Gene Transfer.pptx
- 2. Introduction to Gene Transfer Insertion of unrelated genetic information into cells in the form of DNA is known as gene transfer. The movement of genetic information between organisms is known as gene transfer. Gene transfer can be done by 2 methods Horizontal Gene Transfer Vertical Gene Transfer
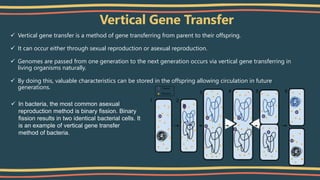
- 3. Vertical Gene Transfer Vertical gene transfer is a method of gene transferring from parent to their offspring. It can occur either through sexual reproduction or asexual reproduction. Genomes are passed from one generation to the next generation occurs via vertical gene transferring in living organisms naturally. By doing this, valuable characteristics can be stored in the offspring allowing circulation in future generations. In bacteria, the most common asexual reproduction method is binary fission. Binary fission results in two identical bacterial cells. It is an example of vertical gene transfer method of bacteria.
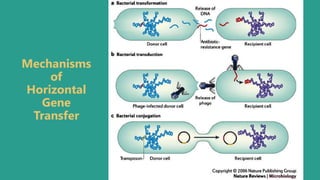
- 4. Horizontal Gene Transfer Horizontal gene transfer is a mechanism in which genetic material is transferred between nonrelated organisms. It is also known as lateral gene transfer. It occurs between different genomes such as between different species. Horizontal gene transferring is made easy due to several types of DNA possessed by organisms. They are mainly mobile genetic elements such as transposons, plasmids, and bacteriophages. It occurs via several mechanisms as follows Transformation Transduction Conjugation
- 5. Bacterial transformation is a process of horizontal gene transfer by which some bacteria take up foreign genetic material (naked DNA) from the environment. Transformation is the process by which an organism acquires exogenous DNA. TRANSFORMATION
- 6. TRANSDUCTION Transduction is the process by which a virus transfers genetic material from one bacterium to another. Viruses called bacteriophages are able to infect bacterial cells and use them as hosts to make more viruses.
- 7. CONJUGATION Conjugation is the process by which one bacterium transfers genetic material to another through direct contact. The donor bacterium carries a DNA sequence called the fertility factor, or F-factor.
- 9. SIGNIFICANCE OF GENE TRANSFER • Gene transfer technology provides the ability to genetically manipulate the cells of higher animals. • Helps to maintain flow of information between bacteria and other organisms. • Helps in gaining resistance to antimicrobial treatments. • Gene transfer provide conservation of genetic properties.
- 10. REFERENCES • Methods of Gene Transfer: Meaning, Applications, Diagrams (embibe.com) • Gene Transfer Technique - MyBioSource Learning Center • Burmeister A. R. (2015). Horizontal Gene Transfer. Evolution, medicine, and public health, 2015(1), 193–194. https://doi.org/10.1093/emph/eov018 • Methods of Gene Transfer: 6 Methods (biologydiscussion.com) • Keeling, P., Palmer, J. Horizontal gene transfer in eukaryotic evolution. Nat Rev Genet 9, 605–618 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2386
- 11. THANK YOU!