cerebellum.pptx
- 1. Cerebellum
- 2. Cerebellum • Largest part of hindbrain • About 150 grams • Separated from medulla & pons by a cavity – fourth ventricle • It controls • Balance • Muscle tone • Co-ordination of voluntary movements
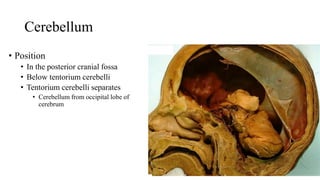
- 3. Cerebellum • Position • In the posterior cranial fossa • Below tentorium cerebelli • Tentorium cerebelli separates • Cerebellum from occipital lobe of cerebrum
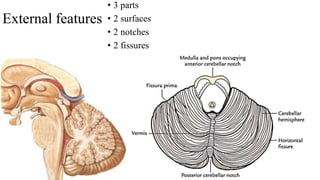
- 4. External features • 3 parts • 2 surfaces • 2 notches • 2 fissures
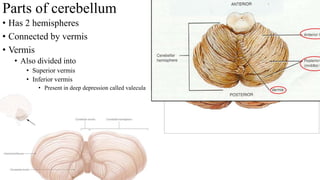
- 5. Parts of cerebellum • Has 2 hemispheres • Connected by vermis • Vermis • Also divided into • Superior vermis • Inferior vermis • Present in deep depression called valecula
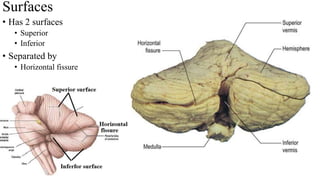
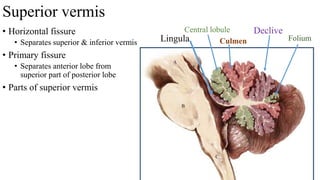
- 6. • Has 2 surfaces • Superior • Inferior • Separated by • Horizontal fissure Surfaces
- 7. Notches • 2 notches • Anterior notch • V – shaped • Lies behind the pons & medulla • Posterior notch • Narrow • Lodges falx cerebelli
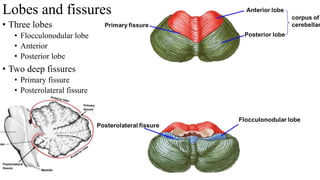
- 8. Fissures • Primary fissure • Lies in superior fissure • V – shaped (apex facing posteriorly) • Separates anterior lobe from posterior lobe • Posterolateral fissure • First fissure to appear • Lies in inferior surface at anterior aspect • Separates flocculonodular lobe from other parts of cerebellum • Horizontal fissure • Lies at the junction of superior and inferior surfaces
- 9. Lobes and fissures • Three lobes • Flocculonodular lobe • Anterior • Posterior lobe • Two deep fissures • Primary fissure • Posterolateral fissure
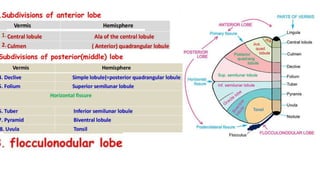
- 10. • Horizontal fissure • Separates superior & inferior vermis • Primary fissure • Separates anterior lobe from superior part of posterior lobe • Parts of superior vermis Lingula Central lobule Superior vermis Culmen Declive Folium
- 11. Inferior vermis • Present in deep depression called valeculla • Posterolateral fissure • Separates inferior part of posterior lobe and flocculonodular lobe Nodule Uvula Pyramid Tuber
- 13. Applied anatomy • Tonsil of cerebellum • Elevated masses on inferior surface of hemispheral portion • Just nearby foramen magnum • If intracranial pressure raises • Tonsil pushed through foramen magnum • Compresses medulla
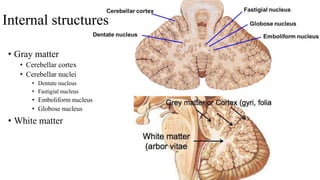
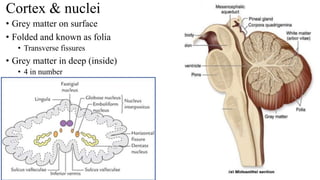
- 14. Internal structures • Gray matter • Cerebellar cortex • Cerebellar nuclei • Dentate nucleus • Fastigial nucleus • Emboliform nucleus • Globose nucleus • White matter
- 15. Cortex & nuclei • Grey matter on surface • Folded and known as folia • Transverse fissures • Grey matter in deep (inside) • 4 in number
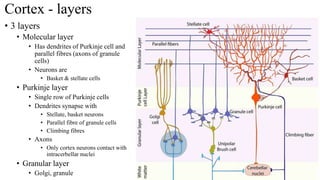
- 16. Cortex - layers • 3 layers • Molecular layer • Has dendrites of Purkinje cell and parallel fibres (axons of granule cells) • Neurons are • Basket & stellate cells • Purkinje layer • Single row of Purkinje cells • Dendrites synapse with • Stellate, basket neurons • Parallel fibre of granule cells • Climbing fibres • Axons • Only cortex neurons contact with intracerbellar nuclei • Granular layer • Golgi, granule
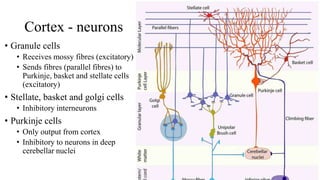
- 17. Cortex - neurons • Granule cells • Receives mossy fibres (excitatory) • Sends fibres (parallel fibres) to Purkinje, basket and stellate cells (excitatory) • Stellate, basket and golgi cells • Inhibitory interneurons • Purkinje cells • Only output from cortex • Inhibitory to neurons in deep cerebellar nuclei
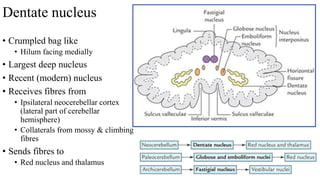
- 18. Dentate nucleus • Crumpled bag like • Hilum facing medially • Largest deep nucleus • Recent (modern) nucleus • Receives fibres from • Ipsilateral neocerebellar cortex (lateral part of cerebellar hemisphere) • Collaterals from mossy & climbing fibres • Sends fibres to • Red nucleus and thalamus
- 19. • Globosus & emboliformis • More recent nuclei • Receives from paravermal cortex (Paleocerebellum) • Sends fibres to red nucleus • Fastigial nucleus • Smallest • Receives fibres from • Vermal & floculo-nodular lobe • Sends fibres to • Vestibular & reticular formation
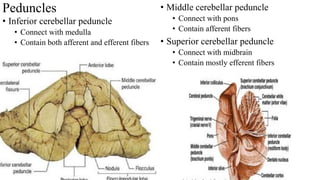
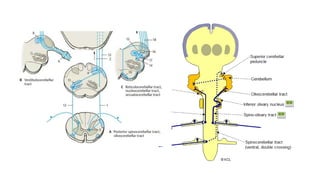
- 20. Peduncles • Inferior cerebellar peduncle • Connect with medulla • Contain both afferent and efferent fibers • Middle cerebellar peduncle • Connect with pons • Contain afferent fibers • Superior cerebellar peduncle • Connect with midbrain • Contain mostly efferent fibers
- 21. Superior cerebellar peduncle • Connects with midbrain • Contains both afferent & efferent • Afferent • Anterior spinocerebellar • Tectocerbellar • Rubrocerebellar • Efferent • Dentatothalamic • Dentatorubral
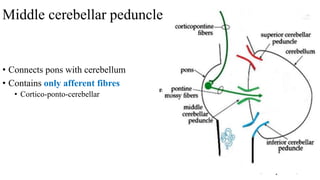
- 22. • Connects pons with cerebellum • Contains only afferent fibres • Cortico-ponto-cerebellar Middle cerebellar peduncle
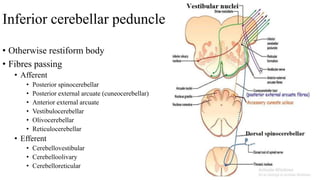
- 23. Inferior cerebellar peduncle • Otherwise restiform body • Fibres passing • Afferent • Posterior spinocerebellar • Posterior external arcuate (cuneocerebellar) • Anterior external arcuate • Vestibulocerebellar • Olivocerebellar • Reticulocerebellar • Efferent • Cerebellovestibular • Cerebelloolivary • Cerebelloreticular
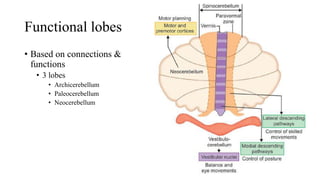
- 24. Functional lobes • Based on connections & functions • 3 lobes • Archicerebellum • Paleocerebellum • Neocerebellum
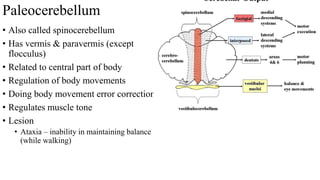
- 25. Archicerebellum • Phylogenetically oldest • Flocculonodular lobe • Control on • Balance & eye movements • Lesions • Trunk ataxia • Staggering gait • Nystagmus • Involuntary rhythmic side-to-side, up and down or circular motion of the eyes
- 26. Archicerebellum - connections • Afferents • From vestibular nuclei • Vestibulo-cerebellar tract • Efferents • Cerebello-vestibular • Cortex & fastigial nuclei to vestibular nuclei • Vestibulospinal • Medial longitudinal • Cerebello-reticular • To pontine & meullary reticular formation • Connected to motor neurons of Spinal cord
- 27. Paleocerebellum • Also called spinocerebellum • Has vermis & paravermis (except flocculus) • Related to central part of body • Regulation of body movements • Doing body movement error correction • Regulates muscle tone • Lesion • Ataxia – inability in maintaining balance (while walking)
- 28. Paleocerebellum- connections • Afferents • Spinocerebellar (anterior & posterior) • Cuneocerebellar • Efferents • Cerebello rubral • From interposed (Globose & emboliform) nuclei to red nucleus • Rubro-spinal
- 29. Neocerebellum - cerebrocerebellum • Formed by lateral part of hemispheres • Planning movement & motor learning • Muscle co-ordination • Lesions • Intention tremor • Dysmetria
- 30. Neocerebellum - connections • Afferents • From cerebral cortex via pontine nuclei • Cortico-pontine-cerebellar pathway • Efferents • Neocortex to dentate nucleus • Dentato-rubro-thalamo- cortical • From cortex to spinal cord & cranial nerve nuclei • Via corticobulbar & cortico spinal tracts
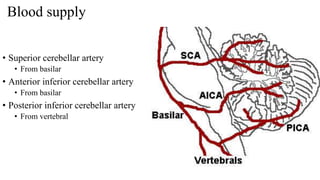
- 31. Blood supply • Superior cerebellar artery • From basilar • Anterior inferior cerebellar artery • From basilar • Posterior inferior cerebellar artery • From vertebral