mechanism of filtration, surface and depth filters
- 1. Filtration Prepared By: Saqib Salman (16103123-041) Department of Chemical Engineering University of Gujrat, Gujrat, Pakistan.
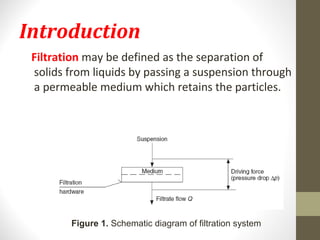
- 2. Introduction Filtration may be defined as the separation of solids from liquids by passing a suspension through a permeable medium which retains the particles. Figure 1. Schematic diagram of filtration system
- 3. The fine apertures necessary for filtration are provided by fabric filter cloths, by meshes and screens of plastics or metals, by beds of solid particles. In some cases, a thin preliminary coat of cake, or of other fine particles, is put on the cloth prior to the main filtration process.
- 4. Types of filtration 1. Surface filters 2. Depth filters
- 5. 1.Surface filters used for cake filtration in which the solids are deposited in the form of a cake on the up-stream side of a relatively thin filter medium. Figure2. Mechanism of cake filtration
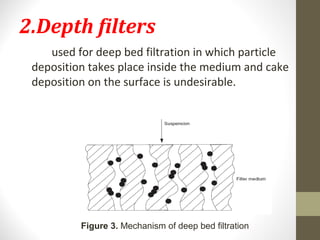
- 6. 2.Depth filters used for deep bed filtration in which particle deposition takes place inside the medium and cake deposition on the surface is undesirable. Figure 3. Mechanism of deep bed filtration
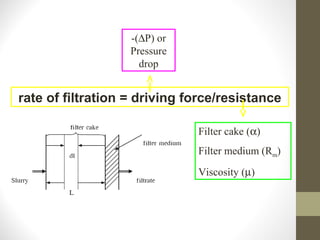
- 7. The fluid passes through the filter medium, which offers resistance to its passage, under the influence of a force which is the pressure differential across the filter. rate of filtration = driving force/resistance
- 8. Filtration Media: It can be considered as the heart of the filtration device or machine. Provides adequate porosity capable of passing liquid through, while retaining solids Medium is characterized by its filtration properties of permeability and retention. It can be • Natural • Synthetic or glass • Woven cloth • Paper • Ceramic
- 9. Factor affected on filtration • Pressure drop ( ∆P ) • Area of filtering surface ( A ) • Viscosity of filtrate ( v ) • Resistance of filter cake ( α ) • Resistance of filter medium ( Rm) • Properties of slurry ( μ , ฯฯฯ )
- 10. rate of filtration = driving force/resistance -(∆P) or Pressure drop Filter cake (α) Filter medium (Rm) Viscosity (µ)