Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block Anesthetic Technique
- 1. Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block Presented By: Dr. Anika Agnihotri
- 2. Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block The inferior alveolar nerve block (IANB), commonly referred to as the mandibular nerve block. It is possibly the most important injection technique in dentistry and the second most frequently used (after infiltration).
- 3. Alternatives Mental nerve block Incisive nerve block Anterior infiltration Periodontal ligament injection (PDL) Gow-Gates Akinosi Intrasental Mental nerve block Incisive nerve block Gow-Gates Akinosi
- 4. n Procedures on multiple mandibular teeth in one quadrant. Surgical procedures on mandibular teeth and supporting structures when supplemented by anaesthesia of lingual and long buccal nerve. When buccal soft tissue anaesthesia (anterior to the mental foramen) is necessary When lingual soft tissue anaesthesia is necessary
- 5. Contraindications Infection or acute inflammation in the area of injection is rare. Patients who are more likely to bite their lip or tongue. (for instance, a very young child or a physically or mentally handicapped adult or child)
- 6. Nerves Anesthetised Inferior alveolar nerve and its subdivisions Occasionally lingual and buccinator nerves Areas Anesthetized Mandibular teeth up to the midline Body of the mandible Inferior portion of the ramus Buccal mucoperiosteum Mucous membrane anterior to the mental foramen (mental nerve) Anterior two thirds of the tongue and floor of the oral cavity (lingual nerve) Lingual soft tissues and periosteum (lingual nerve)
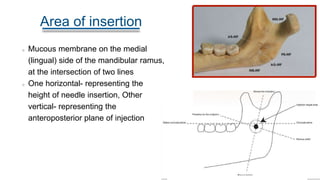
- 7. Area of insertion Mucous membrane on the medial (lingual) side of the mandibular ramus, at the intersection of two lines One horizontal- representing the height of needle insertion, Other vertical- representing the anteroposterior plane of injection
- 8. Needle pathway during insertion
- 9. Landmark Muccobuccal fold Anterior border of ramus of mandible External oblique ridge Retromolar triangle Internal oblique ridge Pterygomandibular ligament Buccal sucking pad Pterygomandibular space
- 10. Signs And Symptoms SUBJECTIVE SYMPTOMS Tingling and numbness of lower lip After the lingual nerve is affected numbness is felt on the tip of the tongue OBJECTIVE SYMPTOMS Instrumentation necessary to demonstrate absence of pain sensation
- 11. Failure of Anaesthesia Injection too low Injection too anterior Accessory innervation Mylohyoid nerve contralateral Incisive nerve innervation