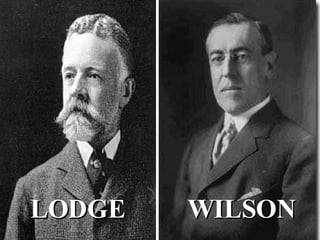The Post War Dream 1919
- 1. The Treaty of Versailles
- 2. 1. Territorial losses - overseas territories, and land in France THE TREATY of VERSAILLES Punish Germany JUNE 28, 1919
- 3. 2. Military restrictions - limits army, forbids navy and air force THE TREATY of VERSAILLES Punish Germany JUNE 28, 1919
- 4. 1. Territorial losses - overseas territories, and land in France 2. Military restrictions - limits army, forbids navy and air force 3. War guilt clause - sole responsibility for war, $33 billion in war reparations 4. League of Nations formed - Germany, Russia excluded THE TREATY of VERSAILLES Punish Germany JUNE 28, 1919
- 5. GERMANY: humiliated, blamed for war, no way to pay back reparations RUSSIA: Russia excluded from League, high casualties, loss of territory GLOBAL Self Determination: NO support for Constitutional government in SE Asia THE TREATY of VERSAILLES “ A flawed peace”
- 6. The Costs of World War I
- 7. “ War doesn’t determine who is right, only who is left”
- 8. TROOPS MOBILIZED Allies Great Britain, France, Russia, U.S 43, 749, 850 Central Powers Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy 24, 249,421
- 9. THE COSTS of WAR 26 million deaths (½ civilians from starvation, disease, exposure) 20 million wounded 10 million became displaced refugees
- 10. THE COSTS of WAR 4 years and 30 countries Historians estimate economic costs of World War I at $350 billion!!
- 12. Great Britain: David Lloyd George “make Germany pay!” Italy: Vittorio Oralando Austrian land claims France: Georges Clemenceau prevent future invasions United States: Woodrow Wilson post war peace The BIG FOUR
- 14. WILSON’S PEACE PLAN “Fourteen Points” - January 1918 No secret alliances/treaties Freedom of the seas Lower tariffs to foster trade Arms reduction ( to lessen militaristic impulses) Self-determination of colonies
- 15. Wilson’s Goals vs. The Goals of France and Great Britain
- 16. France and Great Britain Punish Germany!!!
- 17. Wilson’s GOAL Lasting peace; world peace keeping organization
- 18. The Debate of US entry into the LEAGUE OF NATIONS
- 19. LODGE WILSON
- 22. 1. Territorial losses - overseas territories, and land in France 2. Military restrictions - limits army, forbids navy and air force 3. War guilt clause - sole responsibility for war, $33 billion in war reparations 4. League of Nations formed - Germany, Russia excluded THE TREATY of VERSAILLES Punish Germany JUNE 28, 1919
- 23. LEAGUE OF NATIONS Vote in Senate November 1919 Lodge Amendments, Senate rejection Wilson refuses to Compromise with Senate over concerns Vote in Senate March 1920 Lodge Amendments, Senate rejection
- 24. Senate opinion on the treaty was divided into three distinct views: Supporters . Democrats loyal to Wilson wanted the treaty to be ratified in its original form without any amendments or reservations; some within this group were receptive to a small number of minor changes. Reservationists. This group claimed to be in favor of the treaty, but only after including a series of reservations prior to ratification. Senator Lodge of Massachusetts was the leader of this faction and was personally dedicated to frustrating the aims of his rival, Wilson. Other senators in this group sincerely favored the treaty, but wanted some modification to protect vital American interests. The Reservationists were the largest of the three factions. 3. Irreconcilables. Isolationist senators, including Robert LaFollette of Wisconsin, William E. Borah of Idaho and Hiram Johnson of California, opposed the treaty and American entry into the League of Nations under any circumstances. They had counseled against entering the war in the first place and now opposed participation in European affairs.
- 25. JOURNAL ENTRY: The Treaty of Versailles President Wilson Senator Lodge Based on the reading provide evidence to support WHY (on what grounds) Lodge or Wilson supported or opposed the Treaty and HOW (methods used) they promoted their cause.
- 26. JOURNAL ENTRY: The Battle over the Treaty of Versailles WHY? HOW? WHY? HOW? President Wilson Senator Lodge RESULTS
- 27. CONSTITUTIONAL CONNECTIONS POST WORLD WAR I Find in your Constitution: Presidents Power to negotiate treaties and Senates power to ratify