Dermoid cyst
- 1. DERMOID CYST
- 2. Cyst lined by squamous epithelium containing desquamated cells CONTENTS mixture of sweat, sebum, desquamated epithelial cells, hair
- 3. CLINICAL TYPES CONGENITAL / SEQUESTRATION DERMOID SITE: along lines of embryonic fusion (midline of body or face) FORMATION: dermal cells sequestrated in subcutaneous plane > proliferate & liquify > cyst > grows & indents mesoderm(future bone) > bony defects
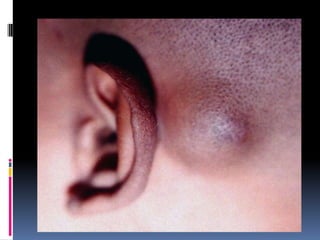
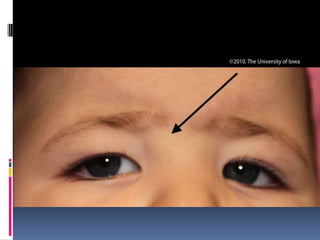
- 4. MEDIAL NASAL DERMOID CYST (root of nose at fusion lines of frontal process) EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL ANGULAR DERMOID ( fusion line of frontonasal and maxillary processes) SUBLINGUAL DERMOID PRE –AURICULAR DERMOID POST AURICULAR DERMOID
- 6. CLINICAL FEATURES Manifests in childhood or adolescence Typically a painless slow growing swelling Soft, cystic, fluctuant, yield to pressure of finger and will not slip away Transillumination negative Putty in consistency No impulse on coughing Underlying bony defect – clue to diagnosis Location along line of fusion
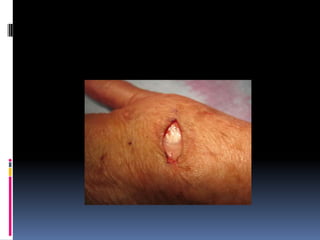
- 8. OTHER TYPES IMPLANTATION DERMOID > in women, tailors, agriculturists who sustain repeated minor injuries > sharp injury- epidermal cells implanted in subcutaneous plane- dermoid cyst > fingers, palm, sole of foot > hard in consistency ( skin is thick)
- 9. TERATOMATOUS DERMOID > arise from totipotent cells > ectodermal, mesodermal, endodermal elements > ovary, testis,retroperitoneum, mediastinum
- 11. TUBULO-EMBRYONIC DERMOID > from ectodermal tubes > thyroglossal cyst, post- anal dermoid
- 12. INVESTIGATIONS BLOOD – TC, DC,Hb,ESR URINE Examination FNAC- X ray- subjacent bone eroded by dermoid Ultrasonography- mass cystic/ solid CT scan- size , shape , local spread
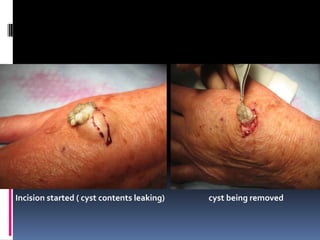
- 13. TREATMENT Excision of the cyst Mass shown ( implantation dermoid) Incision marked
- 14. Incision started ( cyst contents leaking) cyst being removed
- 16. THANK YOU