ANTIHYPERTENSIVES DRUGS MOA , ADVERSE EFFECTS
- 2. The Heart
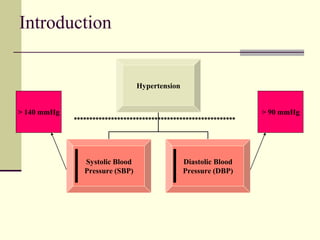
- 3. Introduction Hypertension Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP) Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP) > 140 mmHg > 90 mmHg ****************************************************
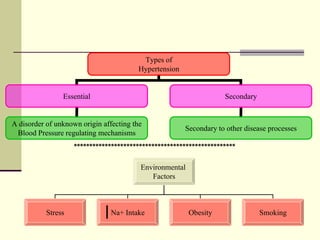
- 4. Types of Hypertension Essential Secondary A disorder of unknown origin affecting the Blood Pressure regulating mechanisms Secondary to other disease processes Environmental Factors Stress Na+ Intake Obesity Smoking ****************************************************
- 5. Treatment – Why? Symptomatic treatment is Mandatory: Damage to the vascular epithelium, paving the path for atherosclerosis (IHD, CVA) or nephropathy due to high intra-glomerular pressure Increased load on heart due to high BP can cause CHF Hypertension, even asymptomatic needs treatment
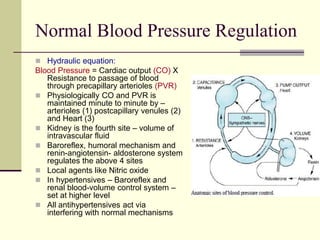
- 6. Normal Blood Pressure Regulation Hydraulic equation: Blood Pressure = Cardiac output (CO) X Resistance to passage of blood through precapillary arterioles (PVR) Physiologically CO and PVR is maintained minute to minute by – arterioles (1) postcapillary venules (2) and Heart (3) Kidney is the fourth site – volume of intravascular fluid Baroreflex, humoral mechanism and renin-angiotensin- aldosterone system regulates the above 4 sites Local agents like Nitric oxide In hypertensives – Baroreflex and renal blood-volume control system – set at higher level All antihypertensives act via interfering with normal mechanisms
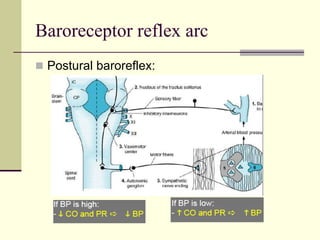
- 7. Baroreceptor reflex arc Postural baroreflex:
- 8. The Renal response Long-term blood pressure control – by controlling blood volume Reduction in renal pressure - intrarenal redistribution of pressure and increased absorption of salt and water Decreased pressure in renal arterioles and sympathetic activity – renin production – angiotensin II production Angiotensin II: Causes direct constriction of renal arterioles Stimulation of aldosterone synthesis – sodium absorption and increase in intravascular blood volume
- 9. Antihypertensive Drugs Diuretics: Thiazides: Hydrochlorothiazide, chlorthalidone High ceiling: Furosemide K+ sparing: Spironolactone, triamterene and amiloride MOA: Acts on Kidneys to increase excretion of Na and H2O – decrease in blood volume – decreased BP Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: Captopril, lisinopril., enalapril, ramipril and fosinopril MOA: Inhibit synthesis of Angiotensin II – decrease in peripheral resistance and blood volume Angiotensin (AT1) blockers: Losartan, candesartan, valsartan and telmisartan MOA: Blocks binding of Angiotensin II to its receptors
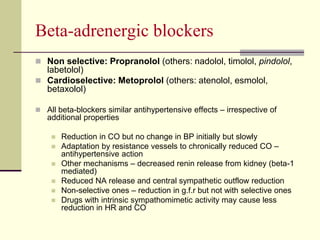
- 10. Antihypertensive Drugs Centrally acting: Clonidine, methyldopa MOA: Act on central α2A receptors to decrease sympathetic outflow – fall in BP ß-adrenergic blockers: Non selective: Propranolol (others: nadolol, timolol, pindolol, labetolol) Cardioselective: Metoprolol (others: atenolol, esmolol, betaxolol) MOA: Bind to beta adrenergic receptors and blocks the activity ß and α – adrenergic blockers: Labetolol and carvedilol α – adrenergic blockers: Prazosin, terazosin, doxazosin, phenoxybenzamine and phentolamine MOA: Blocking of alpha adrenergic receptors in smooth muscles - vasodilatation
- 11. Antihypertensive Drugs – Calcium Channel Blockers (CCB): Verapamil, diltiazem, nifedipine, felodipine, amlodipine, nimodipine etc. MOA: Blocks influx of Ca++ in smooth muscle cells – relaxation of SMCs – decrease BP K+ Channel activators: Diazoxide, minoxidil, pinacidil and nicorandil MOA: Leaking of K+ due to opening – hyper polarization of SMCs – relaxation of SMCs Vasodilators: Arteriolar – Hydralazine (also CCBs and K+ channel activators) Arterio-venular: Sodium Nitroprusside
- 12. Diuretics Drugs causing net loss of Na+ and water in urine Mechanism of antihypertensive action: Initially: diuresis – depletion of Na+ and body fluid volume – decrease in cardiac output Subsequently after 4 - 6 weeks, Na+ balance and CO is regained by 95%, but BP remains low! Q: Why? Answer: reduction in total peripheral resistance (TPR) due to deficit of little amount of Na+ and water (Na+ causes vascular stiffness) Similar effect is seen with sodium restriction (low sodium diet)
- 13. Thiazide diuretics – adverse effects Adverse Effects: Hypokalaemia – muscle pain and fatigue Hyperglycemia: Inhibition of insulin release due to K+ depletion (proinsulin to insulin) – precipitation of diabetes Hyperlipidemia: rise in total LDL level – risk of stroke Hyperurecaemia: inhibition of urate excretion Sudden cardiac death – tosades de pointes (hypokalaemia) All the above metabolic side effects – higher doses (50 – 100 mg per day) But, its observed that these adverse effects are minimal with low doses (12.5 to 25 mg) - Average fall in BP is 10 mm of Hg
- 14. Thiazide diuretics – current status Effects of low dose: No significant hypokalaemia Low incidence of arrhythmia Lower incidence of hyperglycaemia, hyperlipidemia and hyperuricaemia Reduction in MI incidence Reduction in mortality and morbidity JNC recommendation: JNC recommends low dose of thiazide therapy (12.5 – 25 mg per day) in essential hypertension Preferably should be used with a potassium sparing diuretic as first choice in elderly If therapy fails – another antihypertensive but do not increase the thiazide dose Loop diuretics are to be given when there is severe hypertension with retention of body fluids
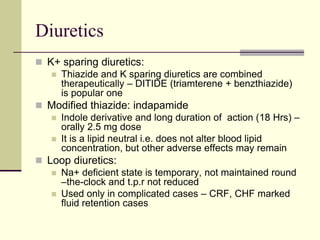
- 15. Diuretics K+ sparing diuretics: Thiazide and K sparing diuretics are combined therapeutically – DITIDE (triamterene + benzthiazide) is popular one Modified thiazide: indapamide Indole derivative and long duration of action (18 Hrs) – orally 2.5 mg dose It is a lipid neutral i.e. does not alter blood lipid concentration, but other adverse effects may remain Loop diuretics: Na+ deficient state is temporary, not maintained round –the-clock and t.p.r not reduced Used only in complicated cases – CRF, CHF marked fluid retention cases
- 16. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors What is Renin - Angiotensin? (Physiological Background)
- 17. RAS - Introduction Renin is a proteolytic enzyme and also called angiotensinogenase It is produced by juxtaglomerular cells of kidney It is secreted in response to: Decrease in arterial blood pressure Decrease Na+ in macula densa Increased sympathetic nervous activity Renin acts on a plasma protein – Angiotensinogen (a glycoprotein synthesized and secreted into the bloodstream by the liver) and cleaves to produce a decapeptide Angiotensin-I Angiotensin-I is rapidly converted to Angiotensin-II (octapeptide) by ACE (present in luminal surface of vascular endothelium) Furthermore degradation of Angiotensin-II by peptidases produce Angiotensin-III Both Angiotensin-II and Angiotensin-III stimulates Aldosterone secretion from Adrenal Cortex (equipotent) AT-II has very short half life – 1 min
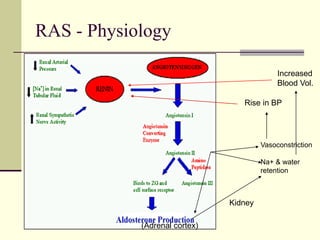
- 18. RAS - Physiology Vasoconstriction Na+ & water retention (Adrenal cortex) Kidney Increased Blood Vol. Rise in BP
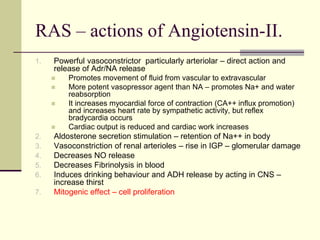
- 19. RAS – actions of Angiotensin-II. 1. Powerful vasoconstrictor particularly arteriolar – direct action and release of Adr/NA release Promotes movement of fluid from vascular to extravascular More potent vasopressor agent than NA – promotes Na+ and water reabsorption It increases myocardial force of contraction (CA++ influx promotion) and increases heart rate by sympathetic activity, but reflex bradycardia occurs Cardiac output is reduced and cardiac work increases 2. Aldosterone secretion stimulation – retention of Na++ in body 3. Vasoconstriction of renal arterioles – rise in IGP – glomerular damage 4. Decreases NO release 5. Decreases Fibrinolysis in blood 6. Induces drinking behaviour and ADH release by acting in CNS – increase thirst 7. Mitogenic effect – cell proliferation
- 20. Angiotensin-II What are the ill effects on chronic ? Volume overload and increased t.p.r Cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling Coronary vascular damage and remodeling Hypertension – long standing will cause ventricular hypertrophy Myocardial infarction – hypertrophy of non-infarcted area of ventricles Renal damage Risk of increased CVS related morbidity and mortality ACE inhibitors reverse cardiac and vascular hypertrophy and remodeling
- 21. Angiotensin-II – Pathophysiological Roles 1. Mineraocorticoid secretion 2. Electrolyte, blood volume and pressure homeostasis: Renin is released when there is changes in blood volume or pressure or decreased Na+ content Intrarenal baroreceptor pathway – reduce tension in the afferent glomerular arterioles by local production of Prostaglandin – intrarenal regulator of blood flow and reabsorption Low Na+ conc. in tubular fluid – macula densa pathway – COX-2 and nNOS are induced – release of PGE2 and PGI2 – more renin release Baroreceptor stimulation increases sympathetic impulse – via beta-1 pathway – renin release Renin release – increased Angiotensin II production – vasoconstriction and increased Na+ and water reabsorption Long term stabilization of BP is achieved – long-loop negative feedback and short-loop negative feedback mechanism 3. Hypertension 4. Secondary hyperaldosteronism
- 22. ACE inhibitors Captopril, lisinopril., enalapril, ramipril and fosinopril etc.
- 23. ACE inhibitors in Hypertension Captopril Sulfhydryl containing dipeptide and abolishes pressor action of Angiotensin-I and not Angiotensin-II and does not block AT receptors Pharmacokinetics: Available only orally, 70% - 75% is absorbed Partly absorbed and partly excreted unchanged in urine Food interferes with its absorption Half life: 2 Hrs, but action stays for 6-12 Hrs
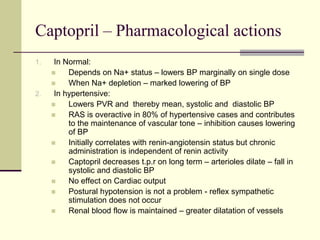
- 24. Captopril – Pharmacological actions 1. In Normal: Depends on Na+ status – lowers BP marginally on single dose When Na+ depletion – marked lowering of BP 2. In hypertensive: Lowers PVR and thereby mean, systolic and diastolic BP RAS is overactive in 80% of hypertensive cases and contributes to the maintenance of vascular tone – inhibition causes lowering of BP Initially correlates with renin-angiotensin status but chronic administration is independent of renin activity Captopril decreases t.p.r on long term – arterioles dilate – fall in systolic and diastolic BP No effect on Cardiac output Postural hypotension is not a problem - reflex sympathetic stimulation does not occur Renal blood flow is maintained – greater dilatation of vessels
- 25. Captopril – Adverse effects Cough – persistent brassy cough in 20% cases – inhibition of bradykinin and substanceP breakdown in lungs Hyperkalemia in renal failure patients with K+ sparing diuretics, NSAID and beta blockers (routine check of K+ level) Hypotension – sharp fall may occur – 1st dose Acute renal failure: CHF and bilateral renal artery stenosis Angioedema: swelling of lips, mouth, nose etc. Rashes, urticaria etc Dysgeusia: loss or alteration of taste Foetopathic: hypoplasia of organs, growth retardation etc Neutripenia Contraindications: Pregnancy, bilateral renal artery stenosis, hypersensitivity and hyperkalaemia
- 26. ACE inhibitors - Enalapril It’s a prodrug – converted to enalaprilate Advantages over captopril: Longer half life – OD (5-20 mg OD) Absorption not affected by food Rash and loss of taste are less frequent Longer onset of action Less side effects
- 27. ACE inhibitors – Ramipril It’s a popular ACEI now It is also a prodrug with long half life Tissue specific – Protective of heart and kidney Uses: Diabetes with hypertension, CHF, AMI and cardio protective in angina pectoris Blacks in USA are resistant to Ramipril – addition of diuretics help Dose: Start with low dose; 2.5 to 10 mg daily
- 28. ACE inhibitors – Lisinopril It’s a lysine derivative Not a prodrug Slow oral absorption – less chance of 1st dose phenomenon Absorption not affected by food and not metabolized – excrete unchanged in urine Long duration of action – single daily dose Doses: available as 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10 1nd 20 mg tab – start with low dose
- 29. ACE inhibitors and hypertension 1st line of Drug: No postural hypotension or electrolyte imbalance (no fatigue or weakness) Safe in asthmatics and diabetics Prevention of secondary hyperaldosteronism and K+ loss Renal perfusion well maintained Reverse the ventricular hypertrophy and increase in lumen size of vessel No hyperuraecemia or deleterious effect on plasma lipid profile No rebound hypertension Minimal worsening of quality of life – general wellbeing, sleep and work performance etc.
- 30. ACE inhibitors – other uses Hypertension Congestive Heart Failure Myocardial Infarction Prophylaxis of high CVS risk subjects Diabetic Nephropathy Schleroderma crisis
- 31. Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) - Angiotensin Receptors: Specific angiotensin receptors have been discovered, grouped and abbreviated as – AT1 and AT2 They are present on the surface of the target cells Most of the physiological actions of angiotensin are mediated via AT1 receptor Transducer mechanisms of AT1 inhibitors: In different tissues show different mechanisms. For example - PhospholipaseC-IP3/DAG-intracellular Ca++ release mechanism – vascular and visceral smooth muscle contraction In myocardium and vascular smooth muscles AT1 receptor mediates long term effects by MAP kinase and others Losartan is the specific AT1 blocker
- 32. Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) - Losartan Competitive antagonist and inverse agonist of AT1 receptor Does not interfere with other receptors except TXA2 Blocks all the actions of A-II - vasoconstriction, sympathetic stimulation, aldosterone release and renal actions of salt and water reabsorption No inhibition of ACE
- 33. Losartan Theoretical superiority over ACEIs: Cough is rare – no interference with bradykinin and other ACE substrates Complete inhibition of AT1 – alternative remains with ACEs Result in indirect activation of AT2 – vasodilatation (additional benefit) Clinical benefit of ARBs over ACEIs – not known However, losartan decreases BP in hypertensive which is for long period (24 Hrs) heart rate remains unchanged and cvs reflxes are not interfered no significant effect in plasma lipid profile, insulin sensitivity and carbohydrate tolerance etc Mild uricosuric effect
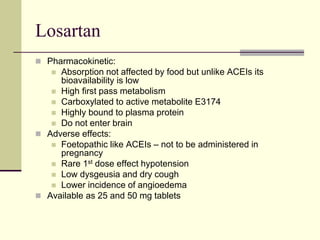
- 34. Losartan Pharmacokinetic: Absorption not affected by food but unlike ACEIs its bioavailability is low High first pass metabolism Carboxylated to active metabolite E3174 Highly bound to plasma protein Do not enter brain Adverse effects: Foetopathic like ACEIs – not to be administered in pregnancy Rare 1st dose effect hypotension Low dysgeusia and dry cough Lower incidence of angioedema Available as 25 and 50 mg tablets
- 35. Beta-adrenergic blockers Non selective: Propranolol (others: nadolol, timolol, pindolol, labetolol) Cardioselective: Metoprolol (others: atenolol, esmolol, betaxolol) All beta-blockers similar antihypertensive effects – irrespective of additional properties Reduction in CO but no change in BP initially but slowly Adaptation by resistance vessels to chronically reduced CO – antihypertensive action Other mechanisms – decreased renin release from kidney (beta-1 mediated) Reduced NA release and central sympathetic outflow reduction Non-selective ones – reduction in g.f.r but not with selective ones Drugs with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity may cause less reduction in HR and CO
- 36. Beta-adrenergic blockers Advantages: No postural hypotension No salt and water retention Low incidence of side effects Low cost Once a day regime Preferred in young non-obese patients, prevention of sudden cardiac death in post infarction patients and progression of CHF Drawbacks (side effects): Fatigue, lethargy (low CO?) – decreased work capacity Loss of libido – impotence Cognitive defects – forgetfulness Difficult to stop suddenly Therefore cardio-selective drugs are preferred now
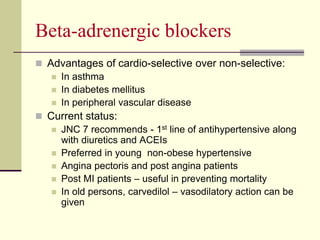
- 37. Beta-adrenergic blockers Advantages of cardio-selective over non-selective: In asthma In diabetes mellitus In peripheral vascular disease Current status: JNC 7 recommends - 1st line of antihypertensive along with diuretics and ACEIs Preferred in young non-obese hypertensive Angina pectoris and post angina patients Post MI patients – useful in preventing mortality In old persons, carvedilol – vasodilatory action can be given
- 38. Αlpha-adrenergic blockers Non selective alpha blockers are not used in chronic essential hypertension (phenoxybenzamine, phentolamine), only used sometimes as in phaechromocytoma Specific alpha-1 blockers like prazosin, terazosin and doxazosine are used PRAZOSIN is the prototype of the alpha-blockers Reduction in t.p.r and mean BP – also reduction in venomotor tone and pooling of blood – reduction in CO Does not produce tachycardia as presynaptic auto (alpha-2) receptors are not inhibited – autoregulation of NA release remains intact
- 39. Αlpha-adrenergic blockers. Adverse effects: Prazosin causes postural hypotension – start 0.5 mg at bed time with increasing dose and upto 10 mg daily Fluid retention in monotherapy Headache, dry mouth, weakness, dry mouth, blurred vision, rash, drowsiness and failure of ejaculation in males Current status: Several advantages – improvement of carbohydrate metabolism – diabetics, lowers LDL and increases HDL, symptomatic improvement in BHP But not used as first line agent, used in addition with other conventional drugs which are failing – diuretic or beta blocker Doses: Available as 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2.5 mg, 5 mg etc. dose:1-4 mg thrice daily (Minipress/Prazopress)
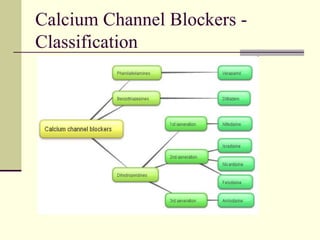
- 40. Calcium Channel Blockers - Classification
- 41. Calcium Channel Blockers – Mechanism of action Three types Ca+ channels in smooth muscles – Voltage sensitive, receptor operated and leak channel Voltage sensitive are again 3 types – L-Type, T-Type and N- Type Normally, L-Type of channels admit Ca+ and causes depolarization – excitation-contraction coupling through phosphorylation of myosin light chain – contraction of vascular smooth muscle – elevation of BP CCBs block L-Type channel: Smooth Muscle relaxation Negative chronotropic, ionotropic and chronotropic effects in heart DHPs have highest smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilator action followed by verapamil and diltiazem Other actions: DHPs have diuretic action
- 42. Calcium Channel Blockers Advantages: Unlike diuretics no adverse metabolic effects but mild adverse effects like – dizziness, fatigue etc. Do not compromise haemodynamics – no impairment of work capacity No sedation or CNS effect Can be given to asthma, angina and PVD patients No renal and male sexual function impairment No adverse fetal effects and can be given in pregnancy Minimal effect on quality of life
- 43. Calcium Channel Blockers – current status As per JNC 7 CCBs are not 1st line of antihypertensive unless indicated – ACEI/diuretics/beta blockers However its been used as 1st line by many because of excellent tolerability and high efficacy Preferred in elderly and prevents stroke CCBs are effective in low Renin hypertension They are next to ACE inhibitors in inhibition of albuminuria and prevention of diabetic nephropathy Immediate acting Nifedipine is not encouraged anymore
- 44. Calcium Channel Blockers Contraindications: Unstable angina Heart failure Hypotension Post infarct cases Severe aortic stenosis Preparation and dosage: Amlodipine – 2.5, 5 and 10 mg tablets (5-10 mg OD) – Stamlo, Amlopres, Amlopin etc. Nimodipine – 30 mg tab and 10 mg/50 ml injection – Vasotop, Nimodip, Nimotide etc.
- 45. Vasodilators - Hydralazine Directly acting vasodilator MOA: hydralazine molecules combine with receptors in the endothelium of arterioles – NO release – relaxation of vascular smooth muscle – fall in BP Subsequenly fall in BP – stimulation of adrenergic system leading to Cardiac stimulation producing palpitation and rise in CO even in IHD and patients – anginal attack Tachycardia Increased Renin secretion – Na+ retention These effects are countered by administration of beta blockers and diuretics However many do not agree to this theory Uses: 1) Moderate hypertension when 1st line fails – with beta-blockers and diuretics 2) Hypertension in Pregnancy, Dose 25-50 mg OD
- 46. Vasodilators - Minoxidil Powerful vasodilator, mainly 2 major uses – antihypertensive and alopecia Prodrug and converted to an active metabolite which acts by hyperpolarization of smooth muscles and thereby relaxation of SM – leading to hydralazine like effects Rarely indicated in hypertension especially in life threatening ones More often in alopecia to promote hair growth Orally not used any more Topically as 2-5% lotion/gel and takes months to get effects MOA of hair growth: Enhanced microcirculation around hair follicles and also by direct stimulation of follicles Alteration of androgen effect of hair follicles
- 47. Sodium Nitroprusside Rapidly and consistently acting vasodilator Relaxes both resistance and capacitance vessels and reduces t.p.r and CO (decrease in venous return) Unlike hydralazine it produces decrease in cardiac work and no reflex tachycardia. Improves ventricular function in heart failure by reducing preload MOA: RBCs convert nitroprusside to NO – relaxation also by non-enzymatically to NO by glutathione Uses: Hypertensive Emergencies, 50 mg is added to 500 ml of saline/glucose and infused slowly with 0.02 mg/min initially and later on titrated with response (wrap with black paper) Adverse effects: All are due release of cyanides (thiocyanate) – palpitation, pain abdomen, disorientation, psychosis, weakness and lactic acidosis.
- 48. Centrally acting Drugs Alpha-Methyldopa: a prodrug Precursor of Dopamine and NA MOA: Converted to alpha methyl noradrenaline which acts on alpha-2 receptors in brain and causes inhibition of adrenergic discharge in medulla – fall in PVR and fall in BP Various adverse effects – cognitive impairement, postural hypotension, positive coomb`s test etc. – Not used therapeutically now except in Hypertension during pregnancy Clonidine: Imidazoline derivative, partial agonist of central alpha-2 receptor Not frequently used now because of tolerance and withdrawal hypertension Read it yourself
- 49. Treatment of hypertension
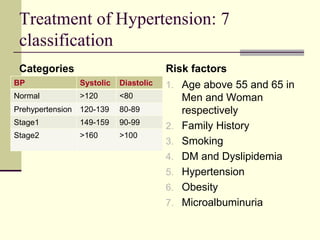
- 50. Treatment of Hypertension: 7 classification Categories BP Systolic Diastolic Normal >120 <80 Prehypertension 120-139 80-89 Stage1 149-159 90-99 Stage2 >160 >100 Risk factors 1. Age above 55 and 65 in Men and Woman respectively 2. Family History 3. Smoking 4. DM and Dyslipidemia 5. Hypertension 6. Obesity 7. Microalbuminuria
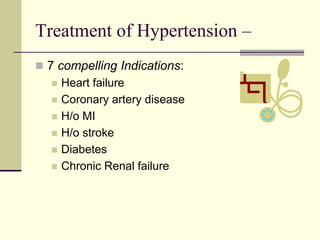
- 51. Treatment of Hypertension – 7 compelling Indications: Heart failure Coronary artery disease H/o MI H/o stroke Diabetes Chronic Renal failure
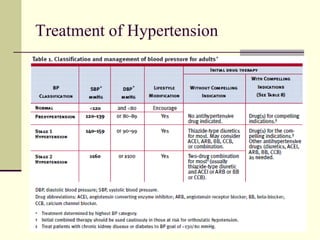
- 52. Treatment of Hypertension
- 53. Treatment of Hypertension – General principles Stage I: Start with a single most appropriate drug with a low dose. Preferably start with Thiazides. Others like beta- blockers, CCBs, ARBs and ACE inhibitors may also be considered. CCB – in case of elderly and stroke prevention. If required increase the dose moderately Partial response or no response – add from another group of drug, but remember it should be a low dose combination If not controlled – change to another low dose combination In case of side effects lower the dose or substitute with other group Stage 2: Start with 2 drug combination – one should be diuretic
- 54. Treatment of Hypertension – combination therapy In clinical practice a large number of patients require combination therapy – the combination should be rational and from different patterns of haemodynamic effects Sympathetic inhibitors (not beta-blockers) and vasodilators + diuretics Diuretics, CCBs, ACE inhibitors and vasodilators + beta blockers (blocks renin release) Hydralazine and CCBs + beta-blockers (tachycardia countered) ACE inhibitors + diuretics 3 (three) Drug combinations: CCB+ACE/ARB+diuretic; CCB+Beta blocker+ diuretic; ACEI/ARB+ beta blocker+diuretic
- 55. Treatment of Hypertension. Never combine: Alpha or beta blocker and clonidine - antagonism Nifedepine and diuretic synergism Hydralazine with DHP or prazosin – same type of action Diltiazem and verapamil with beta blocker – bradycardia Methyldopa and clonidine Hypertension and pregnancy: No drug is safe in pregnancy Avoid diuretics, propranolol, ACE inhibitors, Sodium nitroprusside etc Safer drugs: Hydralazine, Methyldopa, cardioselective beta blockers and prazosin
- 56. Hypertensive Emergencies Cerebrovascular accident or head injury with high BP Left ventricular failure with pulmonary edema due to hypertension Hypertensive encephalopathy Angina or MI with raised BP Acute renal failure with high BP Eclampsia Pheochromocytoma, cheese reaction and clonidine withdrawal Drugs: Sodium Nitroprusside (20-300 mcg/min) – dose titration and monitoring GTN (5-20 mcg/min) – cardiac surgery, LVF, MI and angina Esmolol (0.5 mg/kg bolus) and 50-200mcg/kg/min - useful in reducing cardiac work Phentolamine – pheochromocytoma, cheese reaction nd clonidine withdrawal (5-10 mg IV)
- 57. Desirable to know/learn Classification of Antihypertensive Antihypertensive mechanisms: Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, Beta-blockers, alpha-blockers, CCBs, Vasodilators and central sympatholytics Present status of above mentioned group of Drugs Common Adverse effects of above groups of Drugs Pharmacotherapy of Hypertension Pharmacotherapy of hypertensive emergencies Preparation and dosage of commonly used drugs of above mentioned groups