Fourier series
Download as PPTX, PDF19 likes10,891 views
This document discusses Fourier series and related concepts. It provides definitions and formulas for general Fourier series, Fourier series for discontinuous functions, the change of interval method, Fourier series for even and odd functions, and half range Fourier cosine and sine series. Examples of applications of these Fourier series concepts and techniques are also presented.
1 of 24
Downloaded 367 times



















Recommended
Laplace transform of periodic functions



Laplace transform of periodic functionsSyed Saeed This document discusses the Laplace transform of periodic functions. It begins by defining a periodic function f(t) and derives the Laplace transform of f(t) as an infinite sum. Several examples are then worked through to demonstrate finding the Laplace transform of square waves, triangular waves, and other periodic functions. Transform properties and techniques like using gate functions are employed in the examples. Reference books on circuit analysis and Laplace transforms are also listed.
Fourier series



Fourier seriesShiv Prasad Gupta Presentation on Fourier Series
contents are:-
Euler’s Formula
Functions having point of discontinuity
Change of interval
Even and Odd functions
Half Range series
Harmonic analysis
Fourier Series - Engineering Mathematics



Fourier Series - Engineering MathematicsMd Sadequl Islam In this slide fourier series of Engineering Mathematics has been described. one Example is also added for you. Hope this will help you understand fourier series.
Numerical integration



Numerical integrationMohammed_AQ This document discusses the history and applications of integration. It provides an overview of how integration was developed over time by mathematicians like Archimedes, Gauss, Leibniz, and Newton. It also outlines real-world uses of integration in engineering projects like designing the PETRONAS Towers and Sydney Opera House. The document then explains numerical integration methods like the Trapezoidal Rule, Simpson's Rule, and their variations. It provides formulas and examples of how to apply these rules to approximate definite integrals.
Fourier series Introduction



Fourier series IntroductionRizwan Kazi Its states Periodic function, Fourier series for disontinous function, Fourier series, Intervals, Odd and even functions, Half range fourier series etc. Mostly used as active learning assignment in Degree 3rd sem students.
1532 fourier series



1532 fourier seriesDr Fereidoun Dejahang Mathematics (from Greek μάθημα máthēma, “knowledge, study, learning”) is the study of topics such as quantity (numbers), structure, space, and change. There is a range of views among mathematicians and philosophers as to the exact scope and definition of mathematics
Fourier series



Fourier serieskishor pokar The document discusses Fourier series and two of their applications. Fourier series can be used to represent periodic functions as an infinite series of sines and cosines. This allows approximating functions that are not smooth using trigonometric polynomials. Two key applications are representing forced oscillations, where a periodic driving force can be modeled as a Fourier series, and solving the heat equation, where the method of separation of variables results in a Fourier series representation of temperature over space and time.
Properties of Fourier transform



Properties of Fourier transformMuhammed Afsal Villan The Fourier transform relates a signal in the time domain, x(t), to its frequency domain representation, X(jw). It represents the frequency content of the signal. The Fourier transform is a linear operation, and time shifts in the time domain result in phase shifts in the frequency domain. Differentiation in the time domain corresponds to multiplication by jw in the frequency domain. Convolution becomes simple multiplication in the frequency domain. These properties allow differential equations and systems with convolution to be solved using algebraic operations by working in the frequency domain.
Fourier series



Fourier seriesNaveen Sihag Fourier series can be used to represent periodic and discontinuous functions. The document discusses:
1. The Fourier series expansion of a sawtooth wave, showing how additional terms improve the accuracy of the representation.
2. How Fourier series are well-suited to represent periodic functions over intervals like [0,2π] since the basis functions are also periodic.
3. An example of using Fourier series to analyze a square wave, finding the coefficients for its expansion in terms of sines and cosines.
Second order homogeneous linear differential equations 



Second order homogeneous linear differential equations Viraj Patel 1) The document discusses second order linear homogeneous differential equations, which have the general form P(x)y'' + Q(x)y' + R(x)y = 0.
2) It describes methods for finding the general solution including reduction of order, and discusses the solutions when the coefficients are constants.
3) The general solution depends on the nature of the roots of the auxiliary equation: distinct real roots, repeated real roots, or complex roots.
Introduction to differential equation



Introduction to differential equationIslamic University, Kushtia This document provides an introduction to differential equations. It defines differential equations as equations containing an unknown function and its derivatives. It discusses ordinary differential equations which contain one independent variable and partial differential equations which can contain multiple independent variables. The order of a differential equation refers to the order of the highest derivative term. The degree of a differential equation is the power of the highest order derivative term. Linear differential equations have dependent variables and derivatives that are of degree one and have coefficients that do not depend on the dependent variable. Several examples of different types of differential equations are provided.
Fractional calculus and applications



Fractional calculus and applicationsPlusOrMinusZero This document discusses fractional calculus and its applications. It begins with an introduction to fractional calculus, which involves defining derivatives and integrals of arbitrary real or complex order. Naive approaches to defining fractional derivatives are inconsistent. The document then motivates a rigorous definition by generalizing the formula for differentiation to non-integer orders. This generalized formula reduces to the standard formula when the order is a positive integer.
Linear differential equation



Linear differential equationPratik Sudra This document defines and provides examples of linear differential equations. It discusses:
1) Linear differential equations can be written in the form P(x)y'=Q(x) or P(y)x'=Q(y), where multiplying both sides by an integrating factor μ results in a total derivative.
2) First order linear differential equations of the form P(x)y'=Q(x) have an integrating factor of e∫P(x)dx. The general solution is y(IF)=C.
3) Bernoulli's equation is a differential equation of the form P(x)y'+Q(x)y^n=R(x), where the general solution depends
1st order differential equations



1st order differential equationsNisarg Amin 1) First order ordinary linear differential equations can be expressed in the form dy/dx = p(x)y + q(x), where p and q are functions of x.
2) There are several types of first order linear differential equations, including separable, homogeneous, exact, and linear equations.
3) Separable equations can be solved by separating the variables and integrating both sides. Homogeneous equations involve functions that are homogeneous of the same degree in x and y.
Runge Kutta Method 



Runge Kutta Method Bhavik Vashi This document summarizes the Runge-Kutta methods for solving differential equations numerically. It introduces the first, second, third, and fourth order Runge-Kutta methods and provides the equations for calculating each. An example of using the fourth order Runge-Kutta method to solve the differential equation dy/dx=x+y is shown step-by-step. The example calculates the solution to y(0.2) given y(0)=1 using increments of h=0.1.
Fourier series and its applications by md nazmul islam



Fourier series and its applications by md nazmul islamMd Nazmul Islam The document provides an introduction to Fourier series and their applications. It begins with defining a Fourier series as an expansion of a periodic function in terms of an infinite sum of sines and cosines. It then gives the general formula for a Fourier series representing a function f(x) within the interval [-L, L]. Several examples are shown, including finding the Fourier series for the function f(x)=x from 0 to 2π. Applications of Fourier series discussed include expanding periodic functions outside their intervals, noise cancellation, analyzing oscillating functions, simplifying waves, mapping heat distribution, and signal processing. Electrical circuits are described as equivalent to Fourier series representations of voltage sources. Fourier series are also used in signal processing to represent non
B.Tech-II_Unit-V



B.Tech-II_Unit-VKundan Kumar This document provides an overview of topics in vector integration, including line integrals, surface integrals, and volume integrals. It includes examples of calculating each type of integral. The key theorems covered are Green's theorem, Stokes' theorem, and Gauss's theorem of divergence. Green's theorem relates a line integral around a closed curve to a double integral over the enclosed region. Stokes' theorem relates a line integral around a closed curve to a surface integral over the enclosed surface. Gauss's theorem relates the surface integral of the normal component of a vector field over a closed surface to the volume integral of the divergence of the vector field over the enclosed volume.
Taylor series



Taylor seriesLittle Pari The document discusses the history and development of Taylor series. Some key points:
1) Brook Taylor introduced the general method for constructing Taylor series in 1715, after which they are now named. Taylor series represent functions as infinite sums of terms calculated from derivatives at a single point.
2) Special cases of Taylor series, like the Maclaurin series centered at zero, were explored earlier by mathematicians like Madhava and James Gregory.
3) Taylor series allow functions to be approximated by polynomials and are useful in calculus for differentiation, integration, and approximating solutions to problems in physics.
Linear differential equation with constant coefficient



Linear differential equation with constant coefficientSanjay Singh The document discusses linear differential equations with constant coefficients. It defines the order, auxiliary equation, complementary function, particular integral and general solution. It provides examples of determining the complementary function and particular integral for different types of linear differential equations. It also discusses Legendre's linear equations, Cauchy-Euler equations, and solving simultaneous linear differential equations.
Legendre functions



Legendre functionsSolo Hermelin The document discusses Legendre functions, which are solutions to Legendre's differential equation. Legendre functions arise when solving Laplace's equation in spherical coordinates. Legendre polynomials were first introduced by Adrien-Marie Legendre in 1785 as coefficients in an expansion of Newtonian potential. The document covers topics such as Legendre polynomials, Rodrigues' formula, orthogonality of Legendre polynomials, and associated Legendre functions.
Green Theorem



Green TheoremSarwan Ursani This document discusses Green's theorem, which relates a line integral around a simple closed curve C to a double integral over the plane region D bounded by C. It presents the statement of Green's theorem, which equates the line integral of P dx + Q dy around C to the double integral of (∂Q/∂x - ∂P/∂y) over D. An example problem demonstrates using Green's theorem to evaluate a line integral by transforming it into a double integral. Verifying the equality of the two approaches confirms Green's theorem for the given region.
Laplace transform 



Laplace transform 001Abhishek1 This document contains information about a Laplace transform topic presentation including:
- The names and enrollment numbers of 8 students working on the topic.
- The definition of the Laplace transform and some elementary functions transformed.
- Theorems on shifting, differentiation, integration, and multiplication of Laplace transforms.
- Examples of using Laplace transforms to evaluate integrals and find derivatives.
- The application of Laplace transforms to differential equations.
Fractional Calculus PP



Fractional Calculus PPVRRITC This document discusses fractional calculus and its history. Fractional calculus generalizes differentiation and integration to non-integer orders, starting in the 17th century with ideas from Leibniz. It provides definitions for fractional integration using the Riemann-Liouville approach and fractional differentiation as the inverse of fractional integration. The document serves as an introduction to fractional kinetics and optimal control problems.
presentation on Euler and Modified Euler method ,and Fitting of curve 



presentation on Euler and Modified Euler method ,and Fitting of curve Mukuldev Khunte presentation on Euler and Modified Euler method with working and example ,and Fitting of Nonlinear curve using Method of least square
Cauchy integral theorem & formula (complex variable & numerical method )



Cauchy integral theorem & formula (complex variable & numerical method )Digvijaysinh Gohil 1) The document discusses the Cauchy Integral Theorem and Formula. It states that if a function f(z) is analytic inside and on a closed curve C, then the integral of f(z) around C is equal to 0.
2) It provides examples of evaluating integrals using the Cauchy Integral Theorem when the singularities lie outside the closed curve C.
3) The Cauchy Integral Formula is introduced, which expresses the value of an analytic function F(a) inside C as a contour integral around C. Examples are worked out applying this formula to find the value and derivatives of functions at points inside C.
Laplace equation



Laplace equationalexkhan129 This document discusses techniques for calculating electric potential, including:
1. Laplace's equation and its solutions in 1D, 2D, and 3D, including boundary conditions.
2. The method of images, which uses fictitious "image" charges to solve problems involving conductors. The classical image problem and induced surface charge on a conductor are examined.
3. Other techniques like multipole expansion, separation of variables, and numerical methods like relaxation are mentioned but not explained in detail.
Application of fourier series



Application of fourier seriesGirish Dhareshwar The document discusses sampling and the Fourier transform. It explains that sampling is the process of taking signal samples at intervals, and must be at least twice the maximum frequency to avoid aliasing. It also discusses how the Fourier transform can be used to calculate the frequency, amplitude, and phase of sampled signals to reconstruct the original signal. The Fourier transform of basic functions like 1, cosine, and exponentials are presented.
Laplace Transform And Its Applications



Laplace Transform And Its ApplicationsSmit Shah In this slide given detail description about Laplace Transform And Its Applications formulas examples etc...
Fourier series expansion



Fourier series expansionFrancesco Zoino This document discusses Fourier series expansion and spectral analysis. It explains that while signals exist in the time domain, they can be represented in the frequency domain as a series of sinusoidal components at different frequencies. This frequency domain description is called spectral analysis. Spectral analysis of signals coupled with the frequency response of systems allows for better design work, as the behavior of a linear time-invariant system can be studied using sinusoidal signals. Fourier series expansion represents periodic functions as a series of sinusoidal functions, and was developed based on the work of French mathematician Jean Baptiste Joseph Fourier.
fourier series



fourier series8laddu8 The document discusses Fourier series, which represent periodic functions as an infinite series of sines and cosines. Fourier series can be used to represent functions that are discontinuous or non-differentiable. The key formulas for the Fourier series coefficients are presented. Fourier series expansions take different forms depending on whether the function is even, odd, or defined on different intervals. Half-range Fourier series are also discussed as representations of functions defined on half periods.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Fourier series



Fourier seriesNaveen Sihag Fourier series can be used to represent periodic and discontinuous functions. The document discusses:
1. The Fourier series expansion of a sawtooth wave, showing how additional terms improve the accuracy of the representation.
2. How Fourier series are well-suited to represent periodic functions over intervals like [0,2π] since the basis functions are also periodic.
3. An example of using Fourier series to analyze a square wave, finding the coefficients for its expansion in terms of sines and cosines.
Second order homogeneous linear differential equations 



Second order homogeneous linear differential equations Viraj Patel 1) The document discusses second order linear homogeneous differential equations, which have the general form P(x)y'' + Q(x)y' + R(x)y = 0.
2) It describes methods for finding the general solution including reduction of order, and discusses the solutions when the coefficients are constants.
3) The general solution depends on the nature of the roots of the auxiliary equation: distinct real roots, repeated real roots, or complex roots.
Introduction to differential equation



Introduction to differential equationIslamic University, Kushtia This document provides an introduction to differential equations. It defines differential equations as equations containing an unknown function and its derivatives. It discusses ordinary differential equations which contain one independent variable and partial differential equations which can contain multiple independent variables. The order of a differential equation refers to the order of the highest derivative term. The degree of a differential equation is the power of the highest order derivative term. Linear differential equations have dependent variables and derivatives that are of degree one and have coefficients that do not depend on the dependent variable. Several examples of different types of differential equations are provided.
Fractional calculus and applications



Fractional calculus and applicationsPlusOrMinusZero This document discusses fractional calculus and its applications. It begins with an introduction to fractional calculus, which involves defining derivatives and integrals of arbitrary real or complex order. Naive approaches to defining fractional derivatives are inconsistent. The document then motivates a rigorous definition by generalizing the formula for differentiation to non-integer orders. This generalized formula reduces to the standard formula when the order is a positive integer.
Linear differential equation



Linear differential equationPratik Sudra This document defines and provides examples of linear differential equations. It discusses:
1) Linear differential equations can be written in the form P(x)y'=Q(x) or P(y)x'=Q(y), where multiplying both sides by an integrating factor μ results in a total derivative.
2) First order linear differential equations of the form P(x)y'=Q(x) have an integrating factor of e∫P(x)dx. The general solution is y(IF)=C.
3) Bernoulli's equation is a differential equation of the form P(x)y'+Q(x)y^n=R(x), where the general solution depends
1st order differential equations



1st order differential equationsNisarg Amin 1) First order ordinary linear differential equations can be expressed in the form dy/dx = p(x)y + q(x), where p and q are functions of x.
2) There are several types of first order linear differential equations, including separable, homogeneous, exact, and linear equations.
3) Separable equations can be solved by separating the variables and integrating both sides. Homogeneous equations involve functions that are homogeneous of the same degree in x and y.
Runge Kutta Method 



Runge Kutta Method Bhavik Vashi This document summarizes the Runge-Kutta methods for solving differential equations numerically. It introduces the first, second, third, and fourth order Runge-Kutta methods and provides the equations for calculating each. An example of using the fourth order Runge-Kutta method to solve the differential equation dy/dx=x+y is shown step-by-step. The example calculates the solution to y(0.2) given y(0)=1 using increments of h=0.1.
Fourier series and its applications by md nazmul islam



Fourier series and its applications by md nazmul islamMd Nazmul Islam The document provides an introduction to Fourier series and their applications. It begins with defining a Fourier series as an expansion of a periodic function in terms of an infinite sum of sines and cosines. It then gives the general formula for a Fourier series representing a function f(x) within the interval [-L, L]. Several examples are shown, including finding the Fourier series for the function f(x)=x from 0 to 2π. Applications of Fourier series discussed include expanding periodic functions outside their intervals, noise cancellation, analyzing oscillating functions, simplifying waves, mapping heat distribution, and signal processing. Electrical circuits are described as equivalent to Fourier series representations of voltage sources. Fourier series are also used in signal processing to represent non
B.Tech-II_Unit-V



B.Tech-II_Unit-VKundan Kumar This document provides an overview of topics in vector integration, including line integrals, surface integrals, and volume integrals. It includes examples of calculating each type of integral. The key theorems covered are Green's theorem, Stokes' theorem, and Gauss's theorem of divergence. Green's theorem relates a line integral around a closed curve to a double integral over the enclosed region. Stokes' theorem relates a line integral around a closed curve to a surface integral over the enclosed surface. Gauss's theorem relates the surface integral of the normal component of a vector field over a closed surface to the volume integral of the divergence of the vector field over the enclosed volume.
Taylor series



Taylor seriesLittle Pari The document discusses the history and development of Taylor series. Some key points:
1) Brook Taylor introduced the general method for constructing Taylor series in 1715, after which they are now named. Taylor series represent functions as infinite sums of terms calculated from derivatives at a single point.
2) Special cases of Taylor series, like the Maclaurin series centered at zero, were explored earlier by mathematicians like Madhava and James Gregory.
3) Taylor series allow functions to be approximated by polynomials and are useful in calculus for differentiation, integration, and approximating solutions to problems in physics.
Linear differential equation with constant coefficient



Linear differential equation with constant coefficientSanjay Singh The document discusses linear differential equations with constant coefficients. It defines the order, auxiliary equation, complementary function, particular integral and general solution. It provides examples of determining the complementary function and particular integral for different types of linear differential equations. It also discusses Legendre's linear equations, Cauchy-Euler equations, and solving simultaneous linear differential equations.
Legendre functions



Legendre functionsSolo Hermelin The document discusses Legendre functions, which are solutions to Legendre's differential equation. Legendre functions arise when solving Laplace's equation in spherical coordinates. Legendre polynomials were first introduced by Adrien-Marie Legendre in 1785 as coefficients in an expansion of Newtonian potential. The document covers topics such as Legendre polynomials, Rodrigues' formula, orthogonality of Legendre polynomials, and associated Legendre functions.
Green Theorem



Green TheoremSarwan Ursani This document discusses Green's theorem, which relates a line integral around a simple closed curve C to a double integral over the plane region D bounded by C. It presents the statement of Green's theorem, which equates the line integral of P dx + Q dy around C to the double integral of (∂Q/∂x - ∂P/∂y) over D. An example problem demonstrates using Green's theorem to evaluate a line integral by transforming it into a double integral. Verifying the equality of the two approaches confirms Green's theorem for the given region.
Laplace transform 



Laplace transform 001Abhishek1 This document contains information about a Laplace transform topic presentation including:
- The names and enrollment numbers of 8 students working on the topic.
- The definition of the Laplace transform and some elementary functions transformed.
- Theorems on shifting, differentiation, integration, and multiplication of Laplace transforms.
- Examples of using Laplace transforms to evaluate integrals and find derivatives.
- The application of Laplace transforms to differential equations.
Fractional Calculus PP



Fractional Calculus PPVRRITC This document discusses fractional calculus and its history. Fractional calculus generalizes differentiation and integration to non-integer orders, starting in the 17th century with ideas from Leibniz. It provides definitions for fractional integration using the Riemann-Liouville approach and fractional differentiation as the inverse of fractional integration. The document serves as an introduction to fractional kinetics and optimal control problems.
presentation on Euler and Modified Euler method ,and Fitting of curve 



presentation on Euler and Modified Euler method ,and Fitting of curve Mukuldev Khunte presentation on Euler and Modified Euler method with working and example ,and Fitting of Nonlinear curve using Method of least square
Cauchy integral theorem & formula (complex variable & numerical method )



Cauchy integral theorem & formula (complex variable & numerical method )Digvijaysinh Gohil 1) The document discusses the Cauchy Integral Theorem and Formula. It states that if a function f(z) is analytic inside and on a closed curve C, then the integral of f(z) around C is equal to 0.
2) It provides examples of evaluating integrals using the Cauchy Integral Theorem when the singularities lie outside the closed curve C.
3) The Cauchy Integral Formula is introduced, which expresses the value of an analytic function F(a) inside C as a contour integral around C. Examples are worked out applying this formula to find the value and derivatives of functions at points inside C.
Laplace equation



Laplace equationalexkhan129 This document discusses techniques for calculating electric potential, including:
1. Laplace's equation and its solutions in 1D, 2D, and 3D, including boundary conditions.
2. The method of images, which uses fictitious "image" charges to solve problems involving conductors. The classical image problem and induced surface charge on a conductor are examined.
3. Other techniques like multipole expansion, separation of variables, and numerical methods like relaxation are mentioned but not explained in detail.
Application of fourier series



Application of fourier seriesGirish Dhareshwar The document discusses sampling and the Fourier transform. It explains that sampling is the process of taking signal samples at intervals, and must be at least twice the maximum frequency to avoid aliasing. It also discusses how the Fourier transform can be used to calculate the frequency, amplitude, and phase of sampled signals to reconstruct the original signal. The Fourier transform of basic functions like 1, cosine, and exponentials are presented.
Laplace Transform And Its Applications



Laplace Transform And Its ApplicationsSmit Shah In this slide given detail description about Laplace Transform And Its Applications formulas examples etc...
Viewers also liked (20)
Fourier series expansion



Fourier series expansionFrancesco Zoino This document discusses Fourier series expansion and spectral analysis. It explains that while signals exist in the time domain, they can be represented in the frequency domain as a series of sinusoidal components at different frequencies. This frequency domain description is called spectral analysis. Spectral analysis of signals coupled with the frequency response of systems allows for better design work, as the behavior of a linear time-invariant system can be studied using sinusoidal signals. Fourier series expansion represents periodic functions as a series of sinusoidal functions, and was developed based on the work of French mathematician Jean Baptiste Joseph Fourier.
fourier series



fourier series8laddu8 The document discusses Fourier series, which represent periodic functions as an infinite series of sines and cosines. Fourier series can be used to represent functions that are discontinuous or non-differentiable. The key formulas for the Fourier series coefficients are presented. Fourier series expansions take different forms depending on whether the function is even, odd, or defined on different intervals. Half-range Fourier series are also discussed as representations of functions defined on half periods.
Fourier series basic results



Fourier series basic resultsTarun Gehlot The document discusses Fourier series and polynomials. It defines a Fourier polynomial as a finite sum of trigonometric terms with coefficients. Fourier polynomials are periodic functions. Integral formulas are provided for the coefficients of Fourier series. A theorem states that any periodic function can be associated with a Fourier series whose coefficients are given by the integral formulas. Examples show calculating the Fourier series for some simple periodic functions. The discussion is extended to functions that are periodic over an interval of length L rather than just 2π.
Half range sine and cosine series



Half range sine and cosine seriesChandan S The document discusses half-range Fourier series expansions for functions defined over a finite interval. Specifically, it explains that if a function f(x) is even or odd over the interval [0,L], it can be expressed using either a cosine or sine series just over the interval [0,L]. This is referred to as a half-range Fourier series. Examples are provided of using half-range sine and cosine series to expand specific functions like f(x)=x2 and f(x)=x over intervals like [0,l].
Solved numerical problems of fourier series



Solved numerical problems of fourier seriesMohammad Imran This document is a report by Mohammad Imran on solved numerical problems of Fourier series. It discusses Fourier series and provides solutions to questions involving Fourier series. The report is presented to the Jahangirabad Institute of Technology as part of a semester 2 course on the topic of Fourier series.
Fourier series



Fourier seriesMohammad Shakirul islam A Fourier series may be defined as an expansion of a function in a series of sines and cosines such as.
periodic functions and Fourier series



periodic functions and Fourier seriesUmang Gupta This document discusses periodic functions and Fourier series. A periodic function repeats its values over regular intervals called periods. The Fourier series represents periodic functions as the sum of trigonometric functions (sines and cosines) with different frequencies. The document derives the formulas to calculate the coefficients of the Fourier series from a given periodic function. It involves integrating the function multiplied by sines and cosines over one period of the function.
the fourier series



the fourier seriessafi al amu This document provides an overview of Fourier series and Fourier transforms. It discusses the history of Fourier analysis and how Fourier introduced Fourier series to solve heat equations. It defines Fourier series and covers topics like odd and even functions, half-range Fourier series, and the complex form of Fourier series. The document also discusses the relationship between Fourier transforms and Laplace transforms. It concludes by listing some applications of Fourier analysis in fields like electrical engineering, acoustics, optics, and more.
Laplace periodic function with graph



Laplace periodic function with graphKaushal Surti This document provides information about the Laplace transform of periodic functions. It discusses the Laplace transform of periodic square waves, triangular waves, sawtooth waves, and staircase functions. It also discusses the Laplace transform of full-wave and half-wave rectification of a sine wave. Examples are provided to show how to calculate the Laplace transform of each of these periodic and rectified functions.
1531 fourier series- integrals and trans



1531 fourier series- integrals and transDr Fereidoun Dejahang Mathematics (from Greek μάθημα máthēma, “knowledge, study, learning”) is the study of topics such as quantity (numbers), structure, space, and change. There is a range of views among mathematicians and philosophers as to the exact scope and definition of mathematics
Aplicaicones de las series de fourier

Aplicaicones de las series de fouriernorelis15 Este documento describe los métodos de análisis frecuencial de señales continuas y discretas a través de la serie y transformada de Fourier. Explica cómo la serie de Fourier puede usarse para descomponer señales periódicas en componentes de diferentes frecuencias. También describe la transformada de Fourier y cómo puede aplicarse a señales aperiódicas. Finalmente, cubre el análisis frecuencial de señales discretas a través de la serie de Fourier discreta.
Fourier series and fourier integral



Fourier series and fourier integralashuuhsaqwe - The document discusses Fourier series and integrals.
- Fourier series decomposes a periodic function into a sum of sines and cosines. It is useful for representing periodic and discontinuous functions.
- There are three types of Fourier integrals: the general Fourier integral, Fourier cosine integral, and Fourier sine integral. These are used to represent functions over infinite intervals.
Fourier series example



Fourier series exampleAbi finni This MATLAB code provides an example of plotting a truncated Fourier series representation of a square wave signal. It computes the Fourier series in both complex exponential form (yce) and trigonometric form (yt) up to the Nth term, where N is an odd integer. It plots the original square wave, the truncated Fourier series approximations yce and yt, and their amplitude and phase spectra. The code demonstrates how to calculate and visualize truncated Fourier series representations of a periodic signal.
Introduction to fourier analysis



Introduction to fourier analysisSchool of Design Engineering Fashion & Technology (DEFT), University of Wales, Newport The following presentation is a part of the level 4 module -- Electrical and Electronic Principles. This resources is a part of the 2009/2010 Engineering (foundation degree, BEng and HN) courses from University of Wales Newport (course codes H101, H691, H620, HH37 and 001H). This resource is a part of the core modules for the full time 1st year undergraduate programme.
The BEng & Foundation Degrees and HNC/D in Engineering are designed to meet the needs of employers by placing the emphasis on the theoretical, practical and vocational aspects of engineering within the workplace and beyond. Engineering is becoming more high profile, and therefore more in demand as a skill set, in today’s high-tech world. This course has been designed to provide you with knowledge, skills and practical experience encountered in everyday engineering environments.
Fourier Series for Continuous Time & Discrete Time Signals



Fourier Series for Continuous Time & Discrete Time SignalsJayanshu Gundaniya - Fourier introduced Fourier series in 1807 to solve the heat equation in a metal plate. The heat equation is a partial differential equation describing the distribution of heat in a body over time.
- Prior to Fourier's work, there was no known solution to the heat equation in the general case. Fourier's idea was to model a complicated heat source as a superposition of simple sine and cosine waves.
- This superposition or linear combination of sine and cosine waves is called the Fourier series. It allows any periodic function to be decomposed into the sum of simple oscillating functions. Although originally introduced for heat problems, Fourier series have wide applications in mathematics and physics.
Important Questions of fourier series with theoretical study Engg. Mathem...



Important Questions of fourier series with theoretical study Engg. Mathem...Mohammad Imran This document provides information about Fourier series and even/odd functions from the Jahangirbad Institute of Technology. It defines Fourier series and even/odd functions, lists their properties, and provides 14 important questions about finding Fourier series for various periodic functions over different intervals. The questions aim to find the Fourier series and deduce trigonometric identities.
SDEE: Lectures 3 and 4



SDEE: Lectures 3 and 4Alessandro Palmeri This document summarizes key points from lectures on Fourier analysis and frequency response functions for single degree of freedom oscillators. It recaps concepts like natural frequency, damping ratio, and dynamic amplification factor. It introduces Fourier series as a way to decompose periodic signals into harmonic components. The Fourier transform is presented as a way to study the frequency content of both periodic and non-periodic signals. Examples are given to illustrate the effects of varying parameters in the time and frequency domains.
AEM Fourier series



AEM Fourier seriesSiddhi Viradiya The document discusses Fourier series and their applications. It provides the general forms of the Fourier series for even and odd functions over a periodic interval. The key points are:
- Fourier series can be used to represent functions as an infinite sum of sines and cosines, known as harmonic analysis.
- They have wide applications in fields like signal processing, vibrations, and heat transfer.
- The Fourier series for an even function contains only cosine terms, while an odd function contains only sine terms.
- The Fourier coefficients are found using the orthogonal properties of sines and cosines and integrating the function over the period.
Fourier series and transforms



Fourier series and transformsPepa Vidosa Serradilla This document discusses Fourier series and transforms. It begins by introducing periodic functions and their fundamental periods. It then defines Fourier series and derives the formulas for the Fourier coefficients. Several examples of calculating Fourier series are provided. It also covers Fourier series for functions with any period, complex Fourier series, Parseval's identity and its applications, and Dirichlet's theorem. The key topics of Fourier series, Fourier transforms, and their applications in engineering mathematics are covered over multiple sections.
Indian Films Women Sex Roles



Indian Films Women Sex RolesPublic Federal Company To Analyze the Indian Films Business Strategy in the Industry to motivates the Market using Nudity and Damaged impacts reflected of the women or Girls in the society.
Introduction to fourier analysis



Introduction to fourier analysisSchool of Design Engineering Fashion & Technology (DEFT), University of Wales, Newport
Similar to Fourier series (20)
ilovepdf_merged.pdf



ilovepdf_merged.pdfNaorinHalim This document provides an overview of Fourier series and related concepts. It defines a Fourier series as an expansion of a periodic function in terms of an infinite sum of sines and cosines. It also describes formulas for general Fourier series, solving examples, discontinuous functions, the change of interval method, even and odd functions, and half range Fourier cosine and sine series.
Math 1102-ch-3-lecture note Fourier Series.pdf



Math 1102-ch-3-lecture note Fourier Series.pdfhabtamu292245 1. The document discusses Fourier series and orthogonal functions. It defines orthogonal functions and provides examples of orthogonal function sets, such as cosine and sine functions.
2. The chief advantage of orthogonal functions is that they allow functions to be represented as generalized Fourier series expansions. The orthogonality of the functions helps determine the Fourier coefficients in a simple way using integrals.
3. Euler's formulae give the expressions for calculating the Fourier coefficients a0, an, and bn of a periodic function f(x) from its values over one period using integrals of f(x) multiplied by cosine and sine terms.
Rvtvtbthtbrvrvthrbrhtjrhrjtjrgtjtgrhrpde.ppt



Rvtvtbthtbrvrvthrbrhtjrhrjtjrgtjtgrhrpde.pptshivamvadgama50 The document discusses Fourier series and periodic functions. Some key points:
1. A periodic function f(x) satisfies f(x+T)=f(x) for some period T. The Fourier series of a periodic function f(x) represents f(x) as the sum of sines and cosines with frequencies that are integer multiples of 1/T.
2. The Fourier coefficients are calculated by taking integrals of f(x) multiplied by sine and cosine functions over one period.
3. The Fourier series converges to the average of the left and right limits of f(x) at points of discontinuity, and converges to f(x) itself at points of continuity.
Crib Sheet AP Calculus AB and BC exams



Crib Sheet AP Calculus AB and BC examsA Jorge Garcia This document provides a summary of key concepts that must be known for AP Calculus, including:
- Curve sketching and analysis of critical points, local extrema, and points of inflection
- Common differentiation and integration rules like product rule, quotient rule, trapezoidal rule
- Derivatives of trigonometric, exponential, logarithmic, and inverse functions
- Concepts of limits, continuity, intermediate value theorem, mean value theorem, fundamental theorem of calculus
- Techniques for solving problems involving solids of revolution, arc length, parametric equations, polar curves
- Series tests like ratio test and alternating series error bound
- Taylor series approximations and common Maclaurin series
1.1 Elementary Concepts.pdf



1.1 Elementary Concepts.pdfd00a7ece This document provides information on Fourier series and Fourier coefficients over various intervals. It defines the Fourier series representation of a periodic function f(x) over a general interval (–l, l) and the interval (–π, π). It also gives the formulas for the Fourier coefficients in the cases when f(x) is even or odd. The document concludes with a table of common Fourier series representations and a list of frequently used formulas for computing Fourier coefficients.
1.1 elementary concepts



1.1 elementary conceptsd00a7ece This document provides information on Fourier series and Fourier coefficients over various intervals. It defines the Fourier series representation of a periodic function f(x) over a general interval (–l, l) and the interval (–π, π). It also gives the formulas for the Fourier coefficients in the cases when f(x) is even or odd. The document concludes with a table of common Fourier series representations and a list of frequently used formulas for computing Fourier coefficients.
TPDE_UNIT II-FOURIER SERIES_PPT.pptx



TPDE_UNIT II-FOURIER SERIES_PPT.pptxragavvelmurugan 1. The Fourier series expansion of the function f(x) = x^2 from 0 to 2π consists of only cosine terms.
2. The Fourier coefficients are found to be an = 0 for all odd n, and an = 3/4n^2 for all even n.
3. Evaluating the Fourier series at x = 0 recovers the fact that f(0) = 0, as it must at a point of discontinuity for the original function.
senior seminar



senior seminarJose Stewart This document discusses Fourier series and their applications. It contains the following key points:
1. Fourier introduced Fourier series to solve heat equations through metal plates, expressing functions as infinite sums of sines and cosines.
2. Sine and cosine functions are orthogonal and periodic, allowing any piecewise continuous periodic function to be represented by a Fourier series.
3. The Euler-Fourier formulas relate the Fourier coefficients to the function, allowing the coefficients to be determined.
4. Even functions only have cosine terms, odd only sine, and the Fourier series converges to the average at discontinuities for piecewise continuous functions.
Fourier 3



Fourier 3nugon The document discusses Fourier series and their applications. It begins by introducing how Fourier originally developed the technique to study heat transfer and how it can represent periodic functions as an infinite series of sine and cosine terms. It then provides the definition and examples of Fourier series representations. The key points are that Fourier series decompose a function into sinusoidal basis functions with coefficients determined by integrating the function against each basis function. The series may converge to the original function under certain conditions.
Chapter 4 Fourier Series.pptx



Chapter 4 Fourier Series.pptxAshDenem This document discusses Fourier series and periodic functions. It defines a periodic function as one where f(x+T)=f(x) for some positive number T. The Fourier series of a periodic function with period T can be expressed as the sum of sines and cosines with frequencies that are integer multiples of 1/T. It also discusses even and odd functions, noting that the Fourier series of an even function contains only cosine terms, while the Fourier series of an odd function contains only sine terms. Examples are provided of finding the Fourier series for specific periodic functions.
160280102001 c1 aem



160280102001 c1 aemL.D. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING 1) Fourier series and integrals are used to represent periodic functions as an infinite sum or integral of sines and cosines. They are useful for solving differential equations.
2) The Fourier series of a periodic function f(x) with period T is the sum of its coefficients multiplied by sines and cosines of integer multiples of x/T. The coefficients are calculated using integrals involving f(x).
3) Half range expansions like half range cosines (HRC) and half range sines (HRS) are used when f(x) is defined on a finite interval, by extending it to a periodic function on the entire real line.
Nt lecture skm-iiit-bh



Nt lecture skm-iiit-bhIIIT Bhubaneswar This document discusses network theory and Fourier analysis. It begins by introducing Fourier series, which represent periodic functions as the sum of sinusoidal waves. Both trigonometric and exponential forms of Fourier series are covered. It then discusses Fourier transforms, which extend the frequency spectrum concept to non-periodic functions by assuming an infinite period. Key topics include Fourier series coefficients, amplitude and phase spectra, waveform symmetries, and applications of Fourier analysis in network analysis. Fourier transforms represent the frequency spectrum of non-periodic signals through an integral transform analogous to Fourier series.
Signal & system



Signal & systemGhulam Shabbir This document chapter discusses the characterization and representation of communication signals and systems. It describes how band-pass signals and systems can be represented by equivalent low-pass signals and systems using analytic signal representations and complex envelopes. It also discusses how the response of a band-pass system to a band-pass input signal can be determined from the equivalent low-pass representations. Key topics covered include the Fourier transform, Hilbert transform, and convolution properties used to relate band-pass and low-pass signal and system representations.
Fourier series of odd functions with period 2 l



Fourier series of odd functions with period 2 lPepa Vidosa Serradilla 1) The document provides review material for Exam 3 of Math 285 including definitions of piecewise continuous and piecewise smooth functions and the convergence theorem for Fourier series.
2) It also defines Fourier series for periodic piecewise continuous functions and discusses Fourier sine and cosine series for odd and even functions.
3) Applications of Fourier series include using them to find formal solutions to boundary value problems involving differential equations.
maths ppt.pdf



maths ppt.pdfnihaiqbal1 The document discusses Fourier series and periodic functions. It provides:
- Definitions of Fourier series and periodic functions.
- Examples of periodic functions including trigonometric and other functions.
- Euler's formulae for calculating the coefficients of a Fourier series.
- Integration properties used to solve Fourier series problems.
- Two examples of determining the Fourier series for given periodic functions and using it to deduce mathematical results.
maths ppt.pdf



maths ppt.pdfnihaiqbal1 The document discusses Fourier series and periodic functions. It provides:
- Definitions of Fourier series and periodic functions.
- Examples of periodic functions including trigonometric and other functions.
- Integration properties used to solve Fourier series problems.
- Two examples showing the steps to obtain the Fourier series of given periodic functions in a specified interval.
fourierseries-121010133546-phpapp02.pdf



fourierseries-121010133546-phpapp02.pdfdiehardgamer1 Fourier series can be used to represent periodic functions or functions on an interval. They involve expanding the function as a sum of sines and cosines. Fourier series are useful because they can represent discontinuous functions, unlike Taylor series. When expanding a function over an interval, the Fourier series is only guaranteed to apply over that initial interval unless additional information is given about the periodicity of the function. Fourier series can be adapted to any periodic interval by changing the variables. As an example application, a square wave can be analyzed using its Fourier components via a Fourier series expansion.
Fourier series 2.ppt



Fourier series 2.pptBlisterCount The document discusses Fourier series for functions with an arbitrary period p=2L. It explains that to define the Fourier series in this case, the variable x needs to be replaced with (π/L)x, so that when x=L, the new variable equals π and when x=-L it equals -π. This allows the previous Fourier series formulas to be used with this change of variable. It also discusses even and odd functions and how their Fourier series take the form of either a Fourier cosine series or Fourier sine series, and introduces the concept of a half range expansion which is useful when a function is only defined on a finite interval like between 0 and L.
lecture_6_-_fourier_series_0.pdf



lecture_6_-_fourier_series_0.pdfHendIbrahim35 The document provides an overview of Fourier series. Key points include:
- Fourier series decompose periodic functions into the sum of sines and cosines, allowing representation as a series.
- They are named after Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier who introduced them to solve heat equations.
- Fourier series have advantages like representing discontinuous functions and periodic phenomena with a linear system of harmonics.
- The coefficients of the Fourier series define the contribution of each harmonic term to the overall function representation.
Recently uploaded (20)
Defining the Future of Biophilic Design in Crete.pdf



Defining the Future of Biophilic Design in Crete.pdfARENCOS Biophilic design is emerging as a key approach to enhancing well-being by integrating natural elements into residential architecture. In Crete, where the landscape is rich with breathtaking sea views, lush olive groves, and dramatic mountains, biophilic design principles can be seamlessly incorporated to create healthier, more harmonious living environments.
AI ppt on water jug problem by shivam sharma



AI ppt on water jug problem by shivam sharmaShivamSharma588604 this ppt is made on the topic of water jug problem.
INVESTIGATION OF PUEA IN COGNITIVE RADIO NETWORKS USING ENERGY DETECTION IN D...



INVESTIGATION OF PUEA IN COGNITIVE RADIO NETWORKS USING ENERGY DETECTION IN D...csijjournal Primary User Emulation Attack (PUEA) is one of the major threats to the spectrum sensing in cognitive
radio networks. This paper studies the PUEA using energy detection that is based on the energy of the
received signal. It discusses the impact of increasing the number of attackers on the performance of
secondary user. Moreover, studying how the malicious user can emulate the Primary User (PU) signal is
made. This is the first analytical method to study PUEA under a different number of attackers. The
detection of the PUEA increases with increasing the number of attackers and decreases when changing the
channel from lognormal to Rayleigh fading.
ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-3



ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-3prasadmutkule1 ESIT135 Problem Solving Using Python Notes of Unit-3
How to Build a Speed Sensor using Arduino?



How to Build a Speed Sensor using Arduino?CircuitDigest Learn how to measure speed using IR sensors in this simple DIY project. This tutorial cover circuit diagram, Sensor calibration and speed calculations and optimized Arduino code for real time speed measurements.
AIR FILTER system in internal combustion engine system.ppt



AIR FILTER system in internal combustion engine system.pptthisisparthipan1 air filter system in ic engine
Helium Boosting & Decanting With Hydro Test Machine



Helium Boosting & Decanting With Hydro Test MachinePaskals Fluid Systems Pvt. Ltd. About:
A helium boosting and decanting system is typically used in various industrial applications, particularly in the production and handling of gases, including helium including leak test of reciprocating cylinder. Here’s a brief overview of its components and functions:
Components
1. Helium Storage Tanks: High-pressure tanks that store helium@ 150 bars.
2. Boosting Pumps: Designed to boost helium pressure up to 150 bar, ensuring efficient flow throughout the system.
3. Decanting Unit: Separates liquid helium from gas, facilitating decanting at pressures of up to 2 bars.
4. Pressure Regulators: Maintain and control the pressure of helium during transport.
5. Control Valves: automatic control valve is provided for the flow and direction of helium through the system.
6. Piping and Fittings: High-quality, corrosion-resistant materials for safe transport.
Functions
• Boosting Pressure: The system boosts helium pressure up to 150 bar for various applications.
• Decanting: Safely decants helium, separating liquid from gas at pressures of up to 2 bar.
• Safety Measures: Equipped with relief valves and emergency shut-off systems to handle high pressures safely.
• Monitoring and Control: Sensors and automated controls monitor pressure and flow rates.
Application:
• Cryogenics: Cooling superconducting magnets in MRI machines and particle accelerators.
• Welding: Used as a shielding gas in welding processes.
• Research: Crucial for various scientific applications, including laboratories and space exploration.
Key Features:
• Helium Storage & Boosting System
• Decanting System
• Pressure Regulation & Monitoring
• Valves & Flow Control
• Filtration & Safety Components
• Structural & Material Specifications
• Automation & Electrical Components
Data recovery and Digital evidence controls in digital frensics.pdf



Data recovery and Digital evidence controls in digital frensics.pdfAbhijit Bodhe This topic contain information about Data recovery and Digital evidence controls in cyber and digital awareness
Indian Soil Classification System in Geotechnical Engineering



Indian Soil Classification System in Geotechnical EngineeringRajani Vyawahare This PowerPoint presentation provides a comprehensive overview of the Indian Soil Classification System, widely used in geotechnical engineering for identifying and categorizing soils based on their properties. It covers essential aspects such as particle size distribution, sieve analysis, and Atterberg consistency limits, which play a crucial role in determining soil behavior for construction and foundation design. The presentation explains the classification of soil based on particle size, including gravel, sand, silt, and clay, and details the sieve analysis experiment used to determine grain size distribution. Additionally, it explores the Atterberg consistency limits, such as the liquid limit, plastic limit, and shrinkage limit, along with a plasticity chart to assess soil plasticity and its impact on engineering applications. Furthermore, it discusses the Indian Standard Soil Classification (IS 1498:1970) and its significance in construction, along with a comparison to the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS). With detailed explanations, graphs, charts, and practical applications, this presentation serves as a valuable resource for students, civil engineers, and researchers in the field of geotechnical engineering.
Improving Surgical Robot Performance Through Seal Design.pdf



Improving Surgical Robot Performance Through Seal Design.pdfBSEmarketing Ever wonder how something as "simple" as a seal can impact surgical robot accuracy and reliability? Take quick a spin through this informative deck today, and use what you've learned to build a better robot tomorrow.
Renewable-Energy-Powering-Mozambiques-Economic-Growth.pptx



Renewable-Energy-Powering-Mozambiques-Economic-Growth.pptxRofino Licuco Mozambique, a country with vast natural resources and immense potential, nevertheless faces several economic challenges, including high unemployment, limited access to energy, and an unstable power supply. Underdeveloped infrastructure has slowed the growth of industry and hampered people’s entrepreneurial ambitions, leaving many regions in the dark—literally and figuratively.
https://www.rofinolicuco.net/blog/how-renewable-energy-can-help-mozambique-grow-its-economy
Fourier series
- 1. GUJARAT POWER ENGINEERING AND RESEARCH INSTITUTE ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS FOURIER SERIES
- 2. GROUP MEMBERS Pinky Chaudhari (131040109006) Harwinder Kaur(131040109015) Vibha Patel (131040109044) Samia Zehra (131040109052) Guided By : Prof. Nirav S. Modi
- 3. INDEX Fourier Series General Fourier Discontinuous Functions Change Of Interval Method Even And Odd Functions Half Range Fourier Cosine & Sine Series
- 4. FOURIER SERIES A Fourier series is an expansion of a periodic function in terms of an infinite sum of sines and cosines.
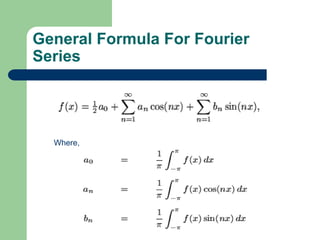
- 5. General Formula For Fourier Series Where,
- 6. Formulas To Solve Examples 2SC = S + S 2CS = S – S 2CC = C + C 2SS = cos(α-β) –cos(α+β) Even*Odd = Odd Even*Even = Even Odd*Odd = Even Odd*Even = Odd
- 7. uv uv1 u 'v2 u''v3 u'''v4 ________ Where, u, u’, u”, u’’’,_ _ _ _ are denoted by derivatives. And V1,v2,v3,v4,_ _ _ _ _ are denoted by integral.
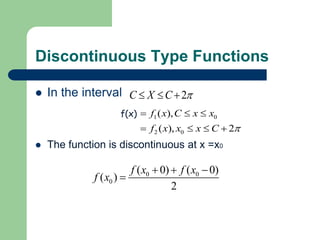
- 8. Discontinuous Type Functions In the interval C X C2 f x C x x f x x x C ( ), ( ), 2 1 0 2 0 f(x) The function is discontinuous at x =x0 f x f x 0 0 0 ( 0) ( 0) ( ) 2 f x
- 9. So Fourier series formula is x C 0 2 a f x dx f x dx 0 1 2 0 1 ( ) ( ) C x x C 0 2 a f x nx dx f x nx dx 1 2 0 x C 0 2 b f x nx dx f x nx dx 1 2 0 1 ( )*sin( ) ( )*sin( ) n C x 1 ( )*cos( ) ( )*cos( ) n C x
- 10. Change Of Interval Method In this method , function has period P=2L , where L is any integer number. In interval 0<x<2L Then l = L/2 When interval starts from 0 then l = L/2 In the interval –L < X < L Then l = L For discontinuous function , Take l = C where C is constant.
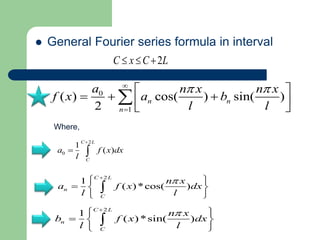
- 11. General Fourier series formula in interval C x C 2L a n x n x f x a b ( ) cos( ) sin( ) 2 n n a f x dx C L 2 2 1 2 1 ( )*cos( ) ( )*sin( ) C L n C n x b f x dx l l n C n x a f x dx l l 0 1 ( ) C L C l 0 1 n l l Where,
- 12. Even Function f (x) f (x) The graph of even function is symmetrical about Y – axis. Examples : 2 2 x , x ,cos x, x cos x, xsin x
- 13. Fourier series for even function 1. In the interval x 0 ( ) cos( ) 1 0 0 2 0 2 n ( ) 2 n ( )*cos( ) n a f x a nx a f x dx a f x nx dx
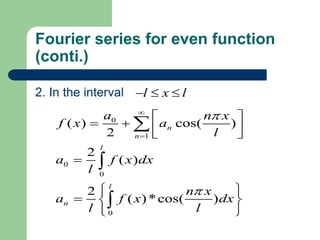
- 14. Fourier series for even function (conti.) 2. In the interval l x l 0 ( ) cos( ) 1 0 0 2 0 2 n ( ) 2 n ( )*cos( ) l l n a n x f x a l a f x dx l n x a f x dx l l
- 15. Odd Function f (x) f (x) The graph of odd function is passing through origin. Examples:- 3 3 x, x , x cos x,sin x, x cos x
- 16. Fourier series for odd function 1. In the interval x f x b nx ( ) sin( ) 1 b f x nx dx 0 2 n ( ) sin( ) n n
- 17. Fourier series for odd function (conti.) In the interval l x l ( ) sin( ) 1 0 2 n ( ) sin( ) n n n f x b x l n b f x x dx l
- 18. Half Range Fourier Cosine Series In this method , we have 0 < x < π or 0 < x < l type interval. In this method , we find only a0 and an . bn = 0
- 19. Half Range Fourier Cosine Series 1.In the interval 0 < x < π 0 ( ) cos( ) 1 0 0 2 0 2 n ( ) 2 n ( )*cos( ) n a f x a nx a f x dx a f x nx dx
- 20. Half Range Fourier Cosine Series(conti.) 2. In the interval 0 < x < l Take l = L 0 ( ) cos( ) 1 0 0 2 0 2 n ( ) 2 n ( )*cos( ) l l n a n x f x a l a f x dx l n x a f x dx l l
- 21. Half Range Fourier Sine Series In this method , we find only bn an =0 a0 =0
- 22. Half Range Fourier Sine Series 1. In interval 0 < x < π f x b nx ( ) sin( ) 1 b f x nx dx 0 2 n ( ) sin( ) n n
- 23. Half Range Fourier Sine Series (conti.) 2. In the interval 0 < x < l ( ) sin( ) 1 0 2 n ( ) sin( ) n n n f x b x l n b f x x dx l
- 24. Thank you!!!










