12. Inter trochanteric fracture
- 1. By :- Dr. Bindesh D. Patel, PT Deputy Registrar P P Savani University Inter-trochanteric fracture
- 2. • May involve either greater trochanter or lesser trochanter or both • Elderly by minor force • Adult by major force • Femoral neck shaft angle is reduced (Coxa vara) • Comminuted and displaced fracture • Very rarely undisplaced fracture
- 3. Diagnosis • Clinical features • History of fall or accident • Pain, swelling, tenderness • Inability to move leg • Physical findings are more marked compared to neck of femur fracture
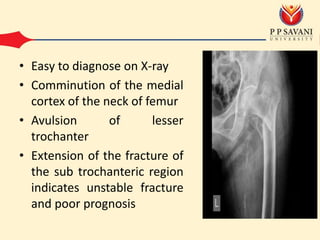
- 4. • Easy to diagnose on X-ray • Comminution of the medial cortex of the neck of femur • Avulsion of lesser trochanter • Extension of the fracture of the sub trochanteric region indicates unstable fracture and poor prognosis
- 5. Treatment • It unites readily • Main objective is to maintain a normal femoral neck shaft angle • In elderly patient, ORIF is preferred to prevent complications
- 6. • Conservative method – Russell’s traction and – Thomas splint
- 7. • Operative method – Internal fixation used are • Dynamic Hip Screw • Ender’s nail • Gamma nail – External fixation is used for patients with bed sores
- 10. Complications • Malunion – Coxa vara – Elderly mild limping while walking and shortening – Suitable shoe raise – Adult – Corrective osteotomy
- 11. • Osteoarthritis – Due to change in hip biomechanics – Pain and stiffness – Physiotherapy treatment – Later trochanteric osteotomy or THR
- 12. Thank you
- 13. Please share the video and subscribe my channel.