk of certain pregnancy complications. This article will delve into the nutritional value of walnuts, their general health benefits, and specifically how they can support a healthy pregnancy. By understanding the benefits of eating walnuts, expectant mothers can make informed choices to nourish themselves and their growing babies. What Are Walnuts? Walnuts are tree nuts from the Juglandaceae family, known for their distinctive shell and the nutritious seed inside. Walnuts are native to Asia and Eastern Europe but are now cultivated worldwide. They are a popular ingredient in various culinary dishes and are also consumed as a snack due to their nutritional value. The two main types of walnuts are English walnuts (Juglans regia) and black walnuts (Juglans nigra), with English walnuts being the most commonly consumed variety. Nutritional Value of Walnuts Walnuts are highly nutritious and packed with various vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats. They are an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which is essential for heart health and foetal brain development. A 28-gram serving of walnuts (about 7 walnuts) contains: 185 calories 4 grams of protein 18 grams of fat (mostly healthy polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats) 2 grams of fibre 1 gram of sugar Walnuts also contain significant amounts of magnesium, copper, manganese, zinc, and selenium. Additionally, they are rich in antioxidants such as quinone, juglone, tannins, and vitamin E. 15 Health Benefits of Walnuts Walnuts have several general health benefits that make them a beneficial food for overall well-being. Let's explore some of these benefits in more detail. Decreasing Inflammation Walnuts contain anti-inflammatory compounds, such as ellagic acid and omega-3 fatty acids, that help reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is linked to heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. By incorporating walnuts into your diet, you can help combat inflammation and lower your risk of these health issues. Cancer Prevention The antioxidants and phytochemicals in walnuts may help protect against certain types of cancer. Studies have shown that consuming walnuts may reduce the risk of breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers. Improves Gut Health The fibre content in walnuts supports healthy digestion and regularity. Walnuts also contain prebiotics, which feed the beneficial bacteria in the gut, promoting a healthy gut microbiome. Boosts Your Brain Walnuts are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants that support brain health and cognitive function. Studies have shown that consuming walnuts can improve memory, concentration, and overall brain function. Good for Diabetes Walnuts can help control blood sugar levels and manage diabetes due to their fibre and healthy fat content. The fibre in walnuts slows down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels. Additionally, the healthy fats in walnuts can improve insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for managing diabetes. Heart Health Walnuts are beneficial for heart health by lowering cholesterol levels, reducing blood pressure, and improving blood vessel function. The omega-3 fatty acids in walnuts help reduce inflammation in the blood vessels, which can lower the risk of heart disease and stroke. Rich in Antioxidants Walnuts contain powerful antioxidants that protect against free radical damage and enhance overall health. Antioxidants such as ellagic acid, vitamin E, and polyphenols help neutralise harmful free radicals that can damage cells and contribute to chronic diseases. Lowers Cholesterol The monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats in walnuts help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Studies have shown that consuming walnuts as part of a healthy diet can reduce LDL cholesterol by up to 10%. This cholesterol-lowering effect can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease. Helps Lower Blood Pressure Walnuts contain arginine, an amino acid that helps relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure. High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke. By including walnuts in your diet, you can help manage your blood pressure and reduce your risk of these serious health issues. Aids in Weight Loss The protein and fibre in walnuts help in satiety and weight management. Walnuts are a nutrient-dense food that can keep you feeling full and satisfied, reducing the likelihood of overeating. Reduces the Risk of Heart Disease The combination of heart-healthy nutrients in walnuts, such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fibre, can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease. This protective effect is attributed to the ability of walnuts to improve cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and support healthy blood vessel function. Supports Fertility While specific fertility benefits during pregnancy are less documented, the general nutritional profile of walnuts supports overall health, which can indirectly benefit reproductive health. The omega-3 fatty acids in walnuts are essential for hormone production and regulation, which play a crucial role in fertility. Additionally, the antioxidants in walnuts can help protect reproductive cells from oxidative stress. Improves Sleep Walnuts contain melatonin, a hormone that helps regulate sleep patterns. Consuming walnuts before bedtime may help improve sleep quality and duration. This is especially beneficial during the third trimester of pregnancy when sleep disturbances are common. Promotes Better Skin The antioxidants in walnuts, such as vitamin E and ellagic acid, can improve skin health and reduce the signs of aging. These antioxidants protect the skin from oxidative damage caused by UV radiation and other environmental stressors. Boosts Metabolism The healthy fats and fibre in walnuts can help boost metabolism and support weight management. Walnuts have a high thermic effect, meaning that the body burns more calories digesting them compared to other food. This metabolic boost can help maintain a healthy weight, which is important for overall health and fertility. Benefits of Walnuts During Pregnancy In addition to their general health benefits, walnuts offer several specific advantages during pregnancy. Let's explore how consuming walnuts can support a healthy pregnancy for both the mother and the developing foetus. Boosts Baby's Brain Development Walnuts are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA, which is crucial for the development of the foetal brain and eyes. DHA is essential for the growth and function of brain cells and plays a vital role in cognitive development. Supports Healthy Weight Gain The combination of protein and fibre in walnuts helps in managing hunger and supporting healthy weight gain during pregnancy, which is essential. Walnuts are a nutrient-dense snack option that can keep expectant mothers feeling full and satisfied between meals. Reduces Risk of Preeclampsia Preeclampsia is a serious pregnancy complication characterised by high blood pressure and potential damage to organ systems. The antioxidants and healthy fats in walnuts may help reduce the risk of preeclampsia by improving blood vessel function and lowering blood pressure. Enhances Mood and Reduces Stress Pregnancy can be an emotionally challenging time, with hormonal changes and the anticipation of motherhood. Walnuts contain omega-3 fatty acids that help improve mood and reduce stress levels, which is particularly beneficial during pregnancy. Strengthens Immunity Walnuts are rich in immunity-boosting minerals and vitamins such as copper, phosphorus, folate, calcium, and manganese. These nutrients help support the immune system and reduce the risk of infections during pregnancy. FAQs How many walnuts per day? It is recommended to consume no more than 10 walnuts per day to avoid digestive issues and excessive weight gain. What are the benefits of walnuts? Walnuts offer numerous health benefits, including reducing inflammation, supporting heart health, improving brain function, aiding in weight management, and reducing the risk of certain cancers. They are also beneficial during pregnancy, supporting foetal brain development, reducing the risk of preeclampsia, and enhancing maternal immune function. Do walnuts reduce belly fat? While walnuts alone may not specifically target belly fat, they can be part of a balanced diet and exercise plan for overall weight management. Are walnuts safe during pregnancy? Walnuts are generally considered safe for most pregnant women when consumed in moderation. However, if you have a nut allergy or are at risk of developing gestational diabetes, it's crucial to consult with your healthcare provider before including walnuts in your diet. What is the best time to eat walnuts during pregnancy? You can enjoy walnuts at any time of the day, as a snack or incorporated into your meals. However, the most important aspect is to include them consistently in your diet to reap their health benefits. Conclusion Walnuts are a nutrient-rich food that supports foetal brain development and maternal heart health during pregnancy. Metropolis Healthcare offers expert prenatal care, nutritional guidance, and convenient diagnostic services, helping expectant mothers prioritise their health and their baby’s well-being. Make informed choices for a healthier pregnancy journey.
Yeast Infection vs. PID: Can a Yeast Infection Lead to Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
Introduction Have you ever wondered about the connection between yeast infections and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)? While both conditions impact the female reproductive system, they differ significantly in causes, symptoms, and treatments. A yeast infection, caused by an overgrowth of Candida, is not typically linked to PID, which usually results from untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia or gonorrhea. However, misdiagnosis or untreated infections can lead to complications. Understanding the differences is essential for proper diagnosis and care. In this article, we'll examine whether yeast infections can cause PID, outline common causes of PID, and share practical tips for prevention and management. What is a yeast infection? A vaginal yeast infection, also known as candidiasis, is a common fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of Candida yeast in the vagina. Symptoms typically include: Itching and burning in the vaginal area Redness and swelling of the vulva Thick, white, cottage cheese-like discharge Yeast infections are usually treated with antifungal medications, which are available in topical or oral forms. These infections can be triggered by various factors, like hormonal changes during pregnancy or menstruation, antibiotic use that disrupts the natural balance of vaginal flora, poor hygiene practices, or a weakened immune system. What is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)? Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is a serious infection of the female reproductive organs, including the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and cervix. It is often caused by bacterial infections, most commonly those resulting from sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like gonorrhoea and chlamydia. Symptoms of PID may include: Pelvic pain Heavy or foul-smelling vaginal discharge Painful urination Bleeding between periods If left untreated, PID can lead to serious long-term complications, including infertility due to scarring or blockages in fallopian tubes, chronic pelvic pain caused by inflammation, and an increased risk of ectopic pregnancies, where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. Can a yeast infection cause PID? No, a yeast infection cannot cause PID. While both conditions can present with similar symptoms, like vaginal discharge, they are caused by different pathogens. Yeast infections are fungal infections, whereas PID is typically caused by bacterial infections, especially those resulting from STIs. However, having a yeast infection and a bacterial STI simultaneously may increase the risk of developing PID. This is because the inflammation caused by the yeast infection can make the reproductive tract more susceptible to bacterial infections. It's important to note that while a yeast infection itself cannot lead to PID, misdiagnosis or delayed treatment of PID can occur if the symptoms are mistaken for those of a yeast infection. This is why it's crucial to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis if you experience persistent or unusual symptoms. Which STIs can cause or raise your risk of PID? The most common STIs that can cause or increase the risk of PID are: Gonorrhea Chlamydia These bacterial STIs can ascend from the vagina or cervix into the upper reproductive tract, leading to PID. It's important to note that other bacterial STIs, like syphilis, do not typically cause PID. Similarly, viral or parasitic STIs such as herpes simplex virus, human papillomavirus (HPV), or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are not associated with PID. What else can cause or increase your risk of PID? Besides STIs, several other factors can increase the risk of developing PID: Ruptured appendix or bowel infections that allow bacteria to enter the reproductive tract Certain surgical procedures like insertion of an intrauterine device (IUD), dilation and curettage (D&C), or surgical abortion Vaginal infections such as bacterial vaginosis Practices like douching, which can push bacteria from the vagina into the upper reproductive tract Preventing Yeast Infections and PID Prevention strategies for yeast infections include: Maintaining good genital hygiene Avoiding tight-fitting clothing Managing diabetes if applicable For PID, the following preventive measures are recommended: Regular STI screening and prompt treatment Using condoms during sexual intercourse to reduce the risk of contracting STIs Avoiding douching and other practices that disrupt the vagina Remember, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in preventing long-term complications associated with PID. When to See a Doctor If you experience any of the following symptoms, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional: Unusual vaginal discharge Pelvic pain Painful urination Bleeding between periods Regular health check-ups and STI screenings are also recommended for women who are sexually active. FAQs Can a yeast infection and PID occur simultaneously? Yes, it is possible to have a yeast infection and PID at the same time, especially if you have a bacterial STI along with a fungal infection. However, it's important to remember that a yeast infection does not cause PID. How can I differentiate between a yeast infection and PID? Differentiating between the two conditions requires a medical evaluation. Yeast infections typically present with itching, redness, and a thick, white discharge, while PID often involves more severe symptoms like pelvic pain, heavy or foul-smelling discharge, and bleeding between periods. A healthcare provider can accurately diagnose the condition through a physical examination, laboratory tests, and a review of your medical history. Conclusion While yeast infections and PID share some similar symptoms, it's crucial to understand that a yeast infection cannot cause PID. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of both conditions are essential for maintaining reproductive health and preventing complications. At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the importance of accurate diagnosis in managing your health. Our state-of-the-art diagnostic labs across India offer comprehensive testing services, including tests for yeast infections and STIs that can lead to PID. Our team of experienced phlebotomists provides convenient at-home sample collection, ensuring your comfort and privacy. Take charge of your reproductive health today by booking a test with Metropolis Healthcare.
Biotin Rich Foods: Benefits During Pregnancy for Mom and Baby
Introduction During pregnancy, a woman's nutritional needs change significantly to support her health and the development of her growing baby. One essential nutrient that plays a crucial role during this time is biotin, a B vitamin that is vital for energy production, cell function, and the growth and development of the foetus. Biotin foods are an important part of a healthy pregnancy diet, as they help prevent deficiencies that can lead to various health issues. In this article, we will explore the top biotin-rich foods for pregnancy and how they benefit both the mother and the baby. List of 12 Biotin-Rich Foods When it comes to natural sources of biotin, there are several nutrient-dense foods that pregnant women can include in their diet. Here are some of the best biotin-rich foods to consider: Eggs Eggs are an excellent source of biotin, with one egg containing approximately 10 mcg of this essential nutrient. They are also a great source of protein, choline, and other vitamins and minerals crucial for foetal development. Sweet Potatoes Sweet potatoes are not only delicious but also packed with nutrients, including biotin. A half cup of cooked sweet potatoes provides about 2.4 mcg of biotin, making them a valuable addition to a pregnant woman's diet. Nuts and Seeds (Almonds, Sunflower Seeds) Nuts and seeds are nutritious snacks that offer a good amount of biotin. For example: Almonds provide about 1.5 mg of biotin per quarter cup Sunflower seeds offer around 2.6 mcg per quarter cup These biotin foods are also rich in protein, fibre, and healthy fats, which are essential for the growth and development of the baby. Avocados Avocados are a nutrient-dense fruit that contains a variety of vitamins and minerals, including biotin. One medium avocado provides approximately 1.85 mcg of biotin, along with healthy fats, fibre, and folate, which are all important for a healthy pregnancy. Cauliflower Cauliflower is a versatile vegetable that contains a small but significant amount of biotin. A half cup of cooked cauliflower provides about 0.4 mcg of biotin, contributing to your daily intake of this essential nutrient. Spinach and Leafy Greens While spinach and other leafy greens may not be the highest sources of biotin, they still contribute to your overall intake. A half cup of cooked spinach contains about 0.5 mcg of biotin and is also rich in folate, iron, and other nutrients crucial for foetal development. Mushrooms Mushrooms, particularly button mushrooms, are a good source of biotin. Approximately 120 grams (20 caps) of canned button mushrooms provide about 2.6 mcg of biotin, making them a tasty and nutritious addition to your pregnancy diet. Bananas Bananas are a convenient and nutritious snack that contains a small amount of biotin. One half cup of sliced banana provides about 0.2 mcg of biotin, along with other essential nutrients like potassium and vitamin C. Dairy Products Dairy products, such as milk, yoghurt, and cheese, are biotin-rich foods that can help you meet your daily requirements. For example: One cup of 2% milk contains about 0.3 mcg of biotin One ounce of cheddar cheese provides approximately 0.4 mcg of biotin In addition to biotin, dairy products are also excellent sources of calcium, protein, and other nutrients essential for foetal growth and development. Salmon Salmon is a nutrient-dense fish that is rich in biotin and omega-3 fatty acids, which are crucial for foetal brain development. A three-ounce serving of cooked salmon contains about 5 mg of biotin, making it one of the best biotin foods for pregnant women. Berries While berries may not be the most prominent sources of biotin, they still contribute to your overall nutritional intake. Berries are rich in antioxidants, vitamin C, and other nutrients that support a healthy pregnancy. Soybeans and Legumes Soybeans and other legumes, such as roasted peanuts, are excellent biotin-rich foods that also provide protein and fibre. Incorporating these foods into your pregnancy diet can help you meet your daily biotin requirements while supporting overall health. Why Biotin-Rich Foods Matter for Hair Growth In addition to supporting foetal development, biotin for hair health is another important consideration during pregnancy. Many women experience changes in their hair's texture and growth during this time, and consuming biotin-rich foods can help maintain healthy hair. Biotin plays a crucial role in the metabolic processes that produce energy and building materials for cells, which is essential for the rapid cell division and DNA replication occurring during foetal development. Furthermore, biotin aids in the synthesis of fatty acids and amino acids, which are vital for the health and growth of hair. Some common questions pregnant women may have about biotin and hair health include: Can biotin deficiency cause hair loss during pregnancy? How much biotin do I need daily to support healthy hair growth? Are there any risks associated with consuming too much biotin during pregnancy? It is essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best dietary and supplementation plan to meet your individual nutritional needs during pregnancy, including your biotin intake for optimal hair health. Conclusion Incorporating biotin-rich foods into your pregnancy diet is crucial for supporting the health and development of both you and your baby. By including a variety of biotin foods like eggs, nuts, sweet potatoes, and salmon, you can ensure that you are getting enough of this essential nutrient to prevent deficiencies and promote overall well-being. Remember, while natural sources of biotin are the best way to meet your daily requirements, it is always important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine if additional supplementation is necessary. By prioritising your nutrition during pregnancy, you are taking a proactive step towards ensuring a healthy future for both yourself and your growing baby. If you have concerns about your biotin intake or overall nutritional status during pregnancy, consider reaching out to Metropolis Healthcare for their comprehensive diagnostic and health check-up services. With a team of qualified professionals and state-of-the-art facilities, Metropolis Healthcare can help you monitor your health and make informed decisions throughout your pregnancy journey.





















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp